(Press-News.org) Anyone who has ever been to a loud concert knows the feeling of ringing ears. Some people experience temporary or even permanent hearing loss or drastic changes in their perception of sound after the loud noises stop. Thanos Tzounopoulos, Ph.D., director of the Pittsburgh Hearing Research Center at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine has focused his scientific career on investigating how hearing works and developing ways to treat tinnitus and hearing loss.
In a paper published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Tzounopoulos and his Pitt collaborators Amantha Thathiah, Ph.D., and Chris Cunningham, Ph.D., discovered a molecular mechanism of noise-induced hearing loss and showed that it could be mitigated with medication.
The study showed that noise-induced hearing loss, which affects millions of Americans, stems from cellular damage in the inner ear that is associated with the excess of free-floating zinc – a mineral that is essential for proper cellular function and hearing. Experiments in mice showed drugs that work as molecular sponges trapping excess zinc can help restore lost hearing or, if administered before an expected loud sound exposure, can protect from hearing loss.
“Noise-induced hearing loss impairs millions of lives but, because the biology of hearing loss is not fully understood, preventing hearing loss has been an ongoing challenge,” said senior author Thanos Tzounopoulos, Ph.D., endowed professor and vice-chair of research of otolaryngology at Pitt.
While some experience noise-induced hearing loss as a result of an acute traumatic injury to the ear, others notice a sudden hearing impairment after being continuously exposed to loud noise, for example in a battlefield or at a construction site. Others notice their hearing deteriorating after attending a loud music show.
Researchers say such noise-induced hearing loss can be debilitating. Some people start hearing sounds that aren’t there, developing a condition called tinnitus, which severely affects a person’s quality of life.
Tzounopoulos’ research, which focuses on the biology of hearing, tinnitus and hearing loss, strived to determine the mechanistic underpinnings of the condition in the effort to lay the groundwork for the development of effective and minimally invasive treatments in the future.
By performing experiments in mice and on isolated cells of the inner ear, researchers found that hours after mice are exposed to loud noise, their inner ear zinc level spikes. Loud sound exposure causes a robust release of zinc into the extra and intracellular space which, ultimately, leads to cellular damage and disrupts normal cell to cell communication.
Thankfully, this discovery opens doors for a possible solution. Experiments showed mice who were treated with a slow-releasing compound that trapped excess free zinc were less prone to hearing loss and were protected from noise-induced damage.
Researchers are currently developing a treatment to be tested in preclinical safety studies with the goal of making it available as a simple, over-the-counter option to protect oneself from hearing loss.
Other authors of the study are first author Brandon Bizup, Ph.D., and co-author Sofie Brutsaert, both of Pitt.
END
Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise – and find a way to prevent it
2024-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Widespread machine learning methods behind ‘link prediction’ are performing very poorly
2024-02-12
As you scroll through any social media feed, you are likely to be prompted to follow or friend another person, expanding your personal network and contributing to the growth of the app itself. The person suggested to you is a result of link prediction: a widespread machine learning (ML) task that evaluates the links in a network — your friends and everyone else’s — and tries to predict what the next links will be.
Beyond being the engine that drives social media expansion, link prediction is also used in a wide range of scientific research, such as predicting the interaction between genes and proteins, and is used by researchers as a benchmark for ...
The hidden rule for flight feathers—and how it could reveal which dinosaurs could fly
2024-02-12
Birds can fly— at least, most of them can. Flightless birds like penguins and ostriches have evolved lifestyles that don’t require flight. However, there’s a lot that scientists don’t know about how the wings and feathers of flightless birds differ from their airborne cousins. In a new study in the journal PNAS, scientists examined hundreds of birds in museum collections and discovered a suite of feather characteristics that all flying birds have in common. These “rules” provide clues as to how the dinosaur ancestors of modern birds first evolved the ability to fly, ...
Machine learning promises to accelerate metabolism research
2024-02-12
A new study shows that it is possible to use machine learning and statistics to address a problem that has long hindered the field of metabolomics: large variations in the data collected at different sites.
“We don’t always know the source of the variation,” said Daniel Raftery, professor of anesthesiology and pain medicine at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle. “It could be because the subjects are different with different genetics, diets and environmental exposures. Or it could be the way samples were collected and ...
Researchers uncover a key link in legume plant-bacteria symbiosis
2024-02-12
Legume plants have the unique ability to interact with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil, known as rhizobia. Legumes and rhizobia engage in symbiotic relations upon nitrogen starvation, allowing the plant to thrive without the need for externally supplied nitrogen. Symbiotic nodules are formed on the root of the plant, which are readily colonized by nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The cell-surface receptor SYMRK (symbiosis receptor-like kinase) is responsible for mediating the symbiotic signal from rhizobia perception to formation of the nodule. ...
Genetic analysis and archaeological insight combine to reveal the ancient origins of the fallow deer
2024-02-12
Modern populations of fallow deer possess hidden cultural histories dating back to the Roman Empire which ought to be factored into decisions around their management and conservation.
New research, bringing together DNA analysis with archaeological insights, has revealed how fallow deer have been repeatedly moved to new territories by humans, often as a symbol of colonial power or because of ancient cultures and religions.
The results show that the animal was first introduced into Britain by the Romans ...
Researchers studying ocean transform faults, describe a previously unknown part of the geological carbon cycle
2024-02-12
Woods Hole, Mass. (February 12, 2024) – Studying a rock is like reading a book. The rock has a story to tell, says Frieder Klein, an associate scientist in the Marine Chemistry & Geochemistry Department at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
The rocks that Klein and his colleagues analyzed from the submerged flanks of the St. Peter and St. Paul Archipelago in the St. Paul’s oceanic transform fault, about 500 km off the coast of Brazil, tells a fascinating and previously unknown story about parts of the geological ...
Salt substitutes help to maintain healthy blood pressure in older adults
2024-02-12
The replacement of regular salt with a salt substitute can reduce incidences of hypertension, or high blood pressure, in older adults without increasing their risk of low blood pressure episodes, according to a recent study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. People who used a salt substitute had a 40% lower incidence and likelihood of experiencing hypertension compared to those who used regular salt.
According to the World Health Organization, hypertension is the leading risk factor for cardiovascular disease and mortality. It affects over 1.4 billion adults and results in 10.8 million deaths per year worldwide. One of the ...
Heart disease risk factors in women highlight need for increased awareness, prevention
2024-02-12
Statement Highlights:
The new scientific statement highlights heart disease as the leading cause of death for women and emerging evidence that has identified several gender-specific risk factors for heart disease in women, including complications during pregnancy and premature menopause.
Compared to men, women also have different symptoms of heart disease, are less likely to receive evidence-based therapies and are more likely to have adverse cardiovascular outcomes after a cardiac event.
Targeted public health interventions ...
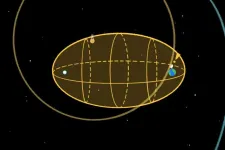
SETI institute employs SETI ellipsoid technique for searching for signals from distant civilizations
2024-02-12
February 12, 2024, Mountain View, CA -- In a paper published in the Astronomical Journal, a team of researchers from the SETI Institute, Berkeley SETI Research Center and the University of Washington reported an exciting development for the field of astrophysics and the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI), using observations from the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) mission to monitor the SETI Ellipsoid, a method for identifying potential signals from advanced civilizations in the ...
Sugar-reduced chocolate with oat flour just as tasty as original, study finds
2024-02-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The secret to making delicious chocolate with less added sugar is oat flour, according to a new study by Penn State researchers. In a blind taste test, recently published in the Journal of Food Science, 25% reduced-sugar chocolates made with oat flour were rated equally, and in some cases preferred, to regular chocolate. The findings provide a new option for decreasing chocolate’s sugar content while maintaining its texture and flavor.
“We were able to show that there is a range in which you can ...