University Hospitals now offering FDA-approved medication for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
UH Brain Health & Memory Center begins LEQEMBI® (lecanemab) infusions for patients
2024-02-09
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND—University Hospitals (UH) Brain Health & Memory Center is now treating patients with LEQEMBI® (lecanemab), a Food and Drug Administration-approved medication for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
“Those with Alzheimer’s disease often have an abnormal buildup of plaques in their brain that contain a protein called beta-amyloid,” said Charles J. Duffy, MD, PhD, neurologist and Director of the Brain Health & Memory Center within the UH Neurological Institute. “Lecanemab is an IV medication designed to target and remove these plaques, and has the potential to slow cognitive and functional decline if started in the early stages of the disease. We’re happy to be able to offer this breakthrough treatment to our patients at UH.”
Lecanemab is administered every two weeks through IV infusion, with each session lasting about one hour. Infusions occur for one year for a total of 26 treatments. Patients are monitored for a period of time after each infusion to ensure there are no negative reactions to the drug.
“This new drug has shown significant promise in clinical trials and may be a treatment option for patients with mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. While there currently is no cure for Alzheimer’s, lecanemab may slow progression of the disease, enhance patients’ ability to participate in daily life, and allow them to live independently for a longer period of time,” explained Dr. Duffy, who also holds the A. William and Joanne Reynolds Chair in Brain Health at UH and is a professor at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine.
Those with symptoms of early Alzheimer’s disease and the confirmed presence of beta-amyloid plaques in the brain may be eligible for treatment with lecanemab. Early symptoms of Alzheimer’s may include: mild cognitive impairment, such as forgetfulness and confusion, and mild dementia, such as difficulty performing familiar tasks. The therapy has not been tested on people with advanced Alzheimer's or those without clinical symptoms.
Although there is no single diagnostic test to confirm Alzheimer’s disease, physicians may use a variety of approaches to help them make a diagnosis and determine if treatment with lecanemab might be appropriate. Tests and procedures may include: Comprehensive personal and family medical history; Mental status tests; Physical and neurological exams; Blood tests; Spinal tap to remove a sample of cerebrospinal fluid for testing; MRI of the brain; and PET scan of the brain to look for the presence of beta-amyloid plaques.
Patients approved to receive lecanemab therapy will be carefully monitored at set intervals as determined by their physician. Subsequent brain MRIs and lab tests will be obtained periodically to monitor for side effects of treatment.
To learn more about this treatment, visit: https://www.uhhospitals.org/services/neurology-and-neurosurgery-services/conditions-and-treatments/brain-health-and-memory/lecanemab-for-alzheimers
###
About University Hospitals / Cleveland, Ohio
Founded in 1866, University Hospitals serves the needs of patients through an integrated network of 21 hospitals (including five joint ventures), more than 50 health centers and outpatient facilities, and over 200 physician offices in 16 counties throughout northern Ohio. The system’s flagship quaternary care, academic medical center, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, is affiliated with Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Northeast Ohio Medical University, Oxford University, the Technion Israel Institute of Technology and National Taiwan University College of Medicine. The main campus also includes the UH Rainbow Babies & Children's Hospital, ranked among the top children’s hospitals in the nation; UH MacDonald Women's Hospital, Ohio's only hospital for women; and UH Seidman Cancer Center, part of the NCI-designated Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. UH is home to some of the most prestigious clinical and research programs in the nation, with more than 3,000 active clinical trials and research studies underway. UH Cleveland Medical Center is perennially among the highest performers in national ranking surveys, including “America’s Best Hospitals” from U.S. News & World Report. UH is also home to 19 Clinical Care Delivery and Research Institutes. UH is one of the largest employers in Northeast Ohio with more than 30,000 employees. Follow UH on LinkedIn, Facebook and Twitter. For more information, visit UHhospitals.org.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-09
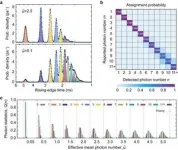
Using single photons as qubits has become a prominent strategy in quantum information technology. Accurately determining the number of photons is crucial in various quantum systems, including quantum computation, quantum communication, and quantum metrology. Photon-number-resolving detectors (PNRDs) play a vital role in achieving this accuracy and have two main performance indicators: resolving fidelity, which measures the probability of accurately recording the number of incident photons, and dynamic range, which describes the maximum resolvable photon number.
Superconducting nanostrip single-photon detectors (SNSPDs) are considered the leading ...
2024-02-09
DURHAM, N.C. -- It might look like a comet or a shooting star, but this time-lapse video is actually a tiny plant root, not much thicker than a human hair, magnified hundreds of times as it grows under the microscope.
Researchers at Duke University have been making such movies by peering at stem cells near the root’s tip and taking snapshots as they divide and multiply over time, using a technique called light sheet microscopy.
The work offers more than a front row seat to the drama of growing roots. By watching how the cells divide in response to certain chemical signals, the team is finding new clues to how stem cells choose one ...
2024-02-09
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Feb. 8, 2024) — A researcher in the University of Kentucky College of Nursing has been selected as a scholar for the Environmental Health Research Institute for Nurse and Clinician Scientists (EHRI-NCS).
EHRI-NCS is a year-long flipped classroom, train-the-trainer and mentorship program aimed at developing a new era of environmental health nursing science. It’s led by Castner Incorporated, a health research company, in partnership with Emory University, Washington State University and University of Alabama in Huntsville.
Stacy Stanifer, Ph.D., an advanced practice registered nurse and an assistant professor of nursing, was selected to participate. ...
2024-02-09
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – UNC School of Medicine researcher Sarah Cohen, PhD, and Ian Windham, a former PhD student from the Cohen lab, have made a new discovery about apolipoprotein E (APOE) – the biggest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease.
Older people who inherited a genetic variant called APOE4 from their parents have a two- or three-times greater risk of developing the late-onset neurodegenerative disease. If researchers can better understand how APOE4 is affecting brain cells, it may help them design effective therapeutics and target the mechanisms causing the enhanced disease risk.
Cohen and Windham performed an exceptionally ...
2024-02-09
In the treatment of aggressive lymphomas and blood cancer (leukaemia), so-called chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR T cells) are increasingly being used. For this therapy, immune cells are taken from patients and programmed by means of genetic engineering to detect proteins on the malignant tumour cells. Back in the body, the CAR T cells then fight the cancer cells. Due to some heavy side effects, this therapy requires extreme caution and long hospital stays. Scientists at University Hospital Cologne are therefore researching ...
2024-02-09
Acting on a proposal from the Institut Pasteur President Yasmine Belkaid, the Institut Pasteur Board of Governors appointed Mariana Mesel-Lemoine as Director of Diversity, Equity and Inclusion on Wednesday February 7, 2024.
This appointment marks a significant milestone in the history of the Institut Pasteur, and it is the first French research institute to establish a position of this kind at such a senior and strategic level. Mariana Mesel-Lemoine will report directly to the President. Her mission will be to propose policy and strategy priorities related to diversity, equity and inclusion for the "Pasteur 2030" Strategic Plan, to oversee ...
2024-02-09
About The Study: In hospitals participating in Get With The Guidelines–Stroke, earlier anticoagulation reversal was associated with improved survival for patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. These findings support intensive efforts to accelerate evaluation and treatment for patients with this devastating form of stroke.
Authors: Kevin N. Sheth, M.D., of the Yale University School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
2024-02-09
Sleep apnea is prevalent among cardio-oncology patients who are at higher risk for congestive heart failure from cancer therapy, according to a new study being presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient course.
Sleep apnea is a disorder of altered breathing while asleep with two types, obstructive (OSA) or central (CSA). Both can be treated to alleviate symptoms and improve cardiovascular outcomes. This study pertains to obstructive sleep apnea. A well-established screening tool for detecting sleep apnea is the STOP-BANG questionnaire utilizing eight questions using ...
2024-02-09
Since December 2019, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has posed a worldwide threat. The emergence of the BA.2.86 variant, a subvariant of Omicron, has raised significant concerns due to its substantial number of mutations. Discovered in August 2023, this variant differs markedly from other existing types such as Omicron XBB (including EG.5.1 and HK.3). Compared with XBB and BA.2, BA.2.86 exhibits more than 30 mutations in its spike protein, contributing to its ability to effectively evade the immune system’s defenses.
Over ...
2024-02-09
Sensory feedback is important for amputees to be able to explore and interact with their environment. Now, researchers have developed a device that allows amputees to sense and respond to temperature by delivering thermal information from the prosthesis’ fingertip to the amputee’s residual limb. The “MiniTouch” device, presented February 9 in the journal Med, uses off-the-shelf electronics, can be integrated into commercially available prosthetic limbs, and does not require surgery. Using the thermally sensitive prosthetic hand, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] University Hospitals now offering FDA-approved medication for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
UH Brain Health & Memory Center begins LEQEMBI® (lecanemab) infusions for patients