(Press-News.org) A research paper published today (14 February 2024) in Nature Cancer details new insights into the role of efferocytosis – the burying of dead cells – in pancreatic cancer that spreads to the liver.
Liver metastasis occurs in 40–50% of people with pancreatic ductal adenosarcoma (PDAC), and there are currently no effective therapies to cure pancreatic cancer patients that have liver metastasis.
Led by University of Liverpool’s Professor Michael Schmid and colleagues, this study found PDAC metastases to show high levels of immunosuppressive macrophages, a type of white blood cell which promotes tumour growth.
The researchers discovered that blocking the efferocytosis pathway during early-stage metastasis prevented this immunosuppressive activity in macrophages, restoring T cell activation and reducing metastatic tumour burden.
Lead author of the study, Professor Michael Schmid said: “In pancreatic cancer, malignant tumour cells often spread to the liver. Our data show that the generation of a supportive metastatic ‘niche’ in the liver is critical for the effective outgrowth of malignant cells at the distant site.
“Our findings suggest that a particular type of immune cells orchestrate the formation of the metastatic niche by reprogramming other immune cells, thereby creating an immunosuppressed metastatic microenvironment, where malignant cells are able to hide from an anti-tumour immune response. Targeting this particular type of innate immune cells or interfering with their immunosuppressive functions could serve as a promising therapeutic approach for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer.”
First author Dr Yuliana Astuti said: “Using single cell technologies, we found an underappreciated diversity of macrophages in pancreatic cancer liver metastases. We identified that in the liver, metastasis associated macrophages with opposite functions co-exist, some exhibiting immunostimulatory and others immunosuppressive features. Interestingly, further temporal analysis revealed that liver metastases is accompanied by increased liver tissue cell death and that the engulfment of dead cells acts as a key driver to reprogram macrophages towards an immunosuppressive phenotype. Our study provides proof-of-principle that tailored targeting of specific macrophages restores tumour immunity and inhibits PDAC metastasis.”
Key contributor Professor Ainhoa Mielgo commented: “Pancreatic cancer is a very aggressive cancer type that often spreads to the liver. We currently have no effective therapies to cure pancreatic cancer patients that have liver metastasis. These findings are really exciting because they reveal a targetable mechanism by which pancreatic cancer cells spread and grow in the liver. Our hope and goal now is to translate these lab discovery into the benefit of patients.”
“This study is a product of a fantastic collaborative effort of scientists, medical oncologists, surgeons and patients working together to find better treatments for pancreatic cancer patients,” Professor Schmid added.
Led by the University of Liverpool, the study also involved researchers from Cancer Research-UK Scotland Institute, the University of Glasgow and the University of Edinburgh.
This research was funded by Cancer Research UK, the Medical Research Council, the North West Cancer Research Fund and Wellcome Trust.
The full study is available here: https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-024-00731-2
Ends
END
Promising new therapeutic approach for treating metastatic pancreatic cancer
2024-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Neuronal insights: flash and freeze-fracture
2024-02-14
Fear and addiction exert significant influence within society. Managing them is often challenging, as they are driven by intricate neuronal circuits in our brains. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms is crucial to intervene when these processes malfunction. Pioneered by scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), the novel “Flash and Freeze-fracture” technique provides a unique glimpse into the respective brain region. The results were recently published in the journal PNAS.
While looking for food, a bird encounters a fox. It gets away just in time, but the sight ...
Tiny crustaceans discovered preying on live jellyfish during harsh Arctic night
2024-02-14
In the dark and cold of the months-long polar night, food resources are limited. Some groups of marine organisms in the polar regions overcome this challenge by going into a metabolic resting state in winter, surviving on reserves accumulated during the short growth season. But others, such as several species of marine zooplankton, have evolved a different strategy: they shift from a specialized to an omnivorous diet during the polar night, profiting from a wide range of potentially less rewarding foods that are available throughout the year.
Now, ...
It's award season: let's celebrate microbes in movies
2024-02-14
Elche (Spain), January 22, 2024. Usually, show business depicts viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms as one of the worst menaces to humankind. Entertainment movies influence the way audiences understand and perceive these topics. Yet, few films accurately portray the science of microbiology and its social implications. Movies and TV series often feature outbreaks of deadly diseases and the efforts of scientists and medical professionals to contain them. However, entertainment movies can also educate the public about the importance and the impact ...
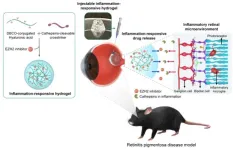
New treatment developed to dramatically slow down the progression of blindness-causing retinal diseases
2024-02-14
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that Dr. Maesoon Im of the Brain Science Institute, together with Prof. Seung Ja Oh of Kyung Hee University and Prof. Kangwon Lee of Seoul National University, successfully incorporated anti-inflammatory drugs into a hydrogel to suppress inflammation in the retina and effectively deliver the drugs to the inflamed area.
Age-related macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa are incurable eye diseases that cause blindness due to the gradual damage of photoreceptor cells, which convert light into biological signals in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Age-related macular degeneration is a condition ...
Menopause and migraines: New findings point to power of prevention
2024-02-14
For middle-aged women plagued by migraines, or hot flashes and night sweats, another worry may linger in the backs of their minds: whether these experiences have set them up for a heart attack, a stroke or another cardiovascular crisis.
After all, past research suggesting such a link during and after menopause has gotten a lot of attention.
But a pair of new studies in the journal Menopause suggest that most of them don’t need to worry as much, especially if they don’t have both migraines and long-term hot flashes and night sweats.
Instead, they should focus on tackling the ...
The combination of migraine and persistent hot flashes could prove deadly
2024-02-14
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Feb 14, 2024)—Hot flashes and migraine (particularly with aura) have been shown to be individual risk factors for cardiovascular disease because of associated poorer heart disease riskfactor profiles. A new study, however, is the first to examine the joint influences of migraine and hot flashes/night sweats (vasomotor symptoms) independent of traditional heart disease risk factors and estrogen use. Research results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Specifically, ...
Acupuncture may curb heightened risk of stroke associated with rheumatoid arthritis
2024-02-14
A course of acupuncture may curb the heightened risk of stroke associated with rheumatoid arthritis, finds a comparative study published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The effects seem to be independent of sex, age, medication use, and co-existing conditions, the findings indicate, prompting the researchers to suggest that the procedure may reduce levels of pro-inflammatory proteins (cytokines) in the body that are linked to cardiovascular disease.
The principal cause of death in people with rheumatoid arthritis is cardiovascular disease. And they are more likely to have a stroke than ...
Poor quality clinical data informing NICE decisions on treatments in over half of cases
2024-02-14
The quality of evidence submitted to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) for informing its decisions to recommend technologies for use in the NHS was poor in more than half of cases, reveals a 20-year analysis, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
And the data quality submitted for health technology appraisals by manufacturers between 2000 and 2019 was consistently poor, with no improvement during that time, the analysis shows.
NICE advises the NHS on the ...
Age when periods first start and early menopause linked to heightened COPD risk
2024-02-14
A range of reproductive factors, including age when periods first start and an early menopause, are all linked to a heightened risk of COPD—the umbrella term for progressive lung conditions that cause breathing difficulties—finds research published online in the journal Thorax.
Miscarriage, stillbirth, infertility, and having 3 or more children are also associated with a heightened risk of COPD, which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, the findings show.
Recent evidence indicates substantial gender differences in susceptibility ...
Hostile environment policies linked to prolonged distress in people with Black Caribbean ancestry
2024-02-14
Psychological distress increased among people with Black Caribbean heritage in the UK, relative to the White population, following the 2014 Immigration Act and the Windrush scandal, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The researchers say their findings, published in The Lancet Psychiatry, suggest a causal link between government policies and a subsequent decline in mental health.
They were investigating the impact of the Immigration Act 2014, requiring landlords, employers, the NHS, banks and the police to check right-to-stay documentation. This was a key part of a set of measures known as the Home Office hostile environment policy, seeking ...