(Press-News.org) A new study from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai shows there is a gender gap between women and men when it comes to exercise.
The findings, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC), show that women can exercise less often than men, yet receive greater cardiovascular gains.
“Women have historically and statistically lagged behind men in engaging in meaningful exercise,” said Martha Gulati, MD, director of Preventive Cardiology in the Department of Cardiology in the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai, the Anita Dann Friedman Chair in Women's Cardiovascular Medicine and Research and co-lead author of the study. “The beauty of this study is learning that women can get more out of each minute of moderate to vigorous activity than men do. It’s an incentivizing notion that we hope women will take to heart.”
Investigators analyzed data from 412,413 U.S. adults utilizing the National Health Interview Survey database. Participants between the time frame of 1997 to 2019—55% of whom were female—provided survey data on leisure-time physical activity. Investigators examined gender-specific outcomes in relation to frequency, duration, intensity and type of physical activity.
“For all adults engaging in any regular physical activity, compared to being inactive, mortality risk was expectedly lower,” said Susan Cheng, MD, MPH, the Erika J. Glazer Chair in Women’s Cardiovascular Health and Population Science, director of the Institute for Research on Healthy Aging in the Department of Cardiology in the Smidt Heart Institute, and senior author of the study. “Intriguingly, though, mortality risk was reduced by 24% in women and 15% in men.”
The research team then studied moderate to vigorous aerobic physical activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, and found that men reached their maximal survival benefit from doing this level of exercise for about five hours per week, whereas women achieved the same degree of survival benefit from exercising just under about 2 ½ hours per week.
Similarly, when it came to muscle-strengthening activity, such as weightlifting or core body exercises, men reached their peak benefit from doing three sessions per week and women gained the same amount of benefit from about one session per week.
Cheng said that women had even greater gains if they engaged in more than 2 ½ hours per week of moderate to vigorous aerobic activity, or in two or more sessions per week of muscle-strengthening activities. The investigators note their findings help to translate a longstanding recognition of sex-specific physiology seen in the exercise lab to a now-expanded view of sex differences in exercise-related clinical outcomes.
With all types of exercise and variables accounted for, Gulati says there’s power in recommendations based on the study’s findings. “Men get a maximal survival benefit when performing 300 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity per week, whereas women get the same benefit from 140 minutes per week,” Gulati said. “Nonetheless, women continue to get further benefit for up to 300 minutes a week.”
Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, chair of the Department of Cardiology in the Smidt Heart Institute and the Lee and Harold Kapelovitz Distinguished Chair in Cardiology, says concrete, novel studies like this don’t happen often.
“I am hopeful that this pioneering research will motivate women who are not currently engaged in regular physical activity to understand that they are in a position to gain tremendous benefit for each increment of regular exercise they are able to invest in their longer-term health,” said Albert, professor of Cardiology.
Other Cedars-Sinai authors include Tzu Yu Huang, MSc; Alan Kwan, MD; David Ouyang, MD; and Joseph Ebinger, MD. Other authors include Hongwei Ji, MD; Kaitlin Casaletto, PhD; Kerrie L. Moreau, PhD; and Hicham Skali, MD, MSc.
Funding: This work was supported in part by NIH grants K23HL153888, K23AG058752, R21HL156132, R01HL142983, R01HL151828, R01HL131532, R01HL143227, R01AG072475, U54AG062319, and U54AG065141, and the Erika J Glazer Family Foundation, National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC2502800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82103908), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2021QH014), Shuimu Scholar Program of Tsinghua University, and National Postdoctoral Innovative Talent Support Program (BX20230189).
# # #
END
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 19, 2024 – University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers discovered a molecular mechanism by which excessive dietary protein could increase atherosclerosis risk. The findings were published in Nature Metabolism today.
The study, which combined small human trials with experiments in mice and cells in a Petri dish, showed that consuming over 22% of dietary calories from protein can lead to increased activation of immune cells that play a role in atherosclerotic plaque formation, driving the disease risk. Furthermore, the scientists showed ...
To prevent an emerging genomic technology from contributing to health disparities, a scientific team funded by the National Institutes of Health has devised new ways to improve a genetic testing method called a polygenic risk score. Since polygenic risk scores have not been effective for all populations, the researchers recalibrated these genetic tests using ancestrally diverse genomic data. As reported in Nature Medicine, the optimized tests provide a more accurate assessment of disease risk across diverse populations.
Genetic tests look at the small differences between individuals’ ...
February 19, 2024, Cleveland: Cleveland Clinic researchers have identified a new pathway that contributes to cardiovascular disease associated with high levels of niacin, a common B vitamin previously recommended to lower cholesterol.
The team, led by Stanley Hazen, M.D., Ph.D., discovered a link between 4PY, a breakdown product from excess niacin, and heart disease. Higher circulating levels of 4PY were strongly associated with development of heart attack, stroke and other adverse cardiac events in large-scale clinical studies. The researchers also showed in preclinical studies that 4PY directly triggers vascular ...
About The Study: Segregated residential and transplant center neighborhoods likely serve as a mechanism of structural racism, contributing to persistent racial disparities in access to live donor kidney transplantation. To promote equitable access, studies should assess targeted interventions (e.g., community outreach clinics) to improve support for potential candidates and donors and ultimately mitigate the effects of segregation.
Authors: Mara A. McAdams-DeMarco, Ph.D., of the New York University Grossman School of Medicine in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
About The Study: The results of this study of 3.2 million people who initiated prescription opioid treatment suggest that prescription opioids were associated with increased risk of serious fall events among adults of all ages, with individuals 85 years or older at greatest risk. These risks should be considered when prescribing opioids, particularly for individuals with preexisting risk factors or when opioids are prescribed at higher doses. Targeted falls prevention efforts may be most effective within the first month following opioid initiation.
Authors: Natasa Gisev, Ph.D., of the National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre, UNSW ...
By analyzing millions of small genetic differences across a person’s genome, researchers can calculate a polygenic risk score to estimate someone’s lifetime odds of developing a certain disease. Over the past decade, scientists have developed these risk scores for dozens of diseases, including heart disease, kidney disease, diabetes, and cancer, with the hope that patients could one day use this information to lower any heightened risk of disease. But determining whether such tests work effectively across all populations, and how they can guide clinical decision-making, has been a challenge.
Now, ...
In the largest genome-wide association study to date on Type 2 diabetes, a team of international researchers, co-led by a University of Massachusetts Amherst genetic epidemiologist, has located 1,289 genetic markers associated with Type 2 diabetes (145 of which are newly identified) and generated risk scores for diabetes complications.
In research published Monday, Feb. 19 in the journal Nature that advances understanding into the inheritability of Type 2 diabetes, the scientists used cutting-edge ...
Dopamine, a chemical messenger in the brain, is mostly known for its role in how we experience pleasure and reward. However, new research from the Champalimaud Foundation (CF) shifts the spotlight towards dopamine’s critical involvement in movement, with implications for our understanding and treatment of symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease (PD).
Imagine the act of walking. It’s something most able-bodied people do without a second thought. Yet it is actually a complex process involving various ...
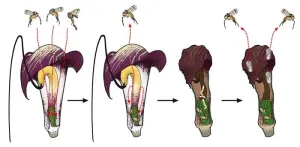
In a group of plants that is famous for luring its pollinators into a death trap, one species offers its flowers as a nursery in exchange. The Kobe University discovery blurs the line between mutualism and parasitism and sheds light on the evolution of complex plant-insect interactions.
Many plants rely on animals for pollination and most offer rewards for the service. Some plants, however, deceive their pollinators, and a famous example is the genus Arisaema. “It is famous as the only plant that achieves pollination at the expense of the pollinator's life,” says Kobe University biologist SUETSUGU Kenji, who is an expert on plant pollination ecology. The plant uses ...
The prospect of the worrisome triple threat of COVID, RSV and flu was assuaged last year by the effectiveness of flu vaccines. Two recent studies from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s VISION Network have found that flu vaccines were effective for all ages against both moderate and severe flu in the U.S. during the 2022-2023 flu season.
Both the pediatric and adult VISION Network studies analyzed flu-associated emergency department (E.D.)/urgent care visits (indicative of moderate disease) and hospitalization (indicative of severe disease) from October 2022 through March 2023, a flu season in which far fewer individuals were social distancing or ...