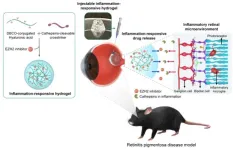
(Press-News.org) The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that Dr. Maesoon Im of the Brain Science Institute, together with Prof. Seung Ja Oh of Kyung Hee University and Prof. Kangwon Lee of Seoul National University, successfully incorporated anti-inflammatory drugs into a hydrogel to suppress inflammation in the retina and effectively deliver the drugs to the inflamed area.
Age-related macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa are incurable eye diseases that cause blindness due to the gradual damage of photoreceptor cells, which convert light into biological signals in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Age-related macular degeneration is a condition that damages the macula, the central part of the retina, and is the number one cause of blindness in people over the age of 65. Retinitis pigmentosa, on the other hand, is a genetic disorder that causes gradual death in the photoreceptor cells in the retina and affects about 1 in 4,000 people worldwide, initially causing night blindness but eventually leading to vision loss.
Currently, there is no effective cure for either disease, and one of the treatments is to inject anti-inflammatory drugs into the eye to slow down the degree of retinal damage. However, these injections only work for as long as the drug remains in the eye, requiring patients to visit a clinic for intraocular injections every four to 12 weeks, depending on how long the effect of the drug lasts.
For the first time, the team utilized a substance that inhibits the inflammatory factor EZH2, which contributes to retinal degeneration, along with an anti-inflammatory agent. When mice with retinal degeneration were injected with the anti-inflammatory drug, the progression of retinal degeneration slowed down.
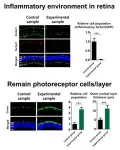
The researchers have successfully developed a hydrogel that slowly degrades upon encountering the enzyme cathepsin, which is typically overexpressed in inflammatory environments, to deliver anti-inflammatory drugs. When the team's drug-loaded inflammation-responsive hydrogel was injected into the eyes of mice suffering from retinal degeneration, inflammatory factors in the retina were reduced to approximately 6.1%. The team also found that the protective effect on photoreceptor cells, which are known to be destroyed by retinal degeneration, was about four times higher than in the control group, effectively delaying vision loss.
Notably, the hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel, which has similar mechanical and optical properties to the vitreous humor of the eye, allows for different rates of hydrogel degradation in each patient, minimizing the need for repeated injections. This newly developed technology is expected to reduce the economic burden and the risk of accidents during outpatient visits for patients with difficulty in mobility due to visual impairment. Additionally, for patients in the early stages of symptoms, reducing the frequency of hospital visits can alleviate inconvenience in daily life.
"For future commercialization, we plan to digitize the amount of drug and hydrogel used, as well as the treatment period, according to the progression of the disease. We also intend to assess the long-term stability of the drug delivery system," said Dr. Maesoon Im of KIST. "In addition to the retinal degenerative diseases, we will investigate inflammation levels in other retinal diseases to see if our inflammation-responsive drug delivery system would work on those conditions," said Prof. Seung Ja Oh of Kyung Hee University.
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho) through the KIST Major Project and Young and Mid-Career Researchers, the Excellent Young Researcher Support Project, the Brain Function Identification and Regulation Technology Development Project, and the Public Benefit Medical Technology Research Project of the Ministry of Health and Welfare (Minister Cho Kyu-hong). The research were published in the latest issue of the international journal 'npj Regenerative Medicine' (IF 7.2, top 19.3% in JCR).
END
New treatment developed to dramatically slow down the progression of blindness-causing retinal diseases
Interactive release of anti-inflammatory drugs depending on the level of retinal degeneration. A customized treatment approach is expected to be developed to reduce patients’ inconvenience of having multiple shots.
2024-02-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Menopause and migraines: New findings point to power of prevention
2024-02-14
For middle-aged women plagued by migraines, or hot flashes and night sweats, another worry may linger in the backs of their minds: whether these experiences have set them up for a heart attack, a stroke or another cardiovascular crisis.
After all, past research suggesting such a link during and after menopause has gotten a lot of attention.
But a pair of new studies in the journal Menopause suggest that most of them don’t need to worry as much, especially if they don’t have both migraines and long-term hot flashes and night sweats.
Instead, they should focus on tackling the ...
The combination of migraine and persistent hot flashes could prove deadly
2024-02-14
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Feb 14, 2024)—Hot flashes and migraine (particularly with aura) have been shown to be individual risk factors for cardiovascular disease because of associated poorer heart disease riskfactor profiles. A new study, however, is the first to examine the joint influences of migraine and hot flashes/night sweats (vasomotor symptoms) independent of traditional heart disease risk factors and estrogen use. Research results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Specifically, ...
Acupuncture may curb heightened risk of stroke associated with rheumatoid arthritis
2024-02-14
A course of acupuncture may curb the heightened risk of stroke associated with rheumatoid arthritis, finds a comparative study published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
The effects seem to be independent of sex, age, medication use, and co-existing conditions, the findings indicate, prompting the researchers to suggest that the procedure may reduce levels of pro-inflammatory proteins (cytokines) in the body that are linked to cardiovascular disease.
The principal cause of death in people with rheumatoid arthritis is cardiovascular disease. And they are more likely to have a stroke than ...
Poor quality clinical data informing NICE decisions on treatments in over half of cases
2024-02-14
The quality of evidence submitted to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) for informing its decisions to recommend technologies for use in the NHS was poor in more than half of cases, reveals a 20-year analysis, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
And the data quality submitted for health technology appraisals by manufacturers between 2000 and 2019 was consistently poor, with no improvement during that time, the analysis shows.
NICE advises the NHS on the ...
Age when periods first start and early menopause linked to heightened COPD risk
2024-02-14
A range of reproductive factors, including age when periods first start and an early menopause, are all linked to a heightened risk of COPD—the umbrella term for progressive lung conditions that cause breathing difficulties—finds research published online in the journal Thorax.
Miscarriage, stillbirth, infertility, and having 3 or more children are also associated with a heightened risk of COPD, which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, the findings show.
Recent evidence indicates substantial gender differences in susceptibility ...
Hostile environment policies linked to prolonged distress in people with Black Caribbean ancestry
2024-02-14
Psychological distress increased among people with Black Caribbean heritage in the UK, relative to the White population, following the 2014 Immigration Act and the Windrush scandal, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The researchers say their findings, published in The Lancet Psychiatry, suggest a causal link between government policies and a subsequent decline in mental health.
They were investigating the impact of the Immigration Act 2014, requiring landlords, employers, the NHS, banks and the police to check right-to-stay documentation. This was a key part of a set of measures known as the Home Office hostile environment policy, seeking ...
Clinical trial shows rheumatoid arthritis drug could prevent disease
2024-02-14
A drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis could also prevent the disease in individuals deemed to be at risk.
Results from a Phase 2b clinical trial, published today in The Lancet by researchers led by King’s College London, provides hope for arthritis sufferers after it was shown that the biologic drug abatacept reduces progression to this agonising chronic inflammatory disease.
Rheumatoid arthritis affects half a million people in the UK and develops when the body’s immune system attacks itself, causing joint pain, swelling and significant disability. The disease most commonly begins in middle age, but much younger age groups can be afflicted, and until ...
Do apes have humor?
2024-02-14
Babies playfully tease others as young as eight months of age. Since language is not required for this behavior, similar kinds of playful teasing might be present in non-human animals. Now cognitive biologists and primatologists from the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA, US), the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB, Germany), Indiana University (IU, US), and the University of California San Diego (UCSD, US) have documented playful teasing in four species of great apes. Like joking behavior in humans, ape teasing is provocative, persistent, and includes elements of surprise and play. Because all four great ape species used playful teasing, it is likely that the ...
New digital therapy reduces anxiety and depression in people living with long-term physical health conditions
2024-02-14
A therapist-guided digital cognitive behavioural therapy reduced distress in 89 per cent of participants living with long-term physical health conditions, a new King’s College London study finds.
Researchers at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London found that people living with long-term conditions who received the therapist-guided digital programme called COMPASS showed a significant reduction in psychological distress (a combined score of anxiety and depression) 12-weeks after starting the study.
194 patients were recruited via long-term condition charities, including Crohn’s & ...
Researchers edge closer to delivering personalized medicine to cancer patients
2024-02-14
For the first time, Purdue researchers prove that measuring mechanical motions in living cancer tissues is a viable and promising approach for predicting chemoresistance
Chemotherapy can save lives, but often a cancer patient may be resistant to their prescribed chemotherapy, which costs the patient valuable time. Chemoresistance is a topic that researchers need to understand better so that they can match the right type of chemo to the right patient, which is called personalized medicine.
An unusual pairing of veterinary scientists and physicists believe ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
How periodontitis-linked bacteria accelerate osteoporosis-like bone loss through the gut
Understanding how cells take up and use isolated ‘powerhouses’ to restore energy function
Ten-point plan to deliver climate education unveiled by experts
[Press-News.org] New treatment developed to dramatically slow down the progression of blindness-causing retinal diseasesInteractive release of anti-inflammatory drugs depending on the level of retinal degeneration. A customized treatment approach is expected to be developed to reduce patients’ inconvenience of having multiple shots.