(Press-News.org) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue in JMIR Neurotechnology exploring brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) that represent the transformative convergence of neuroscience, engineering, and technology. The peer-reviewed journal aims to bridge the gap between clinical neuroscience and information technology by providing a platform for applied human research in the field of neurology.
JMIR Neurotechnology welcomes submissions from scientists, clinicians, and technologists. PhD students and early career researchers are also encouraged to submit. This theme issue invites original contributions on topics that include but are not limited to the following:
Novel BCI technologies, such as optogenetics, augmented reality, and synthetic telepathy
Clinical applications of BCIs in neurological disorders such as epilepsy, Parkinson disease, and stroke
Applications of BCIs in neurorehabilitation and epilepsy
Human-computer interaction, including user-centered design, usability, and accessibility
Machine learning and signal processing for BCIs
Ethical, legal, and social issues involved in the use of BCIs, such as data ownership, cybersecurity, and brain hacking
Neuroplasticity, neurofeedback, and BCI training
BCIs for augmentative and alternative communication
Submit Now
For a limited time only, JMIR Neurotechnology is offering a 50% article processing fee discount on all manuscripts accepted for publication with the use of a valid promo code. For more information, please visit https://neuro.jmir.org/about-journal/article-processing-fees.
Please visit our website for more information on submission guidelines and the peer-review process.
About JMIR Publications:
JMIR Publications is a renowned publisher with a long-standing commitment to advancing digital health research and progressing open science. Our portfolio includes a wide array of prestigious open access, peer-reviewed journals dedicated to the dissemination of high-quality research in the field of digital health. JMIR Publications is celebrating its 25th anniversary in 2024 as the leading open access, digital health publisher.
END
JMIR Neurotechnology invites submissions on brain-computer interfaces (BCIs)
2024-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
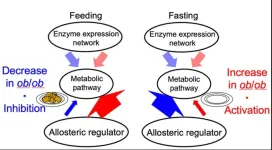
Obesity disrupts normal liver function in mice
2024-02-26
Your liver plays a vital role in your metabolism, the biological process which converts food into energy. We know that being overweight can negatively affect metabolic activity, but not exactly how. To better understand this, researchers compared the livers of mice which were a typical weight with mice which were obese. They were surprised to find that biological regulation of metabolic activity, after a period of feasting and fasting, was reversed between them. In typical mice, allosteric regulation (the process which controls metabolism) was inhibited during feeding and activated when fasting. However, ...
Watch these predatory fish use rapid color changes to coordinate attacks
2024-02-26
Striped marlin are some of the fastest animals on the planet and one of the ocean’s top predators. When hunting in groups, individual marlin will take turns attacking schools of prey fish one at a time. Now a new study reported in the journal Current Biology on February 5 helps to explain how they might coordinate this turn-taking style of attack on their prey to avoid injuring each other. The key, according to the new work, is rapid color changes.
“We documented for the first time rapid color change in a group-hunting predator, the striped marlin, as groups of marlin hunted schools of sardines,” says Alicia Burns of Humboldt University ...
Metal scar found on cannibal star
2024-02-26
When a star like our Sun reaches the end of its life, it can ingest the surrounding planets and asteroids that were born with it. Now, using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT) in Chile, researchers have found a unique signature of this process for the first time — a scar imprinted on the surface of a white dwarf star. The results are published today in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
“It is well known that some white dwarfs — slowly cooling embers of stars like our Sun — are ...
Treating adolescent opioid use disorder in primary care
2024-02-26
About The Study: This survey study found that primary care pediatricians felt less prepared to manage adolescents’ opioid use disorder (OUD) than alcohol, cannabis, or e-cigarette use and were more likely to refer them to offsite care. These results reveal an opportunity for greater workforce training in line with a 2019 survey showing fewer than 1 in 3 pediatric residency programs included education on prescribing OUD medications.
Authors: Scott E. Hadland, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., of Mass General for Children in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The ...
Use of tobacco products and suicide attempts among elementary school–aged children
2024-02-26
About The Study: The findings of this study of 8,988 preadolescent children suggest that the increased risk of suicide attempts, consistently reported for adolescents and adults who smoke cigarettes, extends to a range of emerging tobacco products and manifests among elementary school–aged children. Further investigations are imperative to clarify the underlying mechanisms and to implement effective preventive policies for children.
Authors: Phil H. Lee, Ph.D., of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Study of 1.2+M births in Sydney, Australia reveals associations between excess heat exposure and preterm births
2024-02-26
In the face of increasing temperatures globally, a new Monash-led study of 1.2 million births in Sydney over two decades has shown a strong association between the risk of pre-term birth and exposure to extreme hot temperatures in the third trimester of pregnancy. The data suggested that this association with extreme temperature might be reduced by the level of greenery in a pregnant person’s residential surrounds.
The findings suggest health services should consider preparing for an increase in preterm births as our climate warms.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, looked at the relationship ...
Blindness from some inherited eye diseases may be caused by gut bacteria
2024-02-26
Sight loss in certain inherited eye diseases may be caused by gut bacteria, and is potentially treatable by antimicrobials, finds a new study in mice co-led by a UCL and Moorfields researcher.
The international study observed that in eyes with sight loss caused by a particular genetic mutation, known to cause eye diseases that lead to blindness, gut bacteria were found within the damaged areas of the eye.
The authors of the new paper, published in Cell and jointly led by researchers in China, say their findings suggest that the genetic mutation may relax the body’s defences, thus allowing harmful bacteria to reach the eye and cause blindness.
The gut contains trillions ...
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis articles provide novel insights into previously unknown disease mechanisms
2024-02-26
DCM is the leading cause of heart failure in patients with chronic diabetes. However, the underlying mechanisms of DCM are poorly understood, and treatment options are limited. Another mystery is the regulation of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) in the central nervous system. Moreover, the link between the gut microbiome, microbiota-derived metabolites, and the progression of AD remains unknown. In the December issue of JPA, three articles provide insights into the pathologies of DCM, hippocampal neurotoxicity, and AD, providing a comprehensive ...
Enhancing electrogenerated chemiluminescence of an iridium complex
2024-02-26
Electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) cells, characterized by their self-emissive nature, have gathered significant interest for prospective display applications due to their uncomplicated structure and straightforward fabrication process. These cells are created by sandwiching a solution-based emitting layer between two transparent electrodes. Nevertheless, when compared to other self-emissive devices like light-emitting diodes (LED) and organic LEDs, the luminescent performance of ECL cells ...
The structure of HSV-1 gB bound to a potent neutralizing antibody reveals a conservative antigenic domain across herpesviruses
2024-02-26
Human herpesviruses comprise the alpha, beta, and gamma subfamilies and are a widely prevalent group of DNA-enveloped viruses, capable of establishing lifelong latent infections in humans and causing various diseases. Among them, herpes simplex virus (HSV) belongs to the alpha herpesvirus group and infects a wide population, causing symptoms like oral or genital herpes. As an enveloped virus, HSV possesses a series of glycoproteins involved in virus recognition, adhesion, and infection processes. Among these, gB serves as the viral fusion protein, mediating the fusion between the virus and host cell membranes, and ...