Better diagnosis and treatment of cryptococcosis
2024-02-13
(Press-News.org)
A group of international mycology experts led by Professor Dr Oliver A. Cornely at the University of Cologne has jointly drafted a guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of cryptococcosis, which aims at improving infection management and thus the survival rate of patients. Cryptococcosis is a fungal infection of mainly the lungs that might lead to meningitis. The article ‘Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of cryptococcosis’ was published in the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases.
Cryptococcosis, especially cryptococcal meningitis (CM) as the most fatal form, is responsible for a high fatality rate among patients. It is one of the most widespread invasive fungal infections in the world and is a major threat particularly to people suffering from immunodeficiencies. For example, around one million cases of cryptococcal meningoencephalitis are diagnosed worldwide every year in people with HIV alone, and more than 600,000 people die from the disease each year. Patients who have undergone a bone marrow transplant or organ transplant are also at high risk of infection. It is transmitted through the inhalation of spores from soil. Other organs are then also infected via the bloodstream. The lungs, brain, skin and bones are most frequently affected.
“Invasive fungal infections are often difficult to recognize in everyday work in clinics because they occur so rarely. However, it is particularly important for patients at risk to be treated quickly and appropriately,” said Cornely from Department I of Internal Medicine at University Hospital Cologne and Director of the Institute of Translational Research at the University of Cologne’s CECAD Cluster of Excellence for Aging Research. “At the same time, we must not forget that the conditions for recognizing the infection at an early stage are not equally good everywhere in the world and that resources are sometimes very limited. There are many countries with a high number of cases that are poorly equipped in this respect. As part of our Global Guideline Programme, we would like to contribute to improving this situation.”
The cryptococcosis guideline is designed to support medical staff in handling invasive fungal infections. It is intended to provide practical guidance and support in decision-making and thus improve clinical approaches, diagnosis, management, and aftercare for the benefit of patients.
The project was carried out by the mycological societies ECMM (European Confederation of Medical Mycology) and ISHAM (International Society for Human and Animal Mycology) in collaboration with the ASM (American Society for Microbiology). “More than 70 other international specialist institutions were involved in developing this new guideline. This is a great help for our scientific work and shows how great the interest, but also the need for such recommendations is,” explained Cornely. Authors from 22 countries contributed to this guideline. Dr Christina Chang from Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, and Professor Dr John Robert Perfect from Duke University in Durham, USA, were in charge of the project.
Invasive fungal infections are emergencies. However, as a single pathogen often only occurs very rarely, it is often only discovered late. But patients' lives depend on rapid detection and well-practised procedures. Since 2017, University Hospital Cologne has been home to one of the European Centres of Excellence recognized by the ECMM. At the centre, patients have access to modern testing procedures and treatment options. In addition, the experts under the direction of Professor Cornely serve as advisory contacts for colleagues in Germany and abroad.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-13
Like a Valentine’s Day dinner or a box of chocolates, male fruit flies have their own rituals for wooing a potential mate.
As part of a complex courtship behavior, male flies vibrate their wings to produce a distinctive song that conveys a message to nearby females. Using internal information and cues from females and the environment, males decide moment to moment whether to sing and how.
Although scientists now know a lot about how fly movements produce songs, it was still not clear which cells and circuits in the fly’s nervous system enable the behavior.
Now, using a suite of novel tools, ...
2024-02-13
PULLMAN, Wash. – More time stranded on land means greater risk of starvation for polar bears, a new study indicates.
During three summer weeks, 20 polar bears closely observed by scientists tried different strategies to maintain energy reserves, including resting, scavenging and foraging. Yet nearly all of them lost weight rapidly: on average around 1 kilogram, or 2.2 pounds, per day.
Some have speculated that polar bears might adapt to the longer ice-free seasons due to climate warming by acting like their grizzly bear relatives ...
2024-02-13
Key takeaways
Diabetes remission: Gastric bypass surgery results in high rates of Type-2 diabetes remission five years after the operation, even after patients regain a significant amount of weight.
Gastric bypass vs. sleeve gastrectomy: Patients who underwent sleeve gastrectomy and regained their weight were five times more likely to see their diabetes return than patients who had gastric bypass surgery and regained their weight.
CHICAGO (February 13, 2024): Adults who have obesity and Type 2 diabetes are much more likely to see their diabetes stay in remission if they undergo gastric ...
2024-02-13
WASHINGTON, Feb. 13, 2024 — Breast cancer is on the rise, but new tools for early detection could save lives.
In Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Florida and National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University in Taiwan reported successful results from a hand-held breast cancer screening device that can detect breast cancer biomarkers from a tiny sample of saliva. Their biosensor design uses common components, such as widely available glucose testing strips and ...
2024-02-13
University of Queensland-led research has shown there is more coral reef area across the globe than previously thought, with detailed satellite mapping helping to conserve these vital ecosystems.
Dr Mitchell Lyons from UQ’s School of the Environment, working as part of the Allen Coral Atlas project, said scientists have now identified 348,000 square kilometres of shallow coral reefs, up to 20-30 metres deep.
“This revises up our previous estimate of shallow reefs in the world’s oceans,” Dr Lyons said.
“Importantly, the high-resolution, up-to-date mapping satellite technology also allows us to see what these habitats ...
2024-02-13
About The Study: In this study of 61,000 adults age 45 or older, those who adhered to physical activity guidelines before the pandemic had lower odds of developing or being hospitalized for COVID-19. Thus, higher prepandemic physical activity levels may be associated with reduced odds of SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalization for COVID-19.
Authors: Dennis Muñoz-Vergara, D.V.M., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical
School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.55808)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
2024-02-13
About The Study: Maternal tobacco use during pregnancy was associated with enduring deficits in childhood neurocognition in this study including 11,000 children. Continued research on the association of maternal tobacco use during pregnancy with cognitive performance and brain structure related to language processing skills and episodic memory is needed.
Authors: Hongying Daisy Dai, Ph.D., of the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
2024-02-13
Smelling a familiar scent can help depressed individuals recall specific autobiographical memories and potentially assist in their recovery, discovered a team of University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers and UPMC social workers in a study published today in JAMA Network Open.
The study showed that scents are more effective than words at cueing up a memory of a specific event and could even be used in the clinical setting to help depressed individuals get out of the negative thought cycles and rewire thought patterns, ...
2024-02-13
A cohort study of older adults found that those who followed recommended exercise guidelines before the pandemic had significantly lower odds of being infected or hospitalized from COVID-19 than those who did not follow guidelines
Need another reason to keep up with your exercise routine? Staying active just might protect you from infection and hospitalization from COVID-19. A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, suggests that higher levels of physical activity before the pandemic began in 2020 were associated with a lower likelihood of contracting ...
2024-02-13
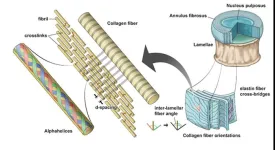
Type 2 diabetes alters the behavior of discs in the vertebral column, making them stiffer, and also causes the discs to change shape earlier than normal. As a result, the disc’s ability to withstand pressure is compromised. This is one of the findings of a new study in rodents from a team of engineers and physicians from the University of California San Diego, UC Davis, UCSF and the University of Utah.
Low back pain is a major cause of disability, often associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. People with Type 2 diabetes face ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Better diagnosis and treatment of cryptococcosis