(Press-News.org) Nearly half of teenagers are worried about having children and many lack knowledge about their reproductive health, find two new studies by UCL researchers.
The studies, published in Human Fertility and Health Education Journal, used survey results from 931 students in England aged 16 to 18, collected between May 2021 and July 2022.
The Human Fertility paper found that a majority of students (64%) still wanted to have children in the future – with nearly half (49%) desiring to have two children.
However, 45% of all participants said that they had concerns about future parenthood –expressing their fears about their ability to have healthy offspring and the lives their children might lead.
When asked what their concerns were, the teenagers responded that fear, self-doubt, health and wellbeing, financial burdens, hinderance to personal aspirations and non-inclusive LGBTQ+ education all played a part in their anxieties.
For example, some students’ desire to have children was influenced by climate change, while others who identified within the LGBTQ+ community felt that the Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) they received at school lacked inclusivity.
Meanwhile, the students who did not want children in the future (36%) cited reasons including: negative associations with pregnancy and childbirth; parenthood apprehension; raising a child in a world with an uncertain future; considering alternative routes to parenthood; and finding children a nuisance.
One female participant said: “The state of the world is in a shambles. Governments are corrupt. The environment is deteriorating … it would be cruel to put a child through any of our problems, especially since they are not getting better.”
Senior author, Professor Joyce Harper (UCL EGA Institute for Women’s Health), said: “Sadly, a number of female students expressed a lack of interest in future parenthood due to their fears about pregnancy and childbirth.
“Shortcomings in fertility education in schools also meant that students were left feeling both ill-informed and negative towards their own fertility and ability to have children.”
Until recently, sex education in the UK focused on puberty, menstruation, sexually-transmitted infections including HIV/AIDS, contraception and abortion.
Guidance in England about sex education remained unchanged for almost 20 years until in September 2020 a new Relationships Education curriculum became compulsory for all primary schools (5-11 year-olds) in England.
Additionally, a compulsory RSE curriculum was brought in for secondary schools (11-18-year-olds) and included the need to teach reproductive health.
However, the second paper, published in Health Education Journal, found there were still significant gaps in young people’s education – and that teenagers are not being taught about key reproductive issues such as endometriosis, infertility and the impact of lifestyle on fertility.
Over half (65%) of the students rated the sex education they’d received as adequate or below and half (49%) said they did not know when a woman was most fertile.
When asked how their education could be improved, students suggested making the curriculum more inclusive and relevant, alongside providing honest, transparent and non-judgemental teaching and boosting sex positivity.
One female participant responded: “All we’ve done in school is go over and over having safe sex and talked about periods which whilst is important is barely scratching the surface of things people need to know about. If miscarriage and infertility were better taught, then that could reduce the guilt and embarrassment people who struggle with it would feel.”
While a male teen added: “Make the education a bit more ‘real world’ in the sense that [currently] it can be difficult to apply current knowledge to what is needed in life.”
Professor Harper added: “It is not surprising that we take so long to diagnose conditions such as endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) when pupils are not taught about these conditions. It seems we are afraid to talk about a ‘normal’ and ‘abnormal’ menstrual cycle.
“With regards to fertility education, most teenagers told us they want children in the future but at school we concentrate on teaching them how not to get pregnant, not how to have a healthy pregnancy.
“The menopause is now included in the Department for Education curriculum and it needs to be taught.
“This is why the International Reproductive Health Education Collaboration* that I co-founded has developed a number of educational resources, including a teacher’s guide which will be available, for free, very soon.”
The research team hope that the study will contribute to the improvement of sex and reproductive health education for students in England.
END
Teenagers need better reproductive health education to tackle parenthood fears
Peer reviewed | Survey
2024-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Data-driven app results in 25% fewer emergency hospital admissions from care homes
2024-02-13
The use of a digital remote monitoring technology in care homes has been found to reduce hospital A&E attendances by 11% and emergency admissions by 25% in a new study from the Health Data Research UK (HDR UK) Better Care programme, published today in Age and Ageing - the official journal of the British Geriatrics Society.
There are over 400,000 people living in care homes across the UK, many of whom will be living with complex medical needs that put them at greater risk of needing emergency healthcare, especially during the winter months.
Through the HDR UK Better Care programme, a collaboration between the universities ...
In rural states, gardening and foraging helped prevent hunger during COVID: Study
2024-02-13
New research on rural New Englanders shows that gardening, hunting, fishing and other HWFP activities are important tools for maintaining food security through extreme events, such as pandemics or climate change events.
University of Vermont and University of Maine researchers found that both food insecurity and home and wild food production (HWFP) – gardening, hunting, fishing, foraging, and having “backyard” poultry or livestock – increased significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic, and those who undertook HWFP activities exhibited improved food security 9-12 months later.
The paper, published in Scientific Reports, surveyed ...
New study finds roughly 1 in 10 pregnant people will develop long COVID
2024-02-13
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL: Feb. 12, 2024 5:45 p.m. Eastern Standard Time
Media Contacts: Karen Addis, APR, karen@addispr.com, +1 (301) 787-2394; Kerri Wade, MPA, kwade@smfm.org, +1 ...
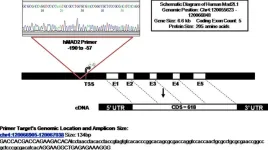
Differential expression of Mad2 gene in human esophageal cancer
2024-02-12
“[...] people of the northeastern region [of India] consume betel quid, consisting of raw areca nut [...]. People often swallow the entire betel-quid after chewing, which is believed to contribute to the development of oral, esophageal, and gastric cancers.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 12, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on February 5, 2024, entitled, “Differential expression of Mad2 gene is consequential to the patterns of histone H3 post-translational modifications in its promoter region in human esophageal ...
RIT's Center for Detectors to work on two NASA projects
2024-02-12
Rochester Institute of Technology’s Center for Detectors has been chosen by NASA for two research programs: Early Stage Innovations (ESI) and Strategic Astrophysics Technology (SAT), with the hope of helping future spacecraft find new discoveries in the vast universe.
Under the leadership of Center for Detectors Director Don Figer, the team will be advancing and characterizing single-photon sensing complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensors to determine if they can survive the harsh radiation environments in NASA missions. The intent is to fly these types of detectors on future missions to find life on Jupiter’s ...
Archaeologists discover oldest known bead in the Americas
2024-02-12
University of Wyoming archaeology Professor Todd Surovell and his team of collaborators have discovered a tube-shaped bead made of bone that is about 12,940 years old.
The bead, found at the La Prele Mammoth site in Converse County, is the oldest known bead in the Americas.
Surovell’s research was published in the peer-reviewed journal Scientific Reports; the paper is titled “Use of hare bone for the manufacture of a Clovis bead.” Members of the research team included people from UW, the Office of the Wyoming State Archaeologist, the University of Manchester, Weber ...
Interferon-gamma drives brain pathology in a mouse model of multiple system atrophy
2024-02-12
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Multiple system atrophy is a rare and fatal neurodegenerative disease, where insoluble inclusions of the protein alpha-synuclein appear in oligodendrocyte cells of the brain. The resulting pathogenesis features neuroinflammation, demyelination and neurodegeneration. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin, an insulating sheath on the axons of nerves.
In 2020, Ashley Harms, Ph.D., and University of Alabama at Birmingham colleagues published an Acta Neuropathologica study that used a mouse model to show that the ...
Drought may drive deadly amphibian disease, researchers find
2024-02-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Pumpkin toadlets are in trouble. Progressively severe droughts are disrupting the microbiomes of the thumbnail-sized orange frogs, potentially leaving them vulnerable to a deadly fungal disease, according to a new study by an international research team. The finding suggests that abnormal rainfall patterns, which are expected to worsen due to climate change and deforestation, may upset mutually beneficial relationships between wildlife and microorganisms, leading to biodiversity decline.
The researchers, led by Penn State doctoral ...
New study finds commonly used antibiotic is a cost-saving treatment for reducing maternal sepsis, death or infection in developing countries
2024-02-12
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL: Feb. 12, 2024, 4:30 PM EST
Media Contacts: Karen Addis, APR, karen@addispr.com, +1 (301) 787-2394; Kerri Wade, MPA, kwade@smfm.org, +1 (202) 236-1780
National ...
Reshaping our understanding of granular systems
2024-02-12
Your morning cereal, a jar of nuts, the sands of distant planets, and even the concrete in your city are all examples of granular systems surrounding us. And such systems are harboring secrets that could change the way we mix things up.
In a new paper published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), scientists at the University of Rochester, including Rachel Glade, an assistant professor of earth and environmental sciences and of mechanical engineering; Fernando David Cúñez, a former postdoctoral research associate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
Largest high-precision 3D facial database built in China, enabling more lifelike digital humans
SwRI upgrades facilities to expand subsurface safety valve testing to new application
Iron deficiency blocks the growth of young pancreatic cells
Selective forest thinning in the eastern Cascades supports both snowpack and wildfire resilience
A sea of light: HETDEX astronomers reveal hidden structures in the young universe
Some young gamers may be at higher risk of mental health problems, but family and school support can help
Reduce rust by dumping your wok twice, and other kitchen tips
High-fat diet accelerates breast cancer tumor growth and invasion
Leveraging AI models, neuroscientists parse canary songs to better understand human speech
Ultraprocessed food consumption and behavioral outcomes in Canadian children
The ISSCR honors Dr. Kyle M. Loh with the 2026 Early Career Impact Award for Transformative Advances in Stem Cell Biology
The ISSCR honors Alexander Meissner with the 2026 ISSCR Momentum Award for exceptional work in developmental and stem cell epigenetics
The ISSCR honors stem cell COREdinates and CorEUstem with the 2026 ISSCR Public Service Award
Minimally invasive procedure effectively treats small kidney cancers
SwRI earns CMMC Level 2 cybersecurity certification
Doctors and nurses believe their own substance use affects patients
Life forms can planet hop on asteroid debris – and survive
Sylvia Hurtado voted AERA President-Elect; key members elected to AERA Council
Mount Sinai and King Saud University Medical City forge a three-year collaboration to advance precision medicine in familial inflammatory bowel disease
AI biases can influence people’s perception of history
Prenatal opioid exposure and well-being through adolescence
Big and small dogs both impact indoor air quality, just differently
Wearing a weighted vest to strengthen bones? Make sure you’re moving
Microbe survives the pressures of impact-induced ejection from Mars
Asteroid samples offer new insights into conditions when the solar system formed
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
[Press-News.org] Teenagers need better reproductive health education to tackle parenthood fearsPeer reviewed | Survey