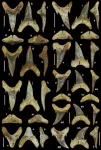
(Press-News.org) Birmingham, AL (February 7, 2024) – Today, a team of scientists is pleased to announce the discovery of a new fossil shark species from Alabama, USA. The team is led by Jun Ebersole, Director of Collections, McWane Science Center, Birmingham, AL, David Cicimurri, Curator of Natural History, South Carolina State Museum in Columbia, and T. Lynn Harrell, Jr., Paleontologist and Fossil Collections Curator at the Geological Survey of Alabama in Tuscaloosa.
The shark is a new species of Palaeohypotodus (pronounced pale-ee-oh-hype-oh-toe-duss), which means “ancient small-eared tooth,” in reference to the small needle-like fangs present on the sides of the teeth. It has been named Palaeohypotodus bizzocoi, for the late Dr. Bruce Bizzoco (1949-2022) of Birmingham, AL. Bizzoco served as a Dean at Shelton State Community College, archaeologist, and was a longtime volunteer at McWane Science Center. The naming of this species honors Dr. Bizzoco’s lifelong commitments to education and the preservation of Alabama’s history.
According to Ebersole, the discovery of this shark was accidental.
“A few years ago, I was looking through the historical fossil collections at the Geological Survey in Alabama and came across a small box of shark teeth that were collected over 100 years ago in Wilcox County,” Ebersole said. “Having documented hundreds of fossil fish species over the last decade, I found it puzzling that these teeth were from a shark that I didn’t recognize.” Ebersole quickly realized that these teeth belonged to a new species.
“Perhaps one of the coolest aspects of this shark, is when it lived – the Paleocene, approximately 65-million-years-ago,” Cicimurri said. This is the time-period from just after the death of the dinosaurs, where over 75% of life on Earth went extinct.”
According to Cicimurri, this shark was a leading predator during the time when the oceans were recovering.
In Alabama, much of the southern half of the state was covered by a shallow tropical to sub- tropical ocean during the Paleocene. “This time period is understudied, which makes the discovery of this new shark species that much more significant,” Harrell said.
“Shark discoveries like this one give us tremendous insights into how ocean life recovers after major extinction events and also allows us to potentially forecast how global events, like climate change, affect marine life today,” Harrell continued.
As part of their study of this ancient shark, the team compared the fossil teeth to those of various living sharks, like Great Whites and Makos. According to Cicimurri, shark teeth differ in shape depending on where they are located in the mouth.
“By studying the jaws and teeth of living sharks, it allowed us to reconstruct the dentition of this ancient species and showed that it had a tooth arrangement that differed from any living shark,” Cicimurri said.
The naming of this shark is part of an ongoing project led by Ebersole and Cicimurri to document Alabama’s fossil fishes. Together, they have confirmed over 400 unique species of fossil sharks and bony fishes, which, according to Ebersole makes Alabama one of the richest places in the world in terms of fossil fish diversity.
The study, titled A new species Palaeohypotodus Glickman, 1964 (Chondrichthyes, Lamniformes) from the lower Paleocene (Danian) Porters Creek Formation, Wilcox County, Alabama, USA, was published today in the open access journal Fossil Record and can be downloaded here: htps://doi.org/10.3897/fr.27.e112800
About McWane Science Center
McWane Science Center is a nonprofit 501 (c)(3) science center, children’s museum, natural history museum, aquarium, and IMAX Dome Theater. Designed to “spark wonder and curiosity about our world through hands-on science,” McWane Science Center has welcomed millions of visitors since opening its doors in 1998. The McWane Collection houses one of the largest collection of fossils in the state of Alabama. For more information, visit www.mcwane.org.
END
New species of 65 million year old fossil shark discovered in Alabama, USA
This shark was one of the ocean’s top predators after the extinction of the dinosaurs
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Time to treatment with intravenous thrombolysis before thrombectomy and functional outcomes in acute ischemic stroke
2024-02-07
About The Study: In patients presenting at thrombectomy-capable stroke centers, the benefit associated with intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) plus thrombectomy versus thrombectomy alone was time dependent and statistically significant only if the time from symptom onset to expected administration of IVT was short in this individual participant data meta-analysis (n = 2,313) of six randomized clinical trials.
Authors: Johannes Kaesmacher, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Bern in Bern, Switzerland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Many hookah manufacturers have not complied with FDA-mandated nicotine warning labels
2024-02-07
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
February 7, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Many Hookah Manufacturers Have Not Complied with FDA-Mandated Nicotine Warning Labels
Only half of the hookah packages assessed in a new study included the required nicotine warnings, two years after this federal regulation was implemented to alert consumers about the health risks of nicotine addiction.
Since August 2018, the US Food & Drug Administration has mandated that all hookah (also known as waterpipe tobacco or shisha) manufacturers include a nicotine warning ...
Endovascular thrombectomy for large ischemic stroke across ischemic injury and penumbra profiles
2024-02-07
About The Study: In this exploratory analysis of a randomized clinical trial of 336 patients with extensive ischemic stroke, endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) improved clinical outcomes across a wide spectrum of infarct volumes, although enrollment of patients with minimal penumbra volume was low. In EVT-treated patients, clinical outcomes worsened as presenting ischemic injury estimates increased.
Authors: Amrou Sarraj, M.D., of University Hospital Cleveland Medical Center—Case Western ...
Apixaban to prevent recurrence after cryptogenic stroke in patients with atrial cardiopathy
2024-02-07
About The Study: In patients with cryptogenic stroke and evidence of atrial cardiopathy without atrial fibrillation, oral anticoagulant therapy with apixaban did not significantly reduce recurrent stroke risk compared with aspirin in this randomized clinical trial that included 1,015 participants.
Authors: Hooman Kamel, M.D., of Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.27188)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
MD Anderson research highlights for February 7, 2024
2024-02-07
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson include a combination treatment for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the discovery of a molecular driver in metastatic breast cancer, an oral combination therapy for high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), a novel method to mechanically destroy ...
UW-developed smart earrings can monitor a person’s temperature
2024-02-07
Smart accessories are increasingly common. Rings and watches track vitals, while Ray-Bans now come with cameras and microphones. Wearable tech has even broached brooches. Yet certain accessories have yet to get the smart touch.
University of Washington researchers introduced the Thermal Earring, a wireless wearable that continuously monitors a user’s earlobe temperature. In a study of six users, the earring outperformed a smartwatch at sensing skin temperature during periods of rest. It also showed promise for monitoring signs of stress, eating, exercise and ovulation.
The smart earring prototype is about ...
Quantum simulation with ultracold fermions unveils pairing pseudogap
2024-02-07
A research team led by Professors PAN Jianwei, YAO Xingcan, and CHEN Yu'ao from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have for the first time observed and quantitatively characterized the many-body pairing pseudogap in unitary Fermi gases. This achievement, pursued by the ultracold atomic community for nearly two decades, resolves longstanding debates regarding the existence of a pairing pseudogap in these gases. It also supports ...
New research uncovers biological drivers of heart disease risk
2024-02-07
New gene mapping technique reveals how genetic alterations in cells lining blood vessels contribute to coronary artery disease, with implications for diagnostic and treatment strategies.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Researchers from the Brigham, the Broad Institute, and Stanford Medicine studied how "deleting" individual genes associated with coronary artery disease (CAD) impacted the expression of all the other genes in a cell to better understand underlying biology of CAD.
The study focused on endothelial cells, which line blood vessels and are increasingly understood to influence CAD risk.
The researchers highlighted a previously unrecognized role for the TLNRD1 gene ...
Resting boosts performance of lithium metal batteries
2024-02-07
Next-generation electric vehicles could run on lithium metal batteries that go 500 to 700 miles on a single charge, twice the range of conventional lithium-ion batteries in EVs today.
But lithium metal technology has serious drawbacks: The battery rapidly loses its capacity to store energy after relatively few cycles of charging and discharging – highly impractical for drivers who expect rechargeable electric cars to operate for years.
Scientists have been testing a variety of new materials and techniques to improve the battery’s cycle life. Now, Stanford University researchers have discovered a low-cost solution: simply drain the battery and let it rest for several hours. ...
Machine learning models for predicting disability and pain following lumbar disc herniation surgery
2024-02-07
About The Study: The findings of this study including 22,000 surgical cases suggest that machine learning models can inform about individual prognosis and aid in surgical decision-making to ultimately reduce ineffective and costly spine care.
Authors: Bjørnar Berg, Ph.D., of Oslo Metropolitan University in Oslo, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.55024)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
[Press-News.org] New species of 65 million year old fossil shark discovered in Alabama, USAThis shark was one of the ocean’s top predators after the extinction of the dinosaurs