(Press-News.org) A revolutionary nanomaterial with huge potential to tackle multiple global challenges could be developed further without acute risk to human health, research suggests.
Carefully controlled inhalation of a specific type of graphene – the world’s thinnest, super strong and super flexible material – has no short-term adverse effects on lung or cardiovascular function, the study shows.
The first controlled exposure clinical trial in people was carried out using thin, ultra-pure graphene oxide – a water-compatible form of the material.
Researchers say further work is needed to find out whether higher doses of this graphene oxide material or other forms of graphene would have a different effect.
The team is also keen to establish whether longer exposure to the material, which is thousands of times thinner than a human hair, would carry additional health risks.
There has been a surge of interest in developing graphene – a material first isolated by scientists in 2004 and which has been hailed as a ‘wonder’ material. Possible applications include electronics, phone screens, clothing, paints and water purification.
Graphene is actively being explored around the world to assist with targeted therapeutics against cancer and other health conditions, and also in the form of implantable devices and sensors. Before medical use, however, all nanomaterials need to be tested for any potential adverse effects.
Researchers from the Universities of Edinburgh and Manchester recruited 14 volunteers to take part in the study under carefully controlled exposure and clinical monitoring conditions.
The volunteers breathed the material through a face mask for two hours while cycling in a purpose-designed mobile exposure chamber brought to Edinburgh from the National Public Health Institute in the Netherlands.
Effects on lung function, blood pressure, blood clotting and inflammation in the blood were measured – before the exposure and at two-hour intervals. A few weeks later, the volunteers were asked to return to the clinic for repeated controlled exposures to a different size of graphene oxide, or clean air for comparison.
There were no adverse effects on lung function, blood pressure or the majority of other biological parameters looked at.
Researchers noticed a slight suggestion that inhalation of the material may influence the way the blood clots, but they stress this effect was very small.
Dr Mark Miller, of the University of Edinburgh’s Centre for Cardiovascular Science, said: “Nanomaterials such as graphene hold such great promise, but we must ensure they are manufactured in a way that is safe before they can be used more widely in our lives.
“Being able to explore the safety of this unique material in human volunteers is a huge step forward in our understanding of how graphene could affect the body. With careful design we can safely make the most of nanotechnology.”
Professor Kostas Kostarelos, of the University of Manchester and the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2) in Barcelona, said: “This is the first-ever controlled study involving healthy people to demonstrate that very pure forms of graphene oxide – of a specific size distribution and surface character – can be further developed in a way that would minimise the risk to human health.
“It has taken us more than 10 years to develop the knowledge to carry out this research, from a materials and biological science point of view, but also from the clinical capacity to carry out such controlled studies safely by assembling some of the world’s leading experts in this field.”
Professor Bryan Williams, Chief Scientific and Medical Officer at the British Heart Foundation, said: “The discovery that this type of graphene can be developed safely, with minimal short term side effects, could open the door to the development of new devices, treatment innovations and monitoring techniques.
“We look forward to seeing larger studies over a longer timeframe to better understand how we can safely use nanomaterials like graphene to make leaps in delivering lifesaving drugs to patients.”
The study is published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-023-01572-3. It was funded by the British Heart Foundation and the UKRI EPSRC.
END
First human trial shows ‘wonder’ material can be developed safely
A revolutionary nanomaterial with huge potential to tackle multiple global challenges could be developed further without acute risk to human health, research suggests
2024-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Towards more efficient catalysts
2024-02-16
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), Harvard Department of Chemistry & Chemical Biology, and Utrecht University have reported on a previously elusive way to improve the selectivity of catalytic reactions, adding a new method of increasing the efficacy of catalysts for a potentially wide range of applications in various industries including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and much more.
The research is published in ...
Laboratory study on conditions for spontaneous excitation of "chorus emission," wave of space plasma
2024-02-16
A dipole magnetic field, created by a ring current, is the most fundamental type of magnetic field that is found both in laboratories and in space. Planetary magnetospheres, such as Jupiter's, effectively confine plasma. The RT-1 project aims to learn from nature and create a magnetosphere-type high-performance plasma to realize advanced fusion energy. Simultaneously, the artificial magnetosphere offers a means to experimentally understand the mechanisms of natural phenomena in a simplified and controlled ...
Advanced artificial photosynthesis catalyst uses CO2 more efficiently to create biodegradable plastics
2024-02-16
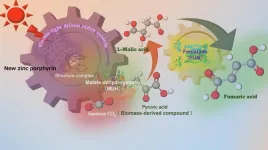
Amid growing global concern over climate change and plastic pollution, researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University are making great strides in the sustainable production of fumaric acid – a component of biodegradable plastics such as polybutylene succinate, which is commonly used for food packaging. The researchers have managed to efficiently produce fumaric acid, which is traditionally derived from petroleum, using renewable resources, carbon dioxide, and biomass-derived compounds.
In a previous study, a research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao of the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at ...
Mystery solved: the oldest fossil reptile from the alps is an historical forgery
2024-02-16
A 280-million-year-old fossil that has baffled researchers for decades has been shown to be, in part, a forgery following new examination of the remnants.
The discovery has led the team led by Dr Valentina Rossi of University College Cork, Ireland (UCC) to urge caution in how the fossil is used in future research.
Tridentinosaurus antiquus was discovered in the Italian alps in 1931 and was thought to be an important specimen for understanding early reptile evolution.
Its body outline, appearing dark against the surrounding rock, was initially interpreted ...
The ties that bind
2024-02-15
Trace metals are nutrient elements, like zinc, that animals and plants need in small amounts to function properly. Animals generally get trace metals in their diets or through environmental exposures, while plants take their trace minerals up from soil. If we get too little, we may experience a deficiency, but the opposite can also be true: too much of a trace metal can be toxic.
Scientists believe that up to 50% of the trace metals in soils and urban environments may be bound to the surfaces of mineral grains — rendering the trace metals ...
New GSA publication addresses dementia care in adults with I/DD
2024-02-15
Addressing Brain Health in Adults With Intellectual Disabilities and Developmental Disabilities: A Companion to the KAER Toolkit for Primary Care Providers is a new publication from the Gerontological Society of America (GSA) designed to address the needs of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD) who develop dementia.
Freely available at geron.org/brainhealth, this companion document:
Raises awareness of unique needs of adults living with I/DD.
Equips and encourages caregivers and health care teams to engage in ...
Inequities in HIV testing, diagnosis and care for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities
2024-02-15
People with disabilities are often at higher risk for exposure to HIV due to barriers in engaging healthcare and other systemic factors and are thus considered a priority for prevention and testing efforts. However, these efforts don’t always extend to people with intellectual disabilities due to the perception that people with intellectual disabilities are mostly asexual.
Researchers at University of Michigan Health conducted one of the largest epidemiological studies of individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities to closely examine where the gaps in HIV care lie and found large disparities in care for Black patients as well as for patients ...
Earthquake fatality measure offers new way to estimate impact on countries
2024-02-15
A new measure that compares earthquake-related fatalities to a country’s population size concludes that Ecuador, Lebanon, Haiti, Turkmenistan, Iran and Portugal have experienced the greatest impact from fatalities in the past five centuries.
The new impact measure, introduced in the Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America by Max Wyss and colleagues at International Centre for Earth Simulation Foundation, is called the earthquake fatality load or EQFL. The EQFL of a particular earthquake is the ratio of earthquake fatalities to the population estimate for the country in the year of the earthquake.
In their study, Wyss, Michel Speiser ...
Using cannabis can ease cravings for street-level drugs, UBC research suggests
2024-02-15
New findings from researchers at the University of British Columbia suggest that cannabis could play a role in addressing the ongoing opioid overdose crisis.
A new publication from Dr. Hudson Reddon, alongside UBC Okanagan’s Dr. Zach Walsh and UBC Vancouver’s Dr. M-J Milloy, observed that using cannabis is associated with decreased use of crystal methamphetamine among people at highest risk of overdose in Vancouver’s Downtown Eastside.
About 45 per cent of the study’s participants reported using cannabis to manage their cravings for stimulant drugs ...
New nuclei can help shape our understanding of fundamental science on Earth and in the cosmos
2024-02-15
EAST LANSING, Mich. – In creating five new isotopes, an international research team working at the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams, or FRIB, at Michigan State University has brought the stars closer to Earth.
The isotopes — known as thulium-182, thulium-183, ytterbium-186, ytterbium-187 and lutetium-190 — were reported Feb. 15 in the journal Physical Review Letters.
These represent the first batch of new isotopes made at FRIB, a user facility for the U.S. Department of Energy ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] First human trial shows ‘wonder’ material can be developed safelyA revolutionary nanomaterial with huge potential to tackle multiple global challenges could be developed further without acute risk to human health, research suggests