(Press-News.org) A recent study led by Assistant Professor Lindsay Jibb of the Lawrence Bloomberg Faculty of Nursing and Scientist at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) found that parents of young children with cancer, along with pediatric cancer clinicians are in favour of an app-based solution that Jibb and her team are creating, to help parents manage their child’s cancer pain at home.
The study published in PLOS Digital Health showed that parents and clinicians not only found the pain management app to be helpful and safe, but also provided them with a sense of empowerment.
“The burden of caring and pain management for these children falls on parents when they are at home, and kids can experience frequent and sometimes severe cancer pain,” says Jibb who holds the Signy Hildur Eaton Chair in Paediatric Nursing Research. “The goal of our mobile app is to ease this burden and help both parents and children receive better quality pain management.”
As part of the qualitative study, participants were also invited to provide recommendations for the digital app. Many of these recommendations focused on accessibility and ease of use, but also the need for the app to be available in multiple languages, and with a gamification component to involve children where appropriate in their own care.
Currently in a pilot stage, the app includes a library of pharmacological advice as well as advice for psychological and physical symptoms children may be experiencing. The algorithm-based instructions tell a parent how to help their child respond to certain types of pain, which can include actions such as belly breathing, stretching, or mindfulness sessions. The advice is targeted to the parent based on their child’s age and development stage.
In addition, a chat feature is being embedded into the app to further address the need for real-time support for parents something that groups such as the Ontario Parents Advocating for Children with Cancer (OPACC) Advisory Group have indicated is of considerable importance. The chat option will connect parents with a nurse in hospital, allowing them to ask questions and seek nurse-led clinical pain support for their child when needed.
“Digital and mobile apps are used for a variety of reasons, and it is surprising that they are not more routinely used in health care. As technology continues to advance, particularly with artificial intelligence, the capacity to connect people who are outside the hospital with real-time care and support will hopefully continue to expand,” says Jibb.
Participants pointed to some challenges the digital app could pose, such as the ability to measure pain thresholds and know when a doctor or clinician should intervene.
“Pain is very subjective, and perhaps even more so for a child. As a result, some of the feedback we have received as part of this study is to ensure that multidimensional pain assessments, multi-modal pain management support, and pain tracking over time are dedicated features in the app,” says Jibb.
This Jibb says, will address the need for a biopsychosocial approach to cancer pain management and ensure that each patient threshold is individualized to patients and their families.
Jibb has currently received funding from the University of Toronto’s Connaught New Researcher Award to support the pilot rollout of this digital cancer pain management app to parents of children with cancer, in early 2024.
END
U of T-led study finds positive support from parents and clinicians for pediatric cancer pain management app
Implementation and design of digital app will feature recommendations from parents and pediatric cancer care clinicians.
2024-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Generating 'buzz' about new products can influence their success
2024-02-20
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- The way companies announce new products or build up hype can often influence their success once those new products hit the market, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York. Whether it's an upcoming blockbuster movie or a new rollout from major companies like Coca-Cola or Apple, the new research shows how companies might use this type of preannouncement marketing to their advantage.
How often have you watched trailers for an upcoming movie and thought, “I can’t wait to see that,” when it hits theaters ...
The immune system’s moonlighters
2024-02-20
Our immune system is remarkably powerful. It quickly assembles teams of cells to eliminate threats inside our bodies. But sometimes, it hits the wrong target. Autoimmune diseases like lupus and multiple sclerosis result from friendly fire—immune cells attacking healthy tissues and organs by mistake. New treatments and therapeutic targets are direly needed for these conditions.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Christopher Vakoc may have stumbled upon a new therapeutic target—one hidden in plain sight. Vakoc and his team discovered that IκBζ, a well-studied protein in the immunology ...
Geographic disparities in access to addiction treatment medication may be linked to race, ethnicity
2024-02-20
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 20, 2024 — Buprenorphine, a life-saving medication for opioid use disorder, is far less accessible in geographic areas of the United States with racially and ethnically diverse populations than in predominantly white areas, according to a new study of pre-pandemic data led by health policy scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health published today in Journal of Addiction Medicine.
The study is among the first to examine buprenorphine access at the local, sub-county level, and the findings point to lack of access to medications for opioid use disorder as a potential ...
The director of the U.S. National Science Foundation on the future of AI
2024-02-20
In an editorial, Sethuraman Panchanathan, director of the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), calls for the responsible and equitable development of artificial intelligence (AI) and promises to use the agency’s resources to work toward democratizing AI research. NSF spends $800 million on AI research in the public interest each year. Panchanathan summarizes some of the benefits AI can offer to scientific research—from accelerating discovery to automating routine tasks—but emphasizes that AI must be safe and accessible. Toward that end, NSF and its partners launched the National Artificial Intelligence Research Resource ...
Unlocking the energetic secrets of collective animal movement: How group behavior reduces energy costs in fish
2024-02-20
Many animals, including apex predators, move in groups. We know this collective behavior is fundamental to the animal’s ability to move in complex environments, but less is known about what drives the behavior because many factors underlie its evolution. Scientists wonder, though, if all these animals share a fundamental drive such as for mating, safety, or perhaps even to save energy.
“The keyword is perhaps,” said Yangfan Zhang, postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology (OEB) at Harvard, “because no one has actually measured this and compared it directly across all animal groups, mainly ...
Wide variation in rates of police killings suggests unnecessary deaths
2024-02-20
One in three police homicides could have been avoided without endangering police or the public, according to a study. Eight percent of all homicides of adult men in the United States are committed by police. Using data from 2008–2017 from the National Officer-Involved Homicide Database, Josh Leung-Gagné compared police homicide rates across the 711 local police departments serving 50,000 or more residents in the United States. One explanation for differing rates of police killings is that some jurisdictions are riskier than others, which necessitates ...
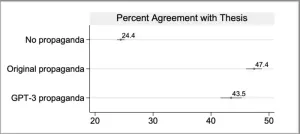
High persuasiveness of propaganda written by AI
2024-02-20
Research participants who read propaganda generated by the AI large language model GPT-3 davinci were nearly as persuaded as those who read real propaganda from Iran or Russia, according to a study. Josh Goldstein and colleagues identified six articles, likely originating from Iranian or Russian state-aligned covert propaganda campaigns, according to investigative journalists or researchers. These articles made claims about US foreign relations, such as the false claim that Saudi Arabia committed to help fund the US-Mexico border wall or the false claim that the US fabricated reports showing that the Syrian government had used chemical weapons. For each ...
Junk DNA in birds may hold key to safe, efficient gene therapy
2024-02-20
The recent approval of a CRISPR-Cas9 therapy for sickle cell disease demonstrates that gene editing tools can do a superb job knocking out genes to cure hereditary disease. But it's still not possible to insert whole genes into the human genome to substitute for defective or deleterious genes.
A new technique that employs a retrotransposon from birds to insert genes into the genome holds more promise for gene therapy, since it inserts genes into a "safe harbor" in the human genome where the insertion won't disrupt essential genes or lead to cancer.
Retrotransposons, or retroelements, are pieces of DNA that, when transcribed ...
Fasting-like diet lowers risk factors for disease, reduces biological age in humans
2024-02-20
Cycles of a diet that mimics fasting can reduce signs of immune system aging, as well as insulin resistance and liver fat in humans, resulting in a lower biological age, according to a new USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology-led study.
The study, which appears in Nature Communications on Feb. 20, adds to the body of evidence supporting the beneficial effects of the fasting-mimicking diet (FMD).
The FMD is a five-day diet high in unsaturated fats and low in overall calories, protein, and carbohydrates and is designed to mimic the effects ...
New model identifies drugs that shouldn’t be taken together
2024-02-20
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Any drug that is taken orally must pass through the lining of the digestive tract. Transporter proteins found on cells that line the GI tract help with this process, but for many drugs, it’s unknown which of those transporters they use to exit the digestive tract.
Identifying the transporters used by specific drugs could help to improve patient treatment because if two drugs rely on the same transporter, they can interfere with each other and should not be prescribed together.
Researchers at MIT, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Duke University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] U of T-led study finds positive support from parents and clinicians for pediatric cancer pain management appImplementation and design of digital app will feature recommendations from parents and pediatric cancer care clinicians.