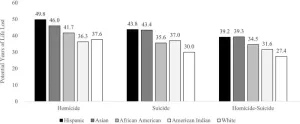
(Press-News.org) In the US, people of color who are killed by violence or die by suicide lose more potential years of life than white victims, according to a new study, which also explored factors that may contribute to these disparities. Gregory Zimmerman of Northeastern University in Boston, US, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on February 7, 2024.
Mounting evidence suggests that, among victims of violence in the US, the average number of potential years of life lost—how much longer the victim would have lived if they survived—is greater for people of color than for white people.
To deepen understanding, Zimmerman and colleagues analyzed data from the National Violent Death Reporting System (NVDRS). The data included a total of 98,617 homicide victims, 230,527 suicide decedents, and 3,962 homicide-suicide perpetrators who died between 2003 and 2019.
In line with prior research, they found that victims who were Hispanic, African American, Asian or Pacific Islander, or American Indian or Alaska Native tended to die at significantly younger ages than white victims.
Next, the researchers used information from the NVDRS and the US Census Bureau’s American Community Survey to explore if these disparities could be statistically explained by known differences in exposure among the different racial and ethnic groups to factors associated with higher risk of violence.
They found that several such factors—including individual differences, socio-familial factors, and characteristics and context of the violent incident—did indeed statistically account for some of the disparities. These factors included educational attainment, mental health problems, access to firearms, medical problems, and financial challenges.
The researchers say their findings suggest that the observed disparities can be addressed, and they identify several directions for such efforts; for instance, by providing communities of color with resources to boost educational opportunities, improve access to childcare, and address intimate partner violence.
The researchers also note the need for further research, as the NVDRS data only captured US deaths and did so incompletely. Furthermore, the study did not account for other factors that could help explain the observed disparities, such as cultural factors and access to quality medical and mental healthcare.
The authors add: “Findings indicated that non-white homicide victims, suicide decedents, and homicide-suicide perpetrators died significantly younger than their white counterparts. Homicide and suicide exact a high societal cost, and the burden of that cost is disproportionately high among persons of color.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0297346
Citation: Zimmerman GM, Fridel EE, Trovato D (2024) Disproportionate burden of violence: Explaining racial and ethnic disparities in potential years of life lost among homicide victims, suicide decedents, and homicide-suicide perpetrators. PLoS ONE 19(2): e0297346. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297346
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
Non-white victims of lethal violence and suicide in the US die significantly younger than their white counterparts
Access to firearms, medical and mental health problems, and socioeconomic factors may help explain inequities
2024-02-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Almost 1 in 5 Indian adults aged 60+ show signs of mild neurocognitive disorder, according to nationally representative data - more than previously recognized
2024-02-07
Almost 1 in 5 Indian adults aged 60+ show signs of mild neurocognitive disorder, according to nationally representative data - more than previously recognized
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0297220
Article Title: Prevalence of DSM-5 mild and major neurocognitive disorder in India: Results from the LASI-DAD
Author Countries: USA, UK, India
Funding: This work was supported by the National Institute on Aging (R01 AG051125 (JL), R01 AG030153 (JL), U01 AG064948 (JL), R01 AG070953 (ALG)). The funders had no role in study design, ...
More biodiverse nature landscapes may better buffer against stress - but only if you notice the difference, per experiment using videos of urban woodland
2024-02-07
More biodiverse nature landscapes may better buffer against stress - but only if you notice the difference, per experiment using videos of urban woodland
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0297179
Article Title: Does increasing biodiversity in an urban woodland setting promote positive emotional responses in humans? A stress recovery experiment using 360-degree videos of an urban woodland
Author Countries: UK
Funding: SF received a PhD Studentship funding from the UKRI Economic and Social Research Council, ...
UK austerity politics correlated with increased frailty in the oldest adults
2024-02-07
The period of austerity politics from 2012 to 2018 was associated with steeper increases in frailty with age compared to pre-austerity between 2002 and 2010, according to a new study published February 7th in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Carys Pugh of the University of Edinburgh, UK, and colleagues.
Previous research has linked a stalling in life expectancy growth to austerity politics implemented in response to the 2008-2009 financial crisis. However, the mechanism through which public spending cuts are associated with decreased life expectancy ...
Psychology study unearths ways to bolster global climate awareness and climate action
2024-02-07
An international team of scientists has created a tool that can aid in increasing climate awareness and climate action globally by highlighting messaging themes shown to be effective through experimental research.
The web-based tool, and the methods undergirding its creation, appears in the journal Science Advances.
The tool stems from a study involving nearly 250 researchers that drew more than 59,000 participants from 63 countries, including Algeria, China, Denmark, Germany, Israel, Japan, New Zealand, Peru, and the United States.
“We ...
Scientists reveal why blueberries are blue
2024-02-07
Tiny external structures in the wax coating of blueberries give them their blue colour, researchers at the University of Bristol can reveal.
This applies to lots of fruits that are the same colour including damsons, sloes and juniper berries.
In the study, published today in Science Advances, researchers show why blueberries are blue despite the dark red colour of the pigments in the fruit skin. Their blue colour is instead provided by a layer of wax that surrounds the fruit which is made up of miniature structures that scatter blue and UV light. This gives blueberries their blue appearance to humans and blue-UV to birds. The chromatic blue-UV reflectance ...
McMaster and ALK researchers discover new cell that remembers allergies
2024-02-07
Researchers with McMaster University and Denmark-based pharmaceutical company ALK-Abello A/S have made a groundbreaking discovery: a new cell that remembers allergies.
The discovery gives scientists and researchers a new target in treating allergies and could lead to new therapeutics. The research, published in Science Translational Medicine on Feb. 7, 2024, coins the brand-new cell as a type-2 memory B cell (MBC2).
“We’ve discovered a type of memory B cell that had unique characteristics and a unique gene ...
England’s oldest became frailer during austerity, study suggests
2024-02-07
The speed at which England’s oldest adults became frailer accelerated during the UK Government’s era of austerity politics, according to a new study.
Researchers say that the rate of frailty in people aged 85 and over in England increased 50 per cent faster per year between 2012 and 2018 compared with the preceding eight years.
The impact of frailty – a decline in a person’s mental and physical resilience to illness and injury – on the oldest in society must be considered should any new austerity measures be introduced, experts warn.
The study, led by researchers from the University of Edinburgh’s ...
Exceptionally rapid tooth development and ontogenetic changes in the feeding apparatus of the Komodo dragon
2024-02-07
Tea Maho and Robert R. Reisz
University of Toronto Mississauga
Kilat, the largest living lizard at the Toronto Metro Zoo, like other members of his species (Varanus komodoensis), truly deserves to be called the Komodo Dragon! Its impressive size and the way it looks at you and tracks your every move makes you realize that it is an apex predator, not unlike a ferocious theropod dinosaur. So, it is not surprising when you look around at his enclosure to find that there are shed teeth sparkling on the ground, a common find when ...
Scientists develop a low-cost device to make cell therapy safer
2024-02-07
CAMBRIDGE, MA – A tiny device built by scientists at MIT and the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology could be used to improve the safety and effectiveness of cell therapy treatments for patients suffering from spinal cord injuries.
In cell therapy, clinicians create what are known as induced pluripotent stem cells by reprogramming some skin or blood cells taken from a patient. To treat a spinal cord injury, they would coax these pluripotent stem cells to become progenitor cells, which are destined to differentiate into spinal cord cells. These progenitors are then transplanted back into ...
Getting to know the ‘ghost’ inside batteries
2024-02-07
An Argonne team developing materials for solid-state batteries took an unexpected detour to investigate tiny short-circuits known as soft-shorts. Their insights will benefit battery researchers around the world.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have shed important new light on what the early signs of battery failure look like. Their study — which relates to a condition called soft-shorts — provides the research community with valuable knowledge and methods to design better electric vehicle (EV) batteries.
The Argonne team’s research focused on all-solid batteries with anodes (negative electrodes) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Non-white victims of lethal violence and suicide in the US die significantly younger than their white counterpartsAccess to firearms, medical and mental health problems, and socioeconomic factors may help explain inequities