(Press-News.org) Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 01:00hrs GMT Thursday 8 February 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals and cells
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing ‘lost’ enzyme
Scientists at the Francis Crick Institute have found a new treatment target for CDKL5 deficiency disorder (CDD), one of the most common types of genetic epilepsy.
CDD causes seizures and impaired development in children, and medications are limited to managing symptoms rather than tackling the root cause of the disease. The disorder involves losing the function of a gene producing the CDKL5 enzyme, which phosphorylates proteins, meaning it adds an extra phosphate molecule to alter their function.
Following recent research from the same lab showing that a calcium channel could be a target for therapy for CDD, the team has now identified a new way to potentially treat CDD by boosting another enzyme’s activity to compensate for the loss of CDKL5.
In research published today in Molecular Psychiatry, the scientists studied mice that don’t make the CDKL5 enzyme. These mice show similar symptoms to people with CDD like impaired learning or social interaction.
The researchers first identified that CDKL5 is active in nerve cells in mice but not in another type of brain cell called an astrocyte. In the nerve cells, they measured the level of phosphorylation of EB2, a molecule known to be targeted by CDKL5, to understand what happens when CDKL5 isn’t produced.
Interestingly, even in mice that don’t produce CDKL5, there was still some EB2 phosphorylation taking place, which suggested that another similar enzyme must also be able to phosphorylate it.
By looking at enzymes similar to CDKL5, the researchers identified that one called CDKL2 also targets EB2 and is present in human neurons. In mice without both CDKL5 and CDKL2, the remaining EB2 phosphorylation almost fully dropped off.
The researchers concluded that, although most activity comes from CDKL5, about 15% is from CDKL2, and the remaining <5% from another enzyme yet to be identified.
Their research suggests that increasing the level of CDKL2 in people who are deficient in CDKL5 could potentially treat some of the effects on the brain in early development.
Sila Ultanir, Group Leader of the Kinases and Brain Development Laboratory at the Crick, said, “CDD is a devastating condition that impacts young children from birth, and we don’t know a huge amount about why losing this one enzyme is so disastrous for the developing brain. Through this research, we’ve identified a potential way to compensate for the loss of CDKL5. If we can increase levels of CDKL2, we might one day be able to stop symptoms from developing or getting worse.”
The researchers are now investigating if mice without CDKL5 can be treated by stimulating their brain cells to produce more CDKL2. The lab is also working with biotechnology companies to identify molecules that increase CDKL2 for potential new medicines for CDD.
Margaux Silvestre, former PhD student at the Crick and now postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research in Frankfurt, said: “Our discoveries offer fresh insights into the expression and regulation of CDKL5 in the brain. Moreover, the identification of CDKL2 as a potential compensatory enzyme provides hope for uncovering better treatments that could truly make a difference in the lives of the children with this devastating condition. This research owes its success to all the authors involved in the publication but also the unwavering support we received from the technical teams at the Crick – a big shoutout to them!”
The research was funded by the Loulou Foundation, a private foundation dedicated to the development of therapeutics and eventual cures for CDD.
-ENDS-
For further information, contact: press@crick.ac.uk or +44 (0)20 3796 5252
Notes to Editors
Reference: Silvestre, M. et al. (2024). Cell-type specific expression, regulation and compensation of CDKL5 activity in mouse brain. Molecular Psychiatry. 10.1038/s41380-024-02434-7.
The Francis Crick Institute is a biomedical discovery institute dedicated to understanding the fundamental biology underlying health and disease. Its work is helping to understand why disease develops and to translate discoveries into new ways to prevent, diagnose and treat illnesses such as cancer, heart disease, stroke, infections, and neurodegenerative diseases.
An independent organisation, its founding partners are the Medical Research Council (MRC), Cancer Research UK, Wellcome, UCL (University College London), Imperial College London and King’s College London.
The Crick was formed in 2015, and in 2016 it moved into a brand new state-of-the-art building in central London which brings together 1500 scientists and support staff working collaboratively across disciplines, making it the biggest biomedical research facility under a single roof in Europe.
http://crick.ac.uk/
END
Researchers identify potential way to treat genetic epilepsy by replacing ‘lost’ enzyme
2024-02-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New guidelines for reporting clinical trials of biofield therapies
2024-02-08
New guidelines for reporting clinical trials of biofield therapies are presented in the peer-reviewed Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (JICM). Biofield therapies (BFTs), such as External Qigong, Healing Touch, Reiki, and Therapeutic Touch, are a related group of integrative medicine interventions in which practitioners use their hands on or above a client’s body to stimulate healing and well-being. Click here to read the article now.
The guidelines call for including details of the intervention protocols relevant to biofield therapy trials. The Reporting Evidence Guidelines comprises ...
Wayne State University awarded $1.4 million from Department of Defense to expand on research findings surrounding prostate cancer
2024-02-08
DETROIT– A team of researchers from Wayne State University was awarded a $1.4 million, three-year grant from the U.S. Department of Defense for the study, “Cytochrome c acetylation drives prostate cancer aggressiveness and Warburg effect.”
The study, led by Maik Hüttemann, Ph.D., professor of molecular medicine and genetics, and biochemistry, microbiology and immunology at Wayne State University’s School of Medicine, aims to establish the role of the protein cytochrome c, which the team proposes is ...
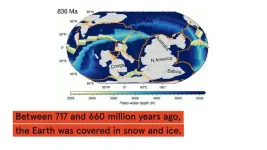
What turned Earth into a giant snowball 700m years ago? Scientists now have an answer
2024-02-08
Australian geologists have used plate tectonic modelling to determine what most likely caused an extreme ice-age climate in Earth’s history, more than 700 million years ago.
The study, published in Geology, helps our understanding of the functioning of the Earth's built-in thermostat that prevents the Earth from getting stuck in overheating mode. It also shows how sensitive global climate is to atmospheric carbon concentration.
“Imagine the Earth almost completely frozen over,” said the study’s lead author, ARC Future Fellow ...
Researchers estimate survival chances during CPR for cardiac arrest
2024-02-08
A person’s chance of surviving while receiving cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) for cardiac arrest in hospital declines rapidly from 22% after one minute to less than 1% after 39 minutes, finds a US study published by The BMJ today.
Similarly, the likelihood of leaving hospital with no major brain damage declines from 15% after one minute of CPR to less than 1% after 32 minutes with no heartbeat.
The researchers say the findings provide insights that may help guide hospital teams, patients and their families in deciding how long to continue resuscitation.
In-hospital ...
Group rehabilitation improves quality of life for people with long covid
2024-02-08
An online programme of physical and mental health rehabilitation can improve quality of life for adults with long covid, finds a trial published by The BMJ today.
The eight week REGAIN programme, delivered in online group sessions, led to sustained improvements in fatigue, pain, and depression compared with usual care.
The researchers say this accessible, resource-efficient programme can be delivered at scale and will assist clinicians in the treatment of this complex condition.
Post-covid-19 condition (commonly known as long covid) ...
Anxiety of headteachers across England “substantially increased” during the pandemic
2024-02-08
The anxiety of headteachers across England increased “substantially” throughout the pandemic, finds the largest study of its type to-date.
The results of the research, which examined thousands of teachers’ anxiety about work at 75 touchpoints from October 2019 to July 2022, show that senior leaders in schools suffered – even “much more” when compared with junior colleagues.
The findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Educational Review, are the latest to demonstrate the mental ...
UTHealth Houston report in NEJM: Deadly fungal infection acquired during surgery in Mexico led to death and brainstem, blood supply injuries
2024-02-08
A life-threatening mold infection known as health care-associated Fusarium solani meningitis can be associated with a delayed, but devastating, injury to the brainstem and its blood supply among those infected, according to physicians from UTHealth Houston.
A report, led by first author Nora Strong, MD, and senior author Luis Ostrosky-Zeichner, MD, was published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. Strong is a second-year postdoctoral fellow in infectious diseases with McGovern Medical ...
Reducing harmful health screenings and overtreatment in older adults
2024-02-08
Study effectively reduced doctors’ actions for overused tests and treatment
Routine testing for prostate cancer, urinary tract infections and blood sugar can result in unnecessary care and serious health problems
Practices stubbornly persist despite lack of evidence
CHICAGO --- When a doctor ordered a routine prostate screening for an 80-year-old man — as doctors often do — a dramatic yellow alert popped up on the electronic health record with dire warnings.
It flashed: “You are ordering a test that no guideline ...
Pregnant women should avoid ultraprocessed, fast foods
2024-02-07
If you’re pregnant, you may want to think twice before making a hamburger run or reaching for a prepackaged pastry, according to research published last month in the journal Environmental International.
Oddly enough it’s not the food that the report targets — not the fries, burgers or even the shakes and cakes — but what touches the food before you eat it.
Research shows that phthalates, a class of chemicals associated with plastics, can shed from the wrapping, packaging and even from plastic gloves worn by food handlers into food. Once consumed during pregnancy, the chemicals can get into the bloodstream, through ...
University of Houston researcher part of $5 million DOD grant to support defense manufacturing
2024-02-07
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) awarded a $5 million grant to the University of Texas Rio Grande Valley (UTRGV)-led America’s Additive Foundry Consortium, which includes the University of Houston as a key partner. This is one of six grants – totaling about $30 million – to help enhance national security through community investments.
The funding will enable the consortium to undertake a $7.5 million project designed to ensure that the U.S. military has a stable supply of domestically produced, high-quality tactical alloys critical for national defense. The ...