Studies find flu vaccines were effective in 2022-2023 flu season
Vaccines reduced risk of both moderate and severe disease for all ages
2024-02-19
(Press-News.org) The prospect of the worrisome triple threat of COVID, RSV and flu was assuaged last year by the effectiveness of flu vaccines. Two recent studies from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s VISION Network have found that flu vaccines were effective for all ages against both moderate and severe flu in the U.S. during the 2022-2023 flu season.
Both the pediatric and adult VISION Network studies analyzed flu-associated emergency department (E.D.)/urgent care visits (indicative of moderate disease) and hospitalization (indicative of severe disease) from October 2022 through March 2023, a flu season in which far fewer individuals were social distancing or wearing masks than during the two previous flu seasons.
Vaccination reduced the risk of flu-related E.D./urgent care visits and hospitalization for those 6 months to 17 years by almost half. For adults, regardless of age, vaccination reduced the risk of E.D. urgent care visits by almost half and reduced the risk of hospitalization by slightly more than a third.
These results led the authors of both studies to conclude that flu vaccination is likely to substantially reduce illness, death and strain on healthcare resources.
“We study the effectiveness of flu and other vaccines to ensure that our processes for forecasting the most effective vaccines are working well and therefore might potentially also be translatable to other diseases as well,” said Shaun Grannis, M.D., M.S., a co-author of both the pediatric and adult VISION Network studies, Regenstrief Institute vice president for data and analytics and a family practice physician. “Given influenza’s significant disease burden -- for example the H1N1 (swine) flu killed over a quarter of a million people worldwide in 2009-2010 -- we want to make sure that we understand virus trends as well as other factors and that we're continuing to do as well as and as much as we can to reduce the flu disease burden.”
Both the pediatric and adult studies evaluated electronic health record (EHR) data from sites across three healthcare systems in California, Utah, Minnesota and Wisconsin.
Flu vaccine effectiveness: 2022-2023 flu season for ages 6 months to 17 years
Vaccination reduced the risk of flu-related E.D./urgent care visits (moderate disease) by 48 percent and hospitalization (severe disease) by 40 percent overall across ages 6 months to 17 years. Broken down by age, risk reduction was greater for those age 6 months to 4 years than older children and adolescents.
Ages 6 months to four years
Vaccination reduced the risk of E.D./urgent care visits (moderate disease) by 53 percent.
Vaccination reduced the risk of hospitalization (severe disease) by 56 percent.
Ages 5 to 17 years
Vaccination reduced the risk of E.D./ urgent care visits (moderate disease) by 38 percent.
Vaccination reduced the risk of hospitalization by 46 percent.
Approximately 30 percent of E.D./critical care visits for acute respiratory illness in children and adolescents were positive for flu, as were 14 percent of hospitalizations.
“Vaccine Effectiveness Against Pediatric Influenza-A-Associated Urgent Care, Emergency Department, and Hospital Encounters During the 2022-2023 Season, VISION Network” is published in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Flu vaccine effectiveness: 2022-2023 flu season for ages 18-64
Vaccine effectiveness was 45 percent against E.D./critical care visits(moderate disease) for adults under age 65. Effectiveness against hospitalization (severe disease) was 23 percent.
Adults younger than 65 typically received standard-dose inactivated vaccines.
Flu vaccine effectiveness: 2022-2023 flu season for ages 65 and older
Vaccine effectiveness was 41 percent against both flu-associated E.D./urgent care visits (moderate disease) and hospitalization (serious disease) for this age group.
Adults age 65 and older typically received enhanced vaccine products.
“Influenza vaccine effectiveness against influenza-A-associated emergency department, urgent care, and hospitalization encounters among U.S. adults, 2022-2023” is published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
“As with COVID, the dynamics of flu differs between children and adults. But we found that for both children and adults, vaccination significantly reduced the need for trips to the E.D, or critical care center and for hospitalization for flu-related illnesses last flu season and this is encouraging,” said Dr. Grannis. “I'm hopeful that we will see similar or even better vaccine effectiveness during the current flu season. Even if they do experience symptoms, people who are vaccinated typically tend to have milder, shorter cases of the flu, a viral illness which can carry a severe disease burden.
“The vaccine effectiveness we saw in last year’s flu season is encouraging. As both a research scientist and a primary care physician, I urge everyone to be vaccinated for flu this year and every year – it’s good for each person’s health and the health of your community.”
About Shaun Grannis, M.D., M.S.
In addition to his role as the vice president for data and analytics at Regenstrief Institute, Shaun Grannis, M.D., M.S., holds the Regenstrief Chair in Medical Informatics and is a professor of family medicine at Indiana University School of Medicine.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-19
February 16, 2024
Contact: Nick Wilson
805-235-8008; nwilso28@calpoly.edu
Second Year of Cal Poly Astronomy Fellowship to Examine High-Energy Particle Jets Near Supermassive Black Holes
SAN LUIS OBISPO — In the second year of the Astronomy Faculty Research Fellowship in Cal Poly’s Bailey College of Science and Mathematics, a research team will study extremely high-energy photons emitted by the extreme environment found near mega-sized black holes.
The fellowship was ...
2024-02-19
Language skills are strong predictors of academic, socioemotional and behavioral outcomes when children enter school. They learn language in preschool years by interacting with others, especially their parents. Book sharing is a popular way parents engage young children in conversation. However, not all parents are comfortable with book sharing and not all children like having books read to them.
A new study on “parent talk” by Florida Atlantic University, in collaboration with Aarhus University in Denmark, provides ...
2024-02-19
Lincoln, Nebraska, Feb. 19, 2024 — A Husker research duo was named a first-round winner in a National Institutes of Health competition aimed at generating solutions for delivering genome-editing technology to the cells of people with rare and common diseases.
Janos Zempleni, Willa Cather Professor of molecular nutrition, and Jiantao Guo, professor of chemistry, were selected as Phase 1 winners in the NIH’s Targeted Genome Editor Delivery Challenge. The challenge is a three-phase competition with prizes totaling $6 million; the University of Nebraska–Lincoln team was among 30 initial recipients announced in December ...
2024-02-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Until recently, Orthacanthus gracilis could have been considered the “John Smith” of prehistoric shark names, given how common it was.
Three different species of sharks from the late Paleozoic Era – about 310 million years ago – were mistakenly given that same name, causing lots of grief to paleontologists who studied and wrote about the sharks through the years and had trouble keeping them apart.
But now Loren Babcock, a professor of earth sciences at The Ohio State University, has finished the arduous task of renaming two of the three sharks – and in the process rediscovered a wealth ...
2024-02-19
A rapid scoping review has been conducted which reveals five common ways in which the health of homeless pet owners and their companion animals is improved.
Ten percent of homeless people keep pets. But little information exists on specific intervention strategies for improving the health of homeless people and their pets who are often the only source of unconditional love or companionship in their life.
The study, published in the Human-Animal Interactions journal, found that the most common ways ...
2024-02-19
Potassium deficiency in agricultural soils is a largely unrecognised but potentially significant threat to global food security if left unaddressed, finds new research involving researchers at UCL, University of Edinburgh and the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology.
The study, published in Nature Food, found that more potassium is being removed from agricultural soils than is being added, throughout many regions of the world. It also gives a series of recommendations for how to mitigate the issue.
Potassium is a vital nutrient for plant growth that ...
2024-02-19
How does our intestine, which can be at least 15 feet long, fit properly inside our bodies? As our digestive system grows, the gut tube goes through a series of dramatic looping and rotation to package the lengthening intestine. Failure of the gut to rotate properly during development results in a prevalent, but poorly understood, birth anomaly called intestinal malrotation. Now, in a study published in the journal Development, scientists from North Carolina State University have uncovered a potential cause of this life-threatening condition.
Intestinal malrotation affects 1 in 500 births but the underlying causes are not well understood. ...
2024-02-19
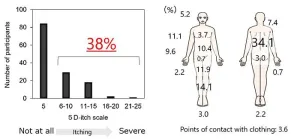
Niigata, Japan – Dr. Yamamoto et al. found the several uremic toxins as one of causes of itching in hemodialysis patients. Hemodialysis patients commonly experience itching on a daily basis, which is distributed throughout their bodies. They developed a "PBUT score" based on highly protein-bound uremic toxins (PBUT) that increase in the body with end-stage kidney disease. The PBUT score was associated with itching in hemodialysis patients.
I. Background of the Study
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) require kidney replacement therapy, such as hemodialysis, to manage their condition. Hemodialysis patients often experience various symptoms, ...
2024-02-19
Communities must be better prepared for flooding in their homes and businesses, an expert warns, as climate change predictions suggest more extreme flooding globally.
Floods still inflict major costs to the economies, livelihoods and wellbeing of communities, with flood risks and impacts set to increase further due to climate change (IPCC, 2021).
Professor of Environmental Management, Lindsey McEwen explains how many experts now believe local communities have critical roles as key actors within flood risk management and disaster risk reduction.
Professor McEwen, author of Flood ...
2024-02-18
Link to video and sound (details below): https://spaces.hightail.com/receive/JwM0o5gQdq
The reproduction of giant sea spiders in Antarctica has been largely unknown to researchers for more than 140 years, until now. University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa scientists traveled to the remote continent and saw first-hand the behaviors of these mysterious creatures, and their findings could have wider implications for marine life and ocean ecosystems in Antarctica and around the world.
Sea spiders, or ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Studies find flu vaccines were effective in 2022-2023 flu season
Vaccines reduced risk of both moderate and severe disease for all ages