(Press-News.org) How does our intestine, which can be at least 15 feet long, fit properly inside our bodies? As our digestive system grows, the gut tube goes through a series of dramatic looping and rotation to package the lengthening intestine. Failure of the gut to rotate properly during development results in a prevalent, but poorly understood, birth anomaly called intestinal malrotation. Now, in a study published in the journal Development, scientists from North Carolina State University have uncovered a potential cause of this life-threatening condition.
Intestinal malrotation affects 1 in 500 births but the underlying causes are not well understood. To find out why gut revolution could go amiss, scientists need to first understand intestinal rotation during normal development, a complex process that still baffles biologists.
The team of scientists, led by Dr Nanette Nascone-Yoder, decided to make use of a well-established system in frogs. “As vertebrates, frogs and humans share a common ancestor and have many similar anatomical features, including an intestine that rotates in a counter-clockwise direction,” explained Dr Nascone-Yoder. “Because frog embryos develop in only a few days and are highly experimentally accessible, they allow us to quickly test new hypotheses about how and why development goes awry during malrotation.”
“Frog embryos develop in a petri dish and are transparent when the intestine is developing, so they can be exposed to drugs or environmental chemicals to screen for substances capable of producing malrotation,” said Dr Nascone-Yoder. One of the compounds the team screened was the herbicide atrazine. They found that exposure to atrazine greatly increased the frequency at which frog intestines rotated in the reverse (clockwise) direction and decided to focus on atrazine to further investigate intestinal malrotation.
Dr Julia Grzymkowski, who led the experimental work of this study, found that exposure to atrazine disrupted metabolism (chemical reactions that provide energy for biological processes) in the frog embryos. Metabolic imbalance in the embryos derailed a series of cellular processes in the gut — cells could not grow, divide and rearrange appropriately to drive the proper intestinal elongation and rotation.
“Although we found that atrazine causes malrotation in frogs, these results do not necessarily mean that this herbicide causes malrotation in humans, because, in our screen, the tadpoles were exposed to 1000-fold higher levels than are typically found in the environment,” Dr Nascone-Yoder emphasised, “but our findings do strongly suggest that disturbing the same cellular metabolic processes affected by atrazine, for example, via exposure to other chemicals in the environment and/or genetic variations that affect metabolism, could contribute to intestinal malrotation in humans.”
This study is just beginning to unravel what happens during embryonic development that leads to intestinal malrotation. Dr Nascone-Yoder’s team hopes to extend this work: “Our results have provided new avenues to explore the underlying causes of this prevalent birth anomaly. We are now starting to dive deeper into the cellular events that coordinate the complicated process of intestinal elongation and rotation.”
END
Poorly coiled frog guts help scientists unravel prevalent human birth anomaly
2024-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
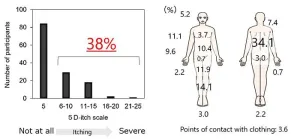
Unveiling uremic toxins linked to itching in hemodialysis patients
2024-02-19
Niigata, Japan – Dr. Yamamoto et al. found the several uremic toxins as one of causes of itching in hemodialysis patients. Hemodialysis patients commonly experience itching on a daily basis, which is distributed throughout their bodies. They developed a "PBUT score" based on highly protein-bound uremic toxins (PBUT) that increase in the body with end-stage kidney disease. The PBUT score was associated with itching in hemodialysis patients.
I. Background of the Study
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) require kidney replacement therapy, such as hemodialysis, to manage their condition. Hemodialysis patients often experience various symptoms, ...
Communities must get prepared for increased flooding due to climate change, expert warns
2024-02-19
Communities must be better prepared for flooding in their homes and businesses, an expert warns, as climate change predictions suggest more extreme flooding globally.
Floods still inflict major costs to the economies, livelihoods and wellbeing of communities, with flood risks and impacts set to increase further due to climate change (IPCC, 2021).
Professor of Environmental Management, Lindsey McEwen explains how many experts now believe local communities have critical roles as key actors within flood risk management and disaster risk reduction.
Professor McEwen, author of Flood ...
Giant Antarctic sea spiders reproductive mystery solved by UH researchers
2024-02-18
Link to video and sound (details below): https://spaces.hightail.com/receive/JwM0o5gQdq
The reproduction of giant sea spiders in Antarctica has been largely unknown to researchers for more than 140 years, until now. University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa scientists traveled to the remote continent and saw first-hand the behaviors of these mysterious creatures, and their findings could have wider implications for marine life and ocean ecosystems in Antarctica and around the world.
Sea spiders, or ...
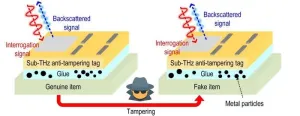
This tiny, tamper-proof ID tag can authenticate almost anything
2024-02-18
A few years ago, MIT researchers invented a cryptographic ID tag that is several times smaller and significantly cheaper than the traditional radio frequency tags (RFIDs) that are often affixed to products to verify their authenticity.
This tiny tag, which offers improved security over RFIDs, utilizes terahertz waves, which are smaller and travel much faster than radio waves. But this terahertz tag shared a major security vulnerability with traditional RFIDs: A counterfeiter could peel the tag off a genuine item and reattach it to a fake, and the authentication system would be none the wiser.
The researchers have now surmounted ...
Viruses that can help ‘dial up’ carbon capture in the sea
2024-02-17
DENVER – Armed with a catalog of hundreds of thousands of DNA and RNA virus species in the world’s oceans, scientists are now zeroing in on the viruses most likely to combat climate change by helping trap carbon dioxide in seawater or, using similar techniques, different viruses that may prevent methane’s escape from thawing Arctic soil.
By combining genomic sequencing data with artificial intelligence analysis, researchers have identified ocean-based viruses and assessed their genomes to find that they “steal” genes from other microbes or cells that process carbon in the sea. Mapping microbial ...
Imageomics poised to enable new understanding of life
2024-02-17
Embargoed until 1:30 p.m. ET, Saturday Feb. 17, 2024
DENVER – Imageomics, a new field of science, has made stunning progress in the past year and is on the verge of major discoveries about life on Earth, according to one of the founders of the discipline.
Tanya Berger-Wolf, faculty director of the Translational Data Analytics Institute at The Ohio State University, outlined the state of imageomics in a presentation on Feb. 17, 2024, at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
“Imageomics ...
Scientists try out stone age tools to understand how they were used
2024-02-17
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University crafted replica stone age tools and used them for a range of tasks to see how different activities create traces on the edge. They found that a combination of macroscopic and microscopic traces can tell us how stone edges were used. Their criteria help separate tools used for wood-felling from other activities. Dated stone edges may be used to identify when timber use began for early humans.
For prehistoric humans, improvements in woodworking technology were revolutionary. While Paleolithic (early stone age) artifacts point to the use of wood for simple tools such as spears ...
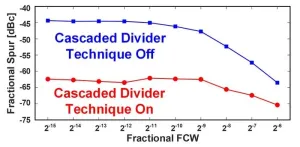
Combating fractional spurs in phase locked loops to improve wireless system performance in Beyond 5G
2024-02-17
Two innovative design techniques lead to substantial improvements in performance in fractional-N phase locked loops (PLLs), report scientists from Tokyo Tech. The proposed methods are aimed to minimize unwanted signals known as fractional spurs, which typically plague PLLs used in many modern radar systems and wireless transceivers. These efforts could open doors to technological improvements in wireless communication, autonomous vehicles, surveillance, and tracking systems in beyond 5G era.
Many emerging and evolving technologies, such as self-driving vehicles, target tracking systems, and remote sensors, rely on the high-speed and error-free operation ...
20th Annual National Jewish Health Respiratory Disease Young Investigators’ Forum calls for abstracts
2024-02-17
DENVER — Young physician investigators interested in research careers in pulmonology, allergy and immunology, pediatric and related programs, are encouraged to submit basic science or clinical research abstracts by June 3, 2024, to be considered for participation in the 20th Annual Respiratory Disease Young Investigators’ Forum. This year’s Forum will take place October 17-20, 2024, in Denver.
The annual event provides career development and research opportunities for fellows and early career faculty. The Forum is a celebration of talent and ingenuity in respiratory medicine. Physician-scientists in fellowship ...
Study highlights importance of genetic sequencing to diagnosis of growth disorders
2024-02-16
In an article published in the Journal of Pediatrics, researchers based in Brazil describe the case of a nine-year-old boy admitted to hospital with multiple symptoms and overlapping conditions that made diagnosis difficult, such as short stature, thin tooth enamel (dental enamel hypoplasia), moderate mental deficiency, speech delay, asthma, mildly altered blood sugar, and a history of recurring infections in infancy.
The team used exome sequencing, in which only the protein-coding portion of the genome is analyzed, to look for genetic mutations, and found them in GCK and BCL11B. ...