(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this urban population-based cohort study of 2,180 participants, no modifiable risk factors of mortality at the level of the individual (e.g., depression or anxiety and substance use) or the family (e.g., household education level) were identified. However, the degree of neighborhood poverty in early childhood was significantly associated with death by unnatural causes (death due to unintentional injury, suicide, and homicide) in early adulthood, suggesting that economic policies are needed to advance health equity in relation to premature mortality.
Authors: Holly C. Wilcox, Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0327)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0327?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=022324
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Childhood factors associated with unnatural death through midadulthood
JAMA Network Open
2024-02-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Severe COVID-19 in vaccinated adults with hematologic cancers in the Veterans Health Administration
2024-02-23
About The Study: In this case-control study including 6,122 patients with hematologic cancers and SARS-CoV-2 infection, odds of severe COVID-19 remained high through mid-2022 despite vaccination, especially in patients requiring treatment.
Authors: Paul A. Monach, M.D., Ph.D., of the VA Boston Cooperative Studies Program in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0288)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Recreational marijuana legalization and workplace injuries among younger workers
2024-02-23
About The Study: In this study, recreational marijuana laws that allow recreational marijuana sales were associated with a 10% increase in workplace injuries among individuals ages 20 to 34. The findings are consistent with the hypothesis that recreational marijuana impedes cognitive function and care among younger workers.
Authors: Joseph J. Sabia, Ph.D., of San Diego State University, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
New study identifies 13 strategies for advancing racial and ethnic equity in the academic health sciences
2024-02-23
BOSTON - Amid continued debate over how to advance diversity and equity in higher education following the Supreme Court’s decision striking down affirmative action, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital and Northeastern University today issued a “roadmap” of strategies to help academic health institutions maintain their commitments to racial and ethnic diversity among their students, staff, and faculty in academic health sciences.
Their recommendations, published in JAMA Health Forum, outline 13 evidence-based strategies for increasing racial and ethnic equity in graduate-level health programs.
“This ...
School focus on grades, test scores linked to violence against teachers
2024-02-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Violence against teachers is likely to be higher in schools that focus on grades and test scores than in schools that emphasize student learning, a new study has found.
Researchers surveyed over 9,000 U.S. teachers shortly before and during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic about their perception of the instructional emphasis in their schools. Participants also reported whether they had been subjected to physical, verbal or property violence – by students, parents, colleagues and/or administrators.
Results ...
Genetic signature may predict response to immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer
2024-02-23
A new study identified a set of 140 genes that may help predict enhanced disease-free survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with a combination of immunotherapy and low-dose radiation. The results, published in Cell Reports Medicine on Feb. 23, suggested that this “gene signature” could be used to identify a subclass of lung tumors that is more likely to be eradicated by immunotherapies.
Immunotherapy has saved countless lives but only 20 to 25 percent of patients respond to this treatment that activates a person’s ...
A study by the UMA and the University of California analyzes how lies affect economic decisions
2024-02-23
Psychology and Economics come together in a recent line of research, led by Ismael Rodríguez-Lara, Professor at the University of Malaga, who studies how lies affect economic decisions.
It is a study developed together with the Professor at the University of California (Santa Barbara, USA) Gary Charness, considered one of the most influential economists in the world within the experimental area, that has analyzed the way in which morality influences the degree of lying in certain economic situations. The results of this research have been published in the scientific journal Economics ...
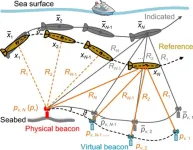
Navigating the depths: Exploration in underwater navigation using acoustic beacons
2024-02-23
New exploration in underwater navigation, a team from the Naval University of Engineering in Wuhan, China, has created novel algorithms that rectify inertial errors using sparse acoustic signals. This exploration offers novel method for the issue of underwater navigation , where traditional satellite systems are ineffective due to their signals' inability to penetrate water effectively.
The increasing demand for precise underwater Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) due to expanding marine exploration and activities highlights the limitations of traditional Global Satellite Navigation Systems (GNSS) ...
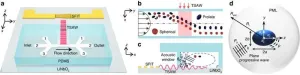
Shaping the future: A new technique for sorting micro-particles unveiled
2024-02-23
Thanks to the rapid progress in tiny tech, we've been mainly using microfluidics to sort tiny particles by size. But now, there's a new way to sort them by shape, which could be a big deal for medical tests and chemistry. This study shows off a new method using sound waves to separate oddly shaped particles from round ones, without needing any labels. This breakthrough could lead to better ways to deliver drugs or diagnose diseases by offering a smarter approach to sort these tiny particles.
In the realm of microfluidics, separating micro-particles based solely on size has been the norm. However, distinguishing these particles ...
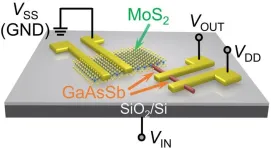
Mixed-dimensional transistors enable high-performance multifunctional electronic devices
2024-02-23
Downscaling of electronic devices, such as transistors, has reached a plateau, posing challenges for semiconductor fabrication. However, a research team led by materials scientists from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) recently discovered a new strategy for developing highly versatile electronics with outstanding performance, using transistors made of mixed-dimensional nanowires and nanoflakes. This innovation paves the way for simplified chip circuit design, offering versatility and low power dissipation in future electronics.
In recent decades, as ...
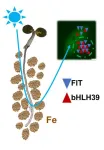
Biomolecular condensates – regulatory hubs for plant iron supply
2024-02-23
Iron is a micronutrient for plants. Biologists from the Institute of Botany at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) describe in a study, which has now been published in the Journal of Cell Biology, that regulatory proteins for iron uptake behave particularly dynamically in the cell nucleus when the cells are exposed to blue light – an important signal for plant growth. They found that the initially homogeneously distributed proteins relocated together into “biomolecular condensates” in the cell nucleus shortly after this exposure.
Both iron deficiencies and excesses are problematic for plants. They ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
[Press-News.org] Childhood factors associated with unnatural death through midadulthoodJAMA Network Open