(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Feb. 20, 2024 — The freshness of animal meat is an essential property determining its quality and safety. With advanced technology capable of preserving food for extended periods of time, meat can be shipped around the globe and consumed long after an animal dies. As global meat consumption rates increase, so too does the demand for effective measures for its age.
Despite the technological advances keeping meat fresh for as long as possible, certain aging processes are unavoidable. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule produced by breathing and responsible for providing energy to cells. When an animal stops breathing, ATP synthesis also stops, and the existing molecules decompose into acid, diminishing first flavor and then safety. Hypoxanthine (HXA) and xanthine are intermediate steps in this transition. Assessing their prevalence in meat indicates its freshness.
In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, researchers from the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, VNU University of Science, Hanoi University of Science and Technology, and the Russian Academy of Sciences developed a biosensor using graphene electrodes modified by zinc oxide nanoparticles to measure HXA. The team demonstrated the sensor’s efficacy on pork meat.
While many HXA sensing methods currently exist, they can be costly and time-consuming and require specialists.
“In comparison to modern food-testing methods, like high-performance liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, atomic and molecular spectroscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, biosensors like our sensor offer superior advantages in time, portability, high sensitivity, and selectivity,” said author Ngo Thi Hong Le.
The sensor is produced using a polyimide film, which is converted into porous graphene using a pulsed laser. The added zinc oxide nanoparticles attract the HXA molecules to the electrode surface. When HXA interacts with the electrode, it oxidizes and transfers its electrons, spiking the electrode’s voltage. The linear relationship between HXA and voltage increase enables easy determination of HXA content.
To assess the sensor’s ability, the researchers tested solutions with known quantities of HXA. After the outstanding performance, the researchers measured the biosensor’s practicality using pork tenderloins purchased from a supermarket. The sensor performed with over 98% accuracy, favorable detection range, and low detection limit.
“In Vietnam, pork is the most consumed meat,” said Le. “Therefore, pork quality monitoring is one of the important requirements in the food industry in our country, which is why we prioritized it.”
More than just pork, any meat product can be evaluated by this biosensor.
###
The article “Nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor based on ZnO nanoparticles/porous graphene for the detection of hypoxanthine in pork meat” is authored by Ngo Thi Hong Le, Nguyen Xuan Viet, Nguyen Van Anh, Ta Ngoc Bach, Phung Thi Thu, Nguyen Thi Ngoc, Do Hung Manh, Vu Hong Ky, Vu Dinh Lam, Victor Kodelov, Svetlana Von Gratowski, Nguyen Hai Binh, and Trinh Xuan Anh. It will appear in AIP Advances on Feb. 20, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0190293). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0190293.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences—applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/adv.
###
END
Fresh meat: New biosensor accurately and efficiently determines meat freshness
Employing a porous graphene electrode with zinc oxide nanoparticles, biosensor identifies aging byproducts in meat
2024-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Large, diverse genetic study of glaucoma implicates vascular and cancer-related genes
2024-02-20
An international genetic study using multiancestry biobanks has identified novel genetic locations associated with primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), the most common type of glaucoma and the leading cause of irreversible blindness globally. The findings, published Feb. 20 in Cell Reports Medicine, detail ancestry- and sex-specific genetic loci associated with POAG and implicate vascular and cancer-related genes in POAG risk.
“Although there has been significant progress using genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to explore the genetic pathophysiology of glaucoma in humans, there is still a lack of understanding of the underlying ...
HPV vaccination among young adults before and during the pandemic
2024-02-20
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination coverage among young adults did not increase during the COVID-19 pandemic compared with prior years. This finding likely reflects pandemic-related disruptions in initiating the HPV vaccine among young adults.
Authors: Kalyani Sonawane, Ph.D., of the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.56875)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for ...
Historical redlining, persistent mortgage discrimination, and race in breast cancer outcomes
2024-02-20
About The Study: In a study of 1,764 women with breast cancer, living in a historically redlined area was associated with increased odds of a diagnosis of estrogen receptor–negative breast cancer in non-Hispanic Black women and increased odds of late-stage diagnosis in non-Hispanic white women. Persistent mortgage discrimination was associated with an increase in breast cancer mortality in non-Hispanic white women, and non-Hispanic Black women were more likely to die of breast cancer no matter where they lived.
Authors: Jasmine M. Miller-Kleinhenz, Ph.D., of Emory University in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Ancient genomes reveal Down Syndrome in past societies
2024-02-20
For many years, researchers at MPI-EVA have been collecting and analyzing ancient DNA from humans who lived during the past tens of thousands of years. Analyzing these data has allowed the researchers to trace the movement and mixing of people, and even to uncover ancient pathogens that affected their lives. However, a systematic study of uncommon genetic conditions had not been attempted. One of those uncommon conditions, known as Down Syndrome, affects nowadays around one in 1,000 births.
To their surprise, Adam “Ben” Rohrlach and colleagues identified six individuals ...
Can a single brain region encode familiarity and recollection?
2024-02-20
NEW YORK, NY — The human brain has the extraordinary ability to rapidly discern a stranger from someone familiar, even as it can simultaneously remember details about someone across decades of encounters. Now, in mouse studies, scientists at Columbia's Zuckerman Institute have revealed how the brain elegantly performs both tasks.
“These findings are the first evidence that a single population of neurons can use different codes to represent novel and familiar individuals,” said co-corresponding author Stefano Fusi, PhD, professor of neuroscience at Columbia’s Vagelos College of Physicians and ...
Pesticides found in kale but at low risk levels
2024-02-20
Kale fans can rest easy knowing pesticides used to grow the hearty greens are unlikely to end up in their salads or smoothies, a new chemical analysis of the superfood suggests.
Conducting novel tests that provide the most complete picture to date of a crop’s chemical makeup, the Johns Hopkins–led team found several pesticides and compounds in Maryland-farmed kale—but no cause for alarm.
“We do see minute traces of pesticides in the kale, but the levels we found are so much lower ...
Stress during pregnancy can lead to early maturation of first-born daughters
2024-02-20
Key takeaways
A UCLA-led research team found a correlation between certain aspects of early puberty in first-born daughters and high levels of prenatal stress in their mothers.
The researchers did not find the same result in boys or in daughters who were not first-born.
This early maturation may enable a first-born daughter to help her mother rear her other children successfully, according to UCLA anthropologist Molly Fox.
A UCLA-led team of researchers has found a correlation between early signs of adrenal puberty in first-born daughters ...
Bar-Ilan University researchers produce “laboratory testicles”
2024-02-20
The testis is responsible for sperm production and testosterone synthesis. Abnormalities in testis development and function lead to disorders of sex development (DSD) and male infertility. Currently, no in vitro system exists for modeling the testis.
Dr. Nitzan Gonen, a researcher specializing in the process of fetal sex determination, together with research students Aviya Stopel, Cheli Lev and Stav Dahari, has succeeded in creating "laboratory testicles" that may significantly advance understanding of the mechanisms involved in sex determination and provide solutions for male infertility, which affects one in 12 men worldwide.
The artificial testicles ...
Zero-index metamaterials and the future
2024-02-20
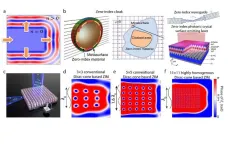
In the realm of materials science, electromagnetic (EM) metamaterials have emerged as a revolutionary class of engineered composites capable of manipulating electromagnetic waves in ways never before possible. Unlike their naturally occurring counterparts, EM metamaterials derive their extraordinary properties from their unique structural arrangements, allowing them to exhibit unattainable electromagnetic characteristics in conventional materials.
One of the most fascinating characteristics of EM metamaterials lies in the realm of zero-index metamaterials (ZIMs). ZIMs possess the ...
If your TV spoke to you, would you buy it? Study finds people spend more on some “talking products”
2024-02-20
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. – In the classic Disney film “Beauty and the Beast,” Lumière, the candelabra character, famously sings with Mrs. Potts, a tea pot, “Be our guest, be our guest. Put our service to the test. Tie your napkin round your neck, Cherie, and we provide the rest.”
When the 1991 Oscar-nominated song co-written by Indiana University alumnus Howard Ashman was released, it hardly seemed realistic that a product could sing its own praises and sell itself to consumers. But artificial intelligence today makes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Fresh meat: New biosensor accurately and efficiently determines meat freshnessEmploying a porous graphene electrode with zinc oxide nanoparticles, biosensor identifies aging byproducts in meat