Using multimodal deep learning to detect malicious traffic with noisy labels
2024-02-27
(Press-News.org)
The success of a deep learning-based network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) relies on large-scale, labeled, realistic traffic. However, automated labeling of realistic traffic, such as by sand-box and rule-based approaches, is prone to errors, which in turn affects deep learning-based NIDS.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Yuefei ZHU published their new research on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
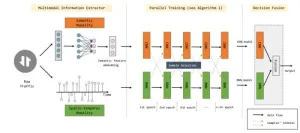
The team proposed MMCo, a Co-teaching-like method using multimodal information and parallel, heterogeneous networks to detect malicious traffic with noisy labels. Unlike existing methods, (1) MMCo is the first LNL method that uses multimodality to maintain disagreement; and (2) the parallel networks in MMCo are heterogeneous and input different modalities of samples, which can mitigate self-control degradation and enhance robustness.
In the research, they choose CNN and RNN to learn semantic and spatio-temporal modal information from the traffic. In each mini-batch, CNN and RNN are fed with different modalities of the same subset. CNN and RNN select for each other the samples they consider more important, i.e., the samples with different distinguish or less loss among all mini-batches. Only these samples will be used for updating the parameters of the networks. The experimental results show that MMCo can maintain a higher disagreement compared with the existing methods, thus helping the classifiers to learn more correct knowledge, with about 10% higher accuracy.
Future work can focus on investigating the analysis of the representations of two networks in multimodal networks using explainable artificial intelligence, which may help identify and clean malicious traffic with noisy labels.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-2386-4
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-02-27
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) reveal that the Snhg11 gene is critical for the function and formation of neurons in the hippocampus. Experiments with mice and human tissues revealed the gene is less active in brains with Down syndrome, potentially contributing to the memory deficits observed in people living with the condition. The findings are published today in the journal Molecular Psychiatry.
Traditionally, much of the focus in genomics has been on protein-coding genes, which in humans constitutes around just 2% of the entire genome. The rest is "dark ...
2024-02-27
In The BMJ today, Keisha Bentley-Edwards at Duke University, North Carolina, and colleagues argue that systemic racism and economic inequality are at the root of disparity in covid-19 outcomes and suggest how to distribute resources more equitably.
The article is part of a series that highlights the lessons that can be learned from the US’s covid-19 experience and the actions that are needed to prevent the loss of another million citizens in the next pandemic and improve and protect population health.
"Rather than waiting for the next pandemic to address systemic failures, the ...
2024-02-27
A group led by researchers at Nagoya University and Meijo University in Japan has developed a disinfection technology that uses low-temperature plasma generated by electricity to cultivate environmentally friendly hydroponically grown crops. This innovative technology sterilizes the crops, promoting plant growth without the use of chemical fertilizers. Their findings appeared in Environmental Technology & Innovations.
In hydroponic agriculture, farmers cultivate plants by providing their roots with a nutrient solution. However, the nutrient solution can become infected with pathogenic E. coli strains, contaminating the crop and leading to foodborne illnesses.
To avoid ...
2024-02-27
Two major studies part-funded by Cancer Research UK reveal that the use of chemotherapy and radiotherapy in the UK has lagged behind comparable countries in the past decade
Patients faced longer waits to begin key cancer treatment, which could be impacting people’s chances of survival in the UK
With an upcoming UK general election, Cancer Research UK is calling on political leaders to step up and ensure patients get the level of care that they deserve
People in the UK were treated with chemotherapy ...
2024-02-27
The mechanisms by which antidepressants and other emotion-focused medications work could be reconsidered due to an important new breakthrough in the understanding of how the gut communicates with the brain.
New research led by Flinders University has uncovered major developments in understanding how the gut communicates with the brain, which could have a profound impact on the make-up and use of medications such as antidepressants.
“The gut-brain axis consists of complex bidirectional neural communication pathway between the brain and the gut, which links emotional and cognitive ...
2024-02-27
In response to the rapidly evolving landscape of data collection and analysis driven by advances in artificial intelligence, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) have established a Research Coordination Network (RCN) dedicated to advancing privacy research and the development, deployment and scaling of privacy enhancing technologies (PETs). Fulfilling a mandate from the "Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence," the initiative advances the recommendations in the National Strategy to Advance ...
2024-02-27
Allyship — the practice of relatively advantaged group members acting with the intention to support, advocate and improve circumstances for relatively disadvantaged groups — is critical to promoting more inclusive and equitable organizations.
Not only are advantaged group members typically received more favorably within an organization than disadvantaged group members would be when they speak out against injustice, their allyship can improve disadvantaged group members’ psychological experience in the organization. For instance, men are more likely to believe other men, compared with women, when they confront sexism. And Black Americans report higher levels of self-esteem ...
2024-02-26
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Dean Mark T. Gladwin, MD, announced today that UMSOM faculty scientists have been selected as key contractors by the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), for the federal agency’s Radiation Nuclear Animal Model Development program. The $3.5 million award that Erika Davies, PhD, Assistant Professor of Radiation Oncology, received to develop Acute Radiation Syndrome Animal Models, has a $16 million potential total. The Division of Translational Radiation Sciences (DTRS), within the Department of Radiation Oncology, will support this project.
Dr. Davies and her colleagues ...
2024-02-26
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have shown for the first time that expensive aberration-corrected microscopes are no longer required to achieve record-breaking microscopic resolution.
The field of microscopy is in the middle of a great revolution. Since the 1800s and the invention of the compound light microscope, there have only been a few major jumps in resolution to see different length scales: from bacteria and cells, to viruses and proteins, and even down to single atoms. Generally, ...
2024-02-26
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ACP Recommends Ways to Better Meet the Health Care ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Using multimodal deep learning to detect malicious traffic with noisy labels