In the realm of materials science, electromagnetic (EM) metamaterials have emerged as a revolutionary class of engineered composites capable of manipulating electromagnetic waves in ways never before possible. Unlike their naturally occurring counterparts, EM metamaterials derive their extraordinary properties from their unique structural arrangements, allowing them to exhibit unattainable electromagnetic characteristics in conventional materials.
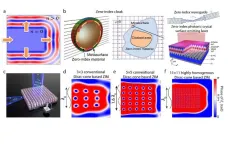
One of the most fascinating characteristics of EM metamaterials lies in the realm of zero-index metamaterials (ZIMs). ZIMs possess the remarkable ability to achieve uniform electromagnetic field distribution over arbitrary shape (Figure 1a). This unique property opens many potential applications, from ultra-compact cloaking devices to arbitrarily shaped waveguides and lenses and photonic crystal surface-emitting lasers (Figure 1b).
Despite their immense potential, ZIMs have faced a significant hurdle in their practical implementation. The homogeneity of ZIMs is often limited by the number of unit cells per free-space wavelength (Figure 1d). This limitation arises from the low permittivities property of the materials used to construct ZIMs. As a result, ZIMs often require large physical space to achieve their effective electromagnetic properties (Figure 1e).
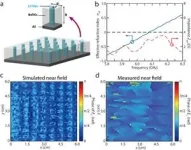
Researchers have overcome this longstanding challenge in a groundbreaking study by developing a highly homogeneous ZIM using a novel combination of high-permittivity materials. As shown in Figure 2a, by employing SrTiO3 ceramic pillars embedded in a BaTiO3 background matrix, they have successfully fabricated a ZIM with an over threefold increase in homogenization level (Figures 1e and 1f), significantly reducing its physical dimensions.
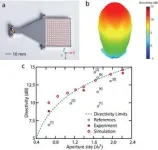
Based on the uniform distribution of the phase of electromagnetic field throughout the ZIM, researchers have demonstrated a high-directivity antenna. By incorporating ZIM in a metallic waveguide (Figure 3a), this antenna has approached the fundamental limitation of directivity in antenna as the aperture size varies from subwavelength regime to a very large scale (Figure 3c).
This breakthrough paves the way for a new era of ZIM-based devices, offering unprecedented performance and compactness. The researchers' achievement has profound implications for a wide range of fields, including wireless communications, remote sensing, and global positioning systems. Moreover, their work opens up new possibilities for fundamental research in ultracompact waveguides, cloaking devices, and superconducting quantum computing.
END
Zero-index metamaterials and the future
2024-02-20
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
If your TV spoke to you, would you buy it? Study finds people spend more on some “talking products”
2024-02-20
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. – In the classic Disney film “Beauty and the Beast,” Lumière, the candelabra character, famously sings with Mrs. Potts, a tea pot, “Be our guest, be our guest. Put our service to the test. Tie your napkin round your neck, Cherie, and we provide the rest.”
When the 1991 Oscar-nominated song co-written by Indiana University alumnus Howard Ashman was released, it hardly seemed realistic that a product could sing its own praises and sell itself to consumers. But artificial intelligence today makes ...
Photon-counting CT improves coronary artery disease assessment
2024-02-20
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Ultrahigh-spatial-resolution photon-counting detector CT improved assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD), allowing for reclassification to a lower disease category in 54% of patients, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The technology has the potential to improve patient management and reduce unnecessary interventions.
Coronary CT angiography is a first-line test in the assessment of coronary artery disease. However, its diagnostic value is limited in patients with severe calcifications, or calcium ...
Annual breast cancer screening beginning at 40 saves lives
2024-02-20
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Annual breast cancer screening beginning at age 40 and continuing to at least age 79 results in the highest reduction in mortality with minimal risks, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Breast cancer is the second most common cause of cancer death for women in the U.S. Despite research demonstrating that consistent participation in screening mammography can reduce breast cancer deaths by 40%, only 50% or less of eligible women actually participate in annual screening.
“There is an ongoing debate over the recommendations for breast cancer screening, specifically ...
NYU’s Jinyoung Park and SueYeon Chung win Sloan Foundation Research Fellowships
2024-02-20
Two New York University faculty have been awarded fellowships from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation: SueYeon Chung, an assistant professor at the Center for Neural Science, and Jinyoung Park, an assistant professor at the Courant Institute for Mathematical Sciences.
The fellowships recognize “exceptional U.S. and Canadian researchers whose creativity, innovation, and research accomplishments make them stand out as the next generation of leaders,” the Sloan Foundation said in announcing this year’s ...
U of T-led study finds positive support from parents and clinicians for pediatric cancer pain management app
2024-02-20
A recent study led by Assistant Professor Lindsay Jibb of the Lawrence Bloomberg Faculty of Nursing and Scientist at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) found that parents of young children with cancer, along with pediatric cancer clinicians are in favour of an app-based solution that Jibb and her team are creating, to help parents manage their child’s cancer pain at home.
The study published in PLOS Digital Health showed that parents and clinicians not only found the pain management app to be helpful and safe, but also provided them with a sense of empowerment.
“The ...
Generating 'buzz' about new products can influence their success
2024-02-20
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- The way companies announce new products or build up hype can often influence their success once those new products hit the market, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York. Whether it's an upcoming blockbuster movie or a new rollout from major companies like Coca-Cola or Apple, the new research shows how companies might use this type of preannouncement marketing to their advantage.
How often have you watched trailers for an upcoming movie and thought, “I can’t wait to see that,” when it hits theaters ...
The immune system’s moonlighters
2024-02-20
Our immune system is remarkably powerful. It quickly assembles teams of cells to eliminate threats inside our bodies. But sometimes, it hits the wrong target. Autoimmune diseases like lupus and multiple sclerosis result from friendly fire—immune cells attacking healthy tissues and organs by mistake. New treatments and therapeutic targets are direly needed for these conditions.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Christopher Vakoc may have stumbled upon a new therapeutic target—one hidden in plain sight. Vakoc and his team discovered that IκBζ, a well-studied protein in the immunology ...
Geographic disparities in access to addiction treatment medication may be linked to race, ethnicity
2024-02-20
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 20, 2024 — Buprenorphine, a life-saving medication for opioid use disorder, is far less accessible in geographic areas of the United States with racially and ethnically diverse populations than in predominantly white areas, according to a new study of pre-pandemic data led by health policy scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health published today in Journal of Addiction Medicine.
The study is among the first to examine buprenorphine access at the local, sub-county level, and the findings point to lack of access to medications for opioid use disorder as a potential ...
The director of the U.S. National Science Foundation on the future of AI
2024-02-20
In an editorial, Sethuraman Panchanathan, director of the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), calls for the responsible and equitable development of artificial intelligence (AI) and promises to use the agency’s resources to work toward democratizing AI research. NSF spends $800 million on AI research in the public interest each year. Panchanathan summarizes some of the benefits AI can offer to scientific research—from accelerating discovery to automating routine tasks—but emphasizes that AI must be safe and accessible. Toward that end, NSF and its partners launched the National Artificial Intelligence Research Resource ...
Unlocking the energetic secrets of collective animal movement: How group behavior reduces energy costs in fish
2024-02-20
Many animals, including apex predators, move in groups. We know this collective behavior is fundamental to the animal’s ability to move in complex environments, but less is known about what drives the behavior because many factors underlie its evolution. Scientists wonder, though, if all these animals share a fundamental drive such as for mating, safety, or perhaps even to save energy.
“The keyword is perhaps,” said Yangfan Zhang, postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology (OEB) at Harvard, “because no one has actually measured this and compared it directly across all animal groups, mainly ...