(Press-News.org) New study finds that persistent COVID-19 infections are surprisingly common, with around one to three in every 100 infections lasting a month or longer.
Some persistent infections had a high number of mutations, suggesting they could act as reservoirs to seed new variants of concern.
People with persistent infections lasting for 30 days or longer were 55% more likely to report having Long Covid than people with more typical infections.
Reinfections with the same variant were rare.
A new study led by the University of Oxford has found that a high proportion of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the general population lead to persistent infections lasting a month or more. The findings have been published today in the journal Nature.
It has long been thought that prolonged COVID-19 infections in immunocompromised individuals may have been the source of the multiple new variants that arose during the coronavirus pandemic and seeded successive waves of infection, including the Alpha and Omicron variants. But until now, the prevalence of persistent COVID-19 infections in the general population and how the virus evolves in these situations remained unknown.
To investigate this, the researchers used data from the Office for National Statistics Covid Infection Survey (ONS-CIS), which tested participants approximately monthly. Of the 90,000+ participants, 3,603 provided two or more positive samples between November 2020 to August 2022 where the virus was sequenced. Of these, 381 individuals tested positive with the same viral infection over a period of a month or longer. Within this group, 54 individuals had a persistent infection which lasted at least two months. The researchers estimate that between one in a thousand to one in 200 (0.1-0.5%) of all infections may become persistent, and last for at least 60 days.
In some cases, individuals remained infected with viral variants that had gone extinct in the general population. In contrast, the researchers found that reinfection with the same variant was very rare, likely due to the host developing immunity to that variant and the variant reducing in frequency to very low levels after a few months.
Of the 381 persistent infections, 65 had three or more PCR tests taken over the course of their infection. Most (82%) of these individuals demonstrated rebounding viral dynamics, experiencing high, then low, then high viral load dynamics. According to the researchers, this demonstrates that the virus can maintain the ability to actively replicate during prolonged infections.
In the study, people with persistent infections were 55% more likely to report having Long-COVID symptoms more than 12 weeks since the start of the infection than people with more typical infections.
Certain individuals showed an extremely high number of mutations, including mutations that define new coronavirus variants, alter target sites for monoclonal antibodies, and introduce changes to the coronavirus spike protein. However, most individuals did not harbour a large number of mutations, suggesting that not every persistent infection will be a potential source for new concerning variants.
Co-lead author of the study Dr Mahan Ghafari (Pandemic Sciences Institute, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford) said: ‘Our observations highlight the continuing importance of community based genomic surveillance both to monitor the emergence and spread of new variants, but also to gain a fundamental understanding of the natural history and evolution of novel pathogens and their clinical implications for patients.’
Co-lead author Dr Katrina Lythgoe (Department of Biology and Pandemic Sciences Institute, University of Oxford) said: ‘Although the link between viral persistence and Long Covid may not be causal, these results suggest persistent infections could be contributing to the pathophysiology of Long Covid. Indeed, many other possible mechanisms have been suggested to contribute to Long Covid including inflammation, organ damage, and micro thrombosis.’
Notes for editors:
For media enquiries, contact
Dr Katrina Lythgoe: katrina.lythgoe@biology.ox.ac.uk
Dr Mahan Ghafari: mahan.ghafari@ndm.ox.ac.uk
The study ‘Prevalence of persistent SARS-CoV-2 in a large community surveillance study’ will be published in Nature at 16:00 GMT/ 11:00 ET Wednesday 21 February at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07029-4 The link will go live once the embargo lifts. To view a copy of the study before this under embargo, contact Dr Mahan Ghafari: mahan.ghafari@ndm.ox.ac.uk
About the University of Oxford
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the eighth year running, and number 3 in the QS World Rankings 2024. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and teaching excellence and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 300 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past five years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
END
Study finds high number of persistent COVID-19 infections in the general population
2024-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers reveal mechanism of drug reactivating tumor suppressors
2024-02-21
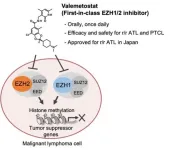
Researchers have revealed the mechanism of a drug shown to be effective in treating certain types of cancer, which targets a protein modification silencing the expression of multiple tumor suppressor genes. They also demonstrated in clinical trials the efficacy of the drug in reducing tumor growth in blood cancer. The findings could lead to longer-term treatments for the disease and therapies for other types of cancer with similar underlying causes.
A team of researchers from the University of Tokyo and their collaborators focused on therapies targeting H3K27me3, a modification on a DNA-packaging histone protein, which plays a large role in regulating ...
UNC Lineberger named as a national research hub for NIH cancer screening study
2024-02-21
CHAPEL HILL, NC – UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center has been selected as one of nine national research sites for the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, newly launched Cancer Screening Research Network (CSRN), which will evaluate promising and emerging cancer screening technologies.
Supporting the Biden-Harris Administration’s Cancer Moonshot initiative, the CSRN will conduct large, multi-center cancer screening studies with diverse populations in a variety of healthcare settings. The studies are designed to identify ...
New study suggests target steps per day for reduced risk of heart failure
2024-02-21
BUFFALO, N.Y. – The science is clear that movement is good for our bodies as we age. But just how much physical activity is beneficial for people over 60? A new study from the University at Buffalo provides an answer, and it’s not 10,000 steps per day.
In fact, the study — published Feb. 21 in JAMA Cardiology — of nearly 6,000 U.S. women aged 63-99 reports that, on average, 3,600 steps per day at a normal pace was associated with a 26% lower risk of developing heart failure.
The observational study from the Women’s Health Initiative ...
NIH launches research network to evaluate emerging cancer screening technologies
2024-02-21
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has launched a clinical trials network to evaluate emerging technologies for cancer screening. The Cancer Screening Research Network (CSRN) will support the Biden-Harris administration’s Cancer Moonshot℠ by investigating how to identify cancers earlier, when they may be easier to treat. Eight groups have received funding from the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of NIH, to carry out the initial activities of the network.
“There are many cancers we still cannot reliably ...
Evidence review: Maternal mental conditions drive climbing death rate in U.S.
2024-02-21
WASHINGTON (Feb. 21, 2024) – Painting a sobering picture, a research team led by Children’s National Hospital culled years of data demonstrating that maternal mental illness is an under-recognized contributor to the death of new mothers. They are calling for urgent action to address this public health crisis in the latest edition of JAMA Psychiatry.
Backed by dozens of peer-reviewed studies and health policy sources, the journal’s special communication comes as maternal mortality soars ...
Scientists from IOCB Prague have improved materials for reconstructive and plastic surgery
2024-02-21
Researchers from IOCB Prague and Ghent University have been working on improving the properties of gelatin-based materials, thereby expanding the possibilities of their use mainly in medicine. In a paper published in ACS Applied Engineering Materials, they have presented 3D-printable materials that can be easily monitored using an X-ray machine or through computed tomography (CT).
Gelatin-based materials have been a hot topic of research in the last ten years because they are straightforward to produce, non-toxic, inexpensive, ...
Nanoscale manipulation of exciton–trion interconversion in a MoSe2 monolayer via tip-enhanced cavity-spectroscopy
2024-02-21
In a significant advancement for next-generation semiconductors, a collaborative research team, led by Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Mingu Kang in the Department of Physics at POSTECH, Professor Yong Doug Suh in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, who concurrently holds the position of Associate Director at the IBS Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM), and Professor Hyun Seok Lee in the Department of Physics at Chungbuk National University, has made groundbreaking discoveries in the field of two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors. Their findings, published in Nano Letters, shed light on the generation and control of trions, providing ...
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy tested for post-covid conditions
2024-02-21
High-dose pressurized oxygen can stress out old immune cells, leaving behind a younger, better functioning immune system. It helped with acute COVID, and now Anders Kjellberg is testing the method for post-covid as well.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, giving patients 100 percent oxygen at a pressure corresponding to 10-20 meters below sea level, has been around for almost 100 years. But the method lacks modern evidence from clinical studies, which also means that there is a lack of knowledge about dosage, all patients receive the same dose.
"When I started my research, I wanted to find out how the treatment should be dosed to different patients," says ...
Revolutionary breakthrough in solar energy: World’s most efficient QD solar cells developed
2024-02-21
A groundbreaking research breakthrough in solar energy has propelled the development of the world’s most efficient quantum dot (QD) solar cell, marking a significant leap towards the commercialization of next-generation solar cells. This cutting-edge QD solution and device have demonstrated exceptional performance, retaining their efficiency even after long-term storage. Led by Professor Sung-Yeon Jang from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, a team of researchers has unveiled ...
New water batteries stay cool under pressure
2024-02-21
A global team of researchers and industry collaborators led by RMIT University has invented recyclable ‘water batteries’ that won’t catch fire or explode.
Lithium-ion energy storage dominates the market due to its technological maturity, but its suitability for large-scale grid energy storage is limited by safety concerns with the volatile materials inside.
Lead researcher Distinguished Professor Tianyi Ma said their batteries were at the cutting edge of an emerging field of aqueous energy storage devices, with breakthroughs that significantly improve the technology’s performance and lifespan.
“What ...