(Press-News.org) Microbially induced corrosion (MIC) is a prevalent issue in marine environments, leading to structural damages such as cracking in concrete infrastructure. This corrosion poses a persistent challenge, significantly reducing the lifespan of marine structures and resulting in substantial economic losses. In response to the need for an effective solution to combat the marine corrosion on concrete, researchers of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University have developed a biomineralization approach to protect marine concrete from MIC.
Prof. Xiang-dong LI, Dean of Faculty of Construction and Environment, Director of Research Institute for Sustainable Urban Development, Chair Professor of Environmental Science and Technology, and Ko Jan Ming Professor in Sustainable Urban Development, has led the research that successfully introduces a novel biomineralization strategy, which effectively isolates marine concrete from MIC, thereby contributing to the achievement of sustainable coastal structures.
MIC on concrete usually occurs in harsh environments with the presence of corrosive microorganisms, such as sewage structures, wastewater treatment plants, and marine structures. The formation of a biomineralized film on concrete surfaces is typically considered to be the major anticorrosion mechanism as it can provide a barrier to inhibit corrosion.
Prof. LI said, “The biomineralization technique serves as an environmentally friendly coating method for controlling concrete corrosion, with minimal impact on the overall biofilm communities. Also, it utilises carbon dioxide to produce mineral precipitates, enhancing the durability of concrete structures. This process not only reduces the carbon footprint and energy consumption of marine infrastructure throughout its lifespan, but also makes a valuable contribution to carbon neutrality and sustainability.”
The study showed the biomineralization treatment effectively prevents corrosion by reducing the total and relative abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB). SRB is a type of anaerobic bacteria and can produce hydrogen sulfide, which is corrosive and can lead to material deterioration.
The biomineralized film acts as a protective layer, controlling sulfate diffusion and isolating the concrete from the corrosive SRB communities. This protective mechanism significantly extends the lifespan of concrete structures. Moreover, this technique has no negative impact on the native marine microbial communities.
Prof. LI added, “If the biomineralized film remains intact, repainting the concrete structures is unnecessary. The utilisation of a single coating treatment eliminates the need for multiple treatments, further minimising the cost and carbon footprint.”
This biomineralization strategy has strong potential for applications in corrosive environments, such as marine environments, sewage environments, and water cooling utilities, where concrete corrosion is induced by corrosive microorganisms.
The research, titled “Biomineralization to prevent microbially induced corrosion on concrete for sustainable marine infrastructure” was published in Environmental Science & Technology. The study employed a combination of chemical and mechanical property measurements of concrete, along with an analysis of the microbial community of biofilms, to evaluate the effectiveness of biomineralization techniques in inhibiting corrosion of marine concrete. These assessments aimed to enhance understanding of MIC development. The results contribute to the development of new techniques for inhabiting corrosion to achieve sustainable marine concrete structures.
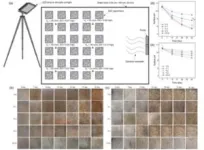
In a sulfate chemical attack, calcium hydroxide and calcium aluminate hydrate will be consumed to form gypsum and ettringite, resulting in expansion stress and matrix fracture (Figure 1a). In an MIC attack, bacteria can colonise the corroded layer, which provides an excellent medium for microorganisms to grow. Microbial activity can extend beyond the corrosion layer near to the surface and spread across the deterioration zone (Figure 1b). Compared with chemical corrosion, MIC causes more severe damage to marine concrete structures. However, the formation of the biomineralized film on the concrete surfaces led to higher surface pH (potential of hydrogen) and lower surface sulfate concentrations, which also acted as a protective layer to control the diffusion of sulfate and isolate the concrete from SRB communities, decreasing internal sulfate levels (Figure 1c).
Considering that the type of colonised surface also affects the treatment effect of biomineralization, the effectiveness of biomineralization will be further investigated for different types of concrete to expand its applicability potential. In addition, the functional prediction can be used in future studies to obtain a mechanistic understanding of the possible metabolic capability of microbial action on concrete corrosion. This understanding is beneficial for uncovering the mystery between SRB and the lifespan of marine concrete structures.
END
PolyU researchers introduce biomineralisation as a sustainable strategy against microbial corrosion in marine concrete
2024-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UBC Okanagan researchers look to the past to improve construction sustainability
2024-02-23
Researchers at UBC Okanagan are revisiting old building practices—the use of by-products and cast-offs—as a way to improve building materials and sustainability of the trade.
A technique known as rammed earth construction uses materials that are alternatives to cement and are often more readily available in the environment. One such alternative is wood fly ash, a by-product of pulp mills and coal-fired power plants, explains Dr. Sumi Siddiqua, with UBC Okanagan’s School of Engineering.
Industry has been trying to find a use for materials like fly ash ...
New study identifies potential gene targets for management of cassava whitefly, key vector of viral diseases threatening African food security
2024-02-23
Whiteflies, particularly the African cassava whitefly (Bemisia tabaci, SSA1-SG1), pose a significant threat to agricultural productivity in Sub-Saharan Africa by transmitting viruses that cause cassava brown streak disease and cassava mosaic virus disease. In a new study published in PeerJ Life & Environment, Dr. Tadeo Kaweesi and his team at the National Agricultural Research Organization identify potential gene targets that could revolutionize the management of this devastating pest and prove vital for food security in the region.
In the article ("In silico prediction of candidate gene targets ...
Twin, the new robotic exoskeleton for lower limbs
2024-02-23
Milan (Italy), 23 February 2024 – TWIN is the name of the new robotic exoskeleton for lower limbs, designed and developed by Rehab Technologies IIT – INAIL, the joint laboratory between the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) and the Prosthetic Center of INAIL (the prosthetic unit of the National Institute for Insurance against Accidents at Work), which will allow patients to wear it more easily. Presented today in Milan during a press conference held at the Museum of Science and Technology, TWIN was demonstrated ...
Mass shooting lockdown drills help schoolchildren feel safer, US study suggests
2024-02-23
Lockdown drills, practiced to help prepare children for shooting incidents at school, make those who have been exposed to violence feel safer – a new study of thousands of students in the US indicates.
The finding, reported in a new peer-reviewed paper published in the Journal of School Violence, contradicts claims that the drills traumatize children, without making them feel safer.
Ensuring that students feel safe – and are safe – in schools is essential for them to learn and thrive, explains ...
Wake-up call for us all to establish regular healthy sleeping patterns
2024-02-23
t’s official. Getting the recommended 7-9 hours of sleep a night is currently out of reach for almost one-third of the population as Flinders University experts found 31% of adults had average sleep durations outside the recommended range.
The global study of thousands of adults published in Sleep Health found only 15% of people slept the recommended 7-9 hours for five or more nights per week – and among those who did achieve an average of 7-9 hours per night over the nine month monitoring period, about 40% ...
Using mussels and silkworm cocoons to stop organ bleeding
2024-02-23
In recent news, there has been a case where a patient experienced pain due to a surgical procedure involving sutures, resulting in the unintended presence of gauze within the patient's body. Gauze is typically employed to control bleeding during medical interventions, aiding in hemostasis. However, when inadvertently left in the body, it can lead to inflammation and infection. Addressing this issue, recent research has been published by researchers focusing on a hemostatic agent derived from mussels and silkworm cocoons. This hemostatic agent has garnered attention in the academic community due to its efficacy in clotting blood and its safety within ...
New research reveals how cancer hijacks immune cells to promote tumour growth
2024-02-23
A new research study led by A*STAR.Singapore Immunology Network (A*STAR.SIgN) has found that neutrophils—one of the most abundant white blood cells in our body—change drastically in certain cancers, adopting a new function whereby they promote tumour growth. By carefully studying neutrophils as soon as they enter the tumour, scientists from A*STAR.SIgN also uncovered ways to accurately differentiate tumour-promoting neutrophils from normal neutrophils present in the rest of the body. Neutrophils play important and irreplaceable roles in fighting infections, ...
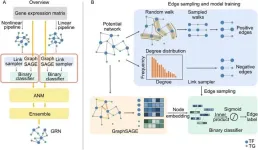
Gene regulatory network inference based on causal discovery integrating with graph neural network
2024-02-23
Gene regulatory networks (GRNs) depict the regulatory mechanisms of genes within cellular systems as a network, offering vital insights for understanding cell processes and molecular interactions that determine cellular phenotypes. Transcriptional regulation, a prevalent type for regulating gene expression, involves the control of target genes (TGs) by transcription factors (TFs). One of the major challenges in inferring GRNs is to establish causal relationships, rather than just correlation, among the various components ...
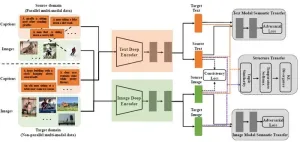
Alignment efficient image-sentence retrieval considering transferable cross-modal representation learning
2024-02-23
Image-sentence retrieval task aims to search images for given sentences and retrieve sentences from image queries. The current retrieval methods are all supervised methods that require a large number of annotations for training. However, considering the labor cost, it is difficult to re-align large amounts of multimodal data in many applications (e.g., medical retrieval), which results in unsupervised multimodal data.
To solve the problem, a research team led by Yang YANG published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and ...
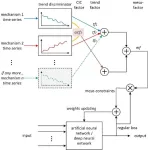
A novel deep learning modeling approach guided by mesoscience—MGDL
2024-02-23
Deep learning modeling that incorporates physical knowledge is currently a hot topic, and a number of excellent techniques have emerged. The most well-known one is the physics-informed neural networks (PINNs). PINN integrates the residuals of the system’s governing partial differential equations (PDEs) and the initial value/boundary conditions into the loss function, thus the resulting model satisfies the constraints of the physical laws represented by the PDEs. However, PINN cannot work if equations among the key physical quantities of the system have not been established. To ...