(Press-News.org) A person’s chance of surviving while receiving cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for cardiac arrest in hospital declines rapidly from 22% after one minute to less than 1% after 39 minutes, finds a US study published by The BMJ today.
Similarly, the likelihood of leaving hospital with no major brain damage declines from 15% after one minute of CPR to less than 1% after 32 minutes with no heartbeat.
The researchers say the findings provide insights that may help guide hospital teams, patients and their families in deciding how long to continue resuscitation.
In-hospital cardiac arrest is a common and catastrophic medical emergency, with only around 25% of patients surviving to hospital discharge.
Studies have shown that a longer resuscitation time for patients with in-hospital cardiac arrest is linked to lower odds of survival, but experts have been unable to make specific recommendations on when to stop resuscitation.
To address this knowledge gap, researchers measured the effect of CPR duration (in minutes) on outcomes for 348,996 US adults (average age 67 years) who had an in-hospital cardiac arrest between 2000 and 2021.
CPR was defined as the interval between the start of chest compression and the first return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) or termination of resuscitation.
The main measures of interest were survival to hospital discharge and favorable functional outcome at hospital discharge, defined as a brain performance score of 1 (good cerebral performance) or 2 (moderate cerebral disability) on a 5-point scale.
After accounting for potentially influential factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, and a range of pre-existing conditions, the results show that of the 348,996 patients, 233,551 (67%) achieved return of spontaneous circulation with an average CPR duration of 7 minutes, whereas 115,445 (33%) did not achieve return of spontaneous circulation with an average CPR duration of 20 minutes.
At one minute’s CPR duration, the probabilities of survival and favorable functional outcome among patients were 22% and 15%, respectively.
But as duration of CPR increased, the probabilities of survival and favorable functional outcome decreased to less than 1% for survival at 39 minutes and less than 1% for favorable functional outcome at 32 minutes.
These are observational findings and the researchers acknowledge that they relied on the assumption that any termination of resuscitation was appropriate. They also point out that collecting time variables during CPR is difficult and they were unable to account for severity of underlying conditions and quality of CPR or post-resuscitation care at each hospital.
However, they say this was a well designed study using the largest in-hospital cardiac arrest dataset in the world, making the findings pertinent for hospitals intending to improve their resuscitation performance.
As such they conclude: “The findings provide resuscitation teams, patients, and their surrogates with insights into the likelihood of favorable outcomes if patients pending the first return of spontaneous circulation continue to receive further cardiopulmonary resuscitation.”
END
Researchers estimate survival chances during CPR for cardiac arrest
New estimates may help guide decisions about how long to continue resuscitation
2024-02-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Group rehabilitation improves quality of life for people with long covid
2024-02-08
An online programme of physical and mental health rehabilitation can improve quality of life for adults with long covid, finds a trial published by The BMJ today.
The eight week REGAIN programme, delivered in online group sessions, led to sustained improvements in fatigue, pain, and depression compared with usual care.
The researchers say this accessible, resource-efficient programme can be delivered at scale and will assist clinicians in the treatment of this complex condition.
Post-covid-19 condition (commonly known as long covid) ...
Anxiety of headteachers across England “substantially increased” during the pandemic
2024-02-08
The anxiety of headteachers across England increased “substantially” throughout the pandemic, finds the largest study of its type to-date.
The results of the research, which examined thousands of teachers’ anxiety about work at 75 touchpoints from October 2019 to July 2022, show that senior leaders in schools suffered – even “much more” when compared with junior colleagues.
The findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Educational Review, are the latest to demonstrate the mental ...
UTHealth Houston report in NEJM: Deadly fungal infection acquired during surgery in Mexico led to death and brainstem, blood supply injuries
2024-02-08
A life-threatening mold infection known as health care-associated Fusarium solani meningitis can be associated with a delayed, but devastating, injury to the brainstem and its blood supply among those infected, according to physicians from UTHealth Houston.
A report, led by first author Nora Strong, MD, and senior author Luis Ostrosky-Zeichner, MD, was published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. Strong is a second-year postdoctoral fellow in infectious diseases with McGovern Medical ...
Reducing harmful health screenings and overtreatment in older adults
2024-02-08
Study effectively reduced doctors’ actions for overused tests and treatment
Routine testing for prostate cancer, urinary tract infections and blood sugar can result in unnecessary care and serious health problems
Practices stubbornly persist despite lack of evidence
CHICAGO --- When a doctor ordered a routine prostate screening for an 80-year-old man — as doctors often do — a dramatic yellow alert popped up on the electronic health record with dire warnings.
It flashed: “You are ordering a test that no guideline ...
Pregnant women should avoid ultraprocessed, fast foods
2024-02-07
If you’re pregnant, you may want to think twice before making a hamburger run or reaching for a prepackaged pastry, according to research published last month in the journal Environmental International.
Oddly enough it’s not the food that the report targets — not the fries, burgers or even the shakes and cakes — but what touches the food before you eat it.
Research shows that phthalates, a class of chemicals associated with plastics, can shed from the wrapping, packaging and even from plastic gloves worn by food handlers into food. Once consumed during pregnancy, the chemicals can get into the bloodstream, through ...
University of Houston researcher part of $5 million DOD grant to support defense manufacturing
2024-02-07
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) awarded a $5 million grant to the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley (UTRGV)-led America’s Additive Foundry Consortium, which includes the University of Houston as a key partner. This is one of six grants – totaling about $30 million – to help enhance national security through community investments.
The funding will enable the consortium to undertake a $7.5 million project designed to ensure that the U.S. military has a stable supply of domestically produced, high-quality tactical alloys critical for national defense. The ...
Researchers measure and control interactions between magnetic ripples using lasers
2024-02-07
One vision for the future of computing involves using ripples in magnetic fields — called magnons — as a basic mechanism. In this application, magnons would be comparable to electricity as the basis for electronics.
In conventional digital technologies, such magnonic systems are expected to be far faster than today’s technologies, from laptops and smartphones to telecommunications. In quantum computing, the advantages of magnonics could include not only quicker speeds but also more stable devices.
A recent study in the journal Nature Physics reports an early-stage discovery along the path ...
Africa could grow more rice -- new study shows how
2024-02-07
Africa’s rice sector has major opportunities to increase its yield gains through improved agronomic practices while avoiding massive land conversion, a study by international scientists including a Husker co-investigator finds. The production advances can be important in meeting Africa’s projected food needs and reducing dependence on imports, the researchers concluded.
Rice demand in Africa is projected to more than double over the next 25 years due to population growth and increased rice consumption. At present, Africa imports nearly 40% of its rice.
“Nearly 15 million hectares of rice are waiting for yield improvement in Africa, ...
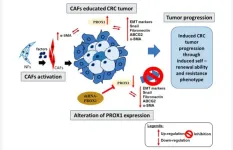
PROX1/α-SMA correlated with colorectal cancer progression, poor outcomes and therapeutic resistance
2024-02-07
“The findings validate the combined PROX1/α-SMA gene set as a prospective prognostic biomarker and a central regulator in CRC progression and its TME.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 7, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 2, entitled, “PROX1 interaction with α-SMA-rich cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitates colorectal cancer progression and correlates with poor clinical outcomes and therapeutic resistance.”
The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a vital role in tumor progression through intricate ...
Ancient rocks improve understanding of tectonic activity between earthquakes
2024-02-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Rocks once buried deep in ancient subduction zones — where tectonic plates collide — could help scientists make better predictions of how these zones behave during the years between major earthquakes, according to a research team from Penn State and Brown University.
Clues from rock formations in Alaska and Japan allowed the scientists to develop a new model to predict the pressure solution activity in subduction zones, the researchers reported in the journal Science Advances. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
IEEE honors Pitt’s Fang Peng with medal in power engineering
SwRI and the NPSS Consortium release new version of NPSS® software with improved functionality
Study identifies molecular cause of taste loss after COVID
Accounting for soil saturation enhances atmospheric river flood warnings
The research that got sick veterans treatment
Study finds that on-demand wage access boosts savings and financial engagement for low-wage workers
Antarctica has lost 10 times the size of Greater Los Angeles in ice over 30 years
Scared of spiders? The real horror story is a world without them
New study moves nanomedicine one step closer to better and safer drug delivery
Illinois team tests the costs, benefits of agrivoltaics across the Midwest
[Press-News.org] Researchers estimate survival chances during CPR for cardiac arrestNew estimates may help guide decisions about how long to continue resuscitation