(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Feb. 13, 2024 — Breast cancer is on the rise, but new tools for early detection could save lives.
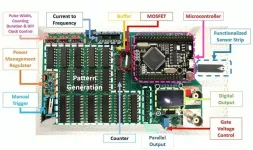
In Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Florida and National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University in Taiwan reported successful results from a hand-held breast cancer screening device that can detect breast cancer biomarkers from a tiny sample of saliva. Their biosensor design uses common components, such as widely available glucose testing strips and the open-source hardware-software platform Arduino.
“Imagine medical staff conducting breast cancer screening in communities or hospitals,” author Hsiao-Hsuan Wan said. “Our device is an excellent choice because it is portable — about the size of your hand — and reusable. The testing time is under five seconds per sample, which makes it highly efficient.”
The device uses paper test strips treated with specific antibodies that interact with the targeted cancer biomarkers. A saliva sample is placed on the strip, and pulses of electricity are sent to electrical contact points on the biosensor device. These pulses cause the biomarkers to bind to the antibodies and alter the charge and capacitance over the electrode. This produces a change in the output signal, which can be measured and translated into digital information about how much biomarker is present.
The design is revolutionary compared to its alternatives. Mammograms, ultrasounds, and MRIs are costly and invasive and require large, specialized equipment, present low-dose radiation exposure, and can take days or weeks to return test results.
“In many places, especially in developing countries, advanced technologies like MRI for breast cancer testing may not be readily available,” Wan said. “Our technology is more cost-effective, with the test strip costing just a few cents and the reusable circuit board priced at $5. We are excited about the potential to make a significant impact in areas where people might not have had the resources for breast cancer screening tests before.”
The biosensor requires just a drop of saliva, and it can provide accurate test results even if the concentration of the cancer biomarker in the sample is only one quadrillionth of a gram, or one femtogram, per milliliter.
“The highlight for me was when I saw readings that clearly distinguished between healthy individuals and those with cancer,” Wan said. “We dedicated a lot of time and effort to perfecting the strip, board, and other components. Ultimately, we’ve created a technique that has the potential to help people all around the world.”
###
The article “High sensitivity saliva-based biosensor in detection of breast cancer biomarkers: HER2 and CA15-3” is authored by Hsiao-Hsuan Wan, Haochen Zhu, Chao-Ching Chiang, Jian-Sian Li, Fan Ren, Cheng-Tse Tsai, Yu-Te Liao, Dan Neal, Josephine F. Esquivel-Upshaw, and Stephen J. Pearton. It will appear in Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B on Feb. 13, 2024 (DOI: 10.1116/6.0003370). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1116/6.0003370.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, an AVS journal published by AIP Publishing, is devoted to publishing reports of original research, letters, and review articles covering multiple disciplines with a focus on microelectronics and nanotechnology. See https://avs.scitation.org/journal/jvb.
ABOUT AVS
AVS is an interdisciplinary, professional society with some 4,500 members worldwide. Founded in 1953, AVS hosts local and international meetings, publishes five journals, serves members through awards, training and career services programs, and supports networking among academic, industrial, government, and consulting professionals. Its members come from across the fields of chemistry, physics, biology, mathematics, engineering, and business and share a common interest in basic science, technology development and commercialization related to materials, interfaces, and processing. https://www.avs.org.
###
END
Would you prefer a mammogram, MRI, or saliva on a test strip?
This hand-held biosensor makes breast cancer screening fast, affordable, and accurate
2024-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Satellites unveil the size and nature of the world’s coral reefs
2024-02-13
University of Queensland-led research has shown there is more coral reef area across the globe than previously thought, with detailed satellite mapping helping to conserve these vital ecosystems.
Dr Mitchell Lyons from UQ’s School of the Environment, working as part of the Allen Coral Atlas project, said scientists have now identified 348,000 square kilometres of shallow coral reefs, up to 20-30 metres deep.
“This revises up our previous estimate of shallow reefs in the world’s oceans,” Dr Lyons said.
“Importantly, the high-resolution, up-to-date mapping satellite technology also allows us to see what these habitats ...
Prepandemic physical activity and risk of COVID-19 diagnosis and hospitalization in older adults
2024-02-13
About The Study: In this study of 61,000 adults age 45 or older, those who adhered to physical activity guidelines before the pandemic had lower odds of developing or being hospitalized for COVID-19. Thus, higher prepandemic physical activity levels may be associated with reduced odds of SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalization for COVID-19.
Authors: Dennis Muñoz-Vergara, D.V.M., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical
School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.55808)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Maternal tobacco use during pregnancy and child neurocognitive development
2024-02-13
About The Study: Maternal tobacco use during pregnancy was associated with enduring deficits in childhood neurocognition in this study including 11,000 children. Continued research on the association of maternal tobacco use during pregnancy with cognitive performance and brain structure related to language processing skills and episodic memory is needed.
Authors: Hongying Daisy Dai, Ph.D., of the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Are you depressed? Scents might help, new study says
2024-02-13
Smelling a familiar scent can help depressed individuals recall specific autobiographical memories and potentially assist in their recovery, discovered a team of University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers and UPMC social workers in a study published today in JAMA Network Open.
The study showed that scents are more effective than words at cueing up a memory of a specific event and could even be used in the clinical setting to help depressed individuals get out of the negative thought cycles and rewire thought patterns, ...
Study finds high levels of physical activity lowered risk of developing COVID-19 infection and hospitalization
2024-02-13
A cohort study of older adults found that those who followed recommended exercise guidelines before the pandemic had significantly lower odds of being infected or hospitalized from COVID-19 than those who did not follow guidelines
Need another reason to keep up with your exercise routine? Staying active just might protect you from infection and hospitalization from COVID-19. A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, suggests that higher levels of physical activity before the pandemic began in 2020 were associated with a lower likelihood of contracting ...
Type 2 diabetes alters the behavior of discs in the vertebral column
2024-02-13
Type 2 diabetes alters the behavior of discs in the vertebral column, making them stiffer, and also causes the discs to change shape earlier than normal. As a result, the disc’s ability to withstand pressure is compromised. This is one of the findings of a new study in rodents from a team of engineers and physicians from the University of California San Diego, UC Davis, UCSF and the University of Utah.
Low back pain is a major cause of disability, often associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. People with Type 2 diabetes face ...
Mount Sinai ophthalmologists develop novel protocol to rapidly diagnose and treat eye stroke
2024-02-13
Ophthalmologists at New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai (NYEE) have created a novel protocol to rapidly diagnose eye stroke and expedite care to prevent irreversible vision loss.
Their study, published Tuesday, February 13, in Ophthalmology, describes using high-resolution retinal imaging in the emergency room, along with rapid remote consultation to confirm diagnosis and expedite care, improving outcomes for eye stroke patients and preserving vision.
“The protocol implements highly sensitive retinal imaging at the patient’s point of entry into the medical system, reducing the need for onsite ophthalmology ...
Scientists study the behaviors of chiral skyrmions in chiral flower-like obstacles
2024-02-13
In nature, the collective motion of some birds and fish, such as flocks of starlings and shoals of sardines, respectively, can generate impressive dynamic phenomena. Their study constitutes active matter science, which has been a topic of great interest for the past three decades. The unique collective dynamics of active matter are governed by the motion of each individual entity, the interactions among them, as well as their interaction with the environment. Recent studies show that some self-propelling molecules and bacteria show circular motion with a fixed chirality (the property of an object where it cannot be superimposed upon its mirror image through any number of rotations ...
If we can't untangle this mess, Norway's blue industry will never be green
2024-02-13
Lost fishing lines and ropes are a growing problem. As a leading fishing nation, Norway, with its long coastline and fish-rich waters, is particularly vulnerable to marine litter. A new study from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) shows that only a third of all ropes produced and sold in Norway can be recycled in a sustainable way.
The rest are burned, buried, sent out of the country - or just pile up and contribute to something called ghost fishing. That's when lost or abandoned fishing gear, floating in the ocean or anchored to the bottom, inadvertently continues to catch marine creatures long ...
National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) celebrates Dr. Yung-Chi Cheng's three decades of pioneering research and recent partnership with Astrazeneca China
2024-02-13
The National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) proudly celebrates the outstanding contributions of Dr. Yung-Chi Cheng, the Henry Bronson Professor of Pharmacology and Medicine at Yale University. Dr. Cheng's relentless dedication over the past three decades has led to an experimental botanical drug, YIV-906, to enter various phase II human trials and establishing a now clinical-stage platform biotechnology company committed to developing groundbreaking medicines targeting cancer and aging-related diseases.
NFCR has been a vital and steadfast supporter of Dr. Cheng's pioneering work, providing more than $2.5 MM ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Would you prefer a mammogram, MRI, or saliva on a test strip?This hand-held biosensor makes breast cancer screening fast, affordable, and accurate