(Press-News.org) University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Dean Mark T. Gladwin, MD, announced today that UMSOM faculty scientists have been selected as key contractors by the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), for the federal agency’s Radiation Nuclear Animal Model Development program. The $3.5 million award that Erika Davies, PhD, Assistant Professor of Radiation Oncology, received to develop Acute Radiation Syndrome Animal Models, has a $16 million potential total. The Division of Translational Radiation Sciences (DTRS), within the Department of Radiation Oncology, will support this project.
Dr. Davies and her colleagues are working with BARDA to advance the development of radiologic and nuclear countermeasures. This is part of a broader effort to enhance national preparedness for radiation accidents and emergencies. “We’re trying to develop and test new treatments that can be used in a terror attack scenario that involves high radiation exposure,” said Dr. Davies. “We are developing robust animal models that will translate well to humans.”
BARDA is part of the Office of the Secretary for Preparedness and Response in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS).
Currently, relatively few medical treatments are available to counter radiological and nuclear threats as FDA approval requires extensive preclinical efficacy and safety data to support drug approval. Many more such agents are needed, based on the range of options that could be employed by terrorists, the need for urgent intervention following radiation exposure, and the medical complexities of acute and chronic radiation injury.
“The DTRS is uniquely positioned to provide leading expertise in medical countermeasures research,” said William Regine, MD, the Isadore & Fannie Schneider Foxman Chair of Radiation Oncology at UMSOM. “We are bridging first-in-class radiation science with contract research to increase the likelihood of survival in a radiation or nuclear incident, while simultaneously identifying a potential new class of therapeutics for cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy.”
Almost a decade ago research by DTRS faculty and staff led to the approval of the first drug to treat the deleterious effects of radiation exposure following a nuclear incident based on efficacy data generated in animal models. Animal models are especially important in preparing for radiation emergencies, because the efficacy of most experimental treatments cannot be tested in humans.
“DTRS is able to develop different experimental models through its world class ‘Good Laboratory Practice’-compliant testing facility, which houses one of the nation’s most well-equipped suites of technologies supporting radiation research,” said Dr. Gladwin who is the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean of UMSOM, and Vice President for Medical Affairs at University of Maryland, Baltimore. “Our faculty’s collaborative expertise from across the broadest spectrum of countermeasure investigations, allow the rapid configuration and implementation of solutions-oriented approaches to even the most difficult challenges.”
The work with BARDA will include multiple individual projects that draw on changing configurations of DTRS experts, instrumentation, and specialized resources, as well as on collaborations with other UMSOM and University of Maryland, Baltimore investigators.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic, and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has more than $500 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2023, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #10 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 16 percent (#32) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu
END
UM School of Medicine awarded $3.5 million in federal funding to expand medical countermeasures program
2024-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
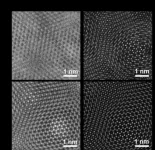
Reimagining electron microscopy: Bringing high-end resolution to lower-cost microscopes
2024-02-26
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have shown for the first time that expensive aberration-corrected microscopes are no longer required to achieve record-breaking microscopic resolution.
The field of microscopy is in the middle of a great revolution. Since the 1800s and the invention of the compound light microscope, there have only been a few major jumps in resolution to see different length scales: from bacteria and cells, to viruses and proteins, and even down to single atoms. Generally, ...
ACP recommends ways to better meet the health care and social needs of unhoused populations
2024-02-26
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ACP Recommends Ways to Better Meet the Health Care ...
University of Technology Sydney chooses Figshare to drive the discoverability of non-traditional research outputs
2024-02-26
Figshare, a leading provider of institutional repository infrastructure that supports open research, is pleased to announce that the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) has chosen Figshare to support them in sharing, showcasing and managing their research reports and non-traditional research outputs.
UTS – Australia’s leading technology university – will use its Figshare repository and its integration with the Australian Research Data Commons Datacite DOI minting service to drive the discoverability and increase the impact of their research reports and non-traditional research outputs, ...
Five grand challenges for the future at the interface of engineering and medicine
2024-02-26
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Just imagine this, the creation of:
An artificially intelligent machine that acts as a human exocortex, a system that will interface with and make an old brain tick normally.
Human cells that can sense metastatic cancer or the boundaries of solid tumors and respond with killing of tumor cells, release of inflammatory payloads or bioluminescence to help guide surgical removal.
Manufactured vaccines that prevent or impede a cancer, block opioid action or reverse autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis.
These are a few of the far-reaching ideas put forward by 50 international biomedical engineering ...
Australian researcher's journey from kangaroo whisperer to global dance sensation
2024-02-26
Dr Weliton Menário Costa, a PhD graduate from The Australian National University (ANU), has been announced the overall winner of the 2024 global Dance Your PhD contest after wowing judges with his wickedly creative and quirky dance submission, ‘Kangaroo Time (Club Edit)’.
One of the world's leading researchers in kangaroo behaviour, he is the first person from ANU to win the Dance Your PhD competition, and just the fourth person from an Australian institution to do so since its inception in 2008.
Better known as ‘WELI’, the singer-songwriter, creator and biologist weaves together a funky beat, original songwriting, drag queens and Brazilian funk dancers ...
Black carbon sensor could fill massive monitoring gaps
2024-02-26
Black carbon is the most dangerous air pollutant you’ve never heard of. Its two main sources, diesel exhaust and wood smoke from wildfires and household heating, produce ultrafine air particles that are up to 25 times more of a health hazard per unit compared to other types of particulate matter. Despite its danger, black carbon is understudied due to a lack of monitoring equipment. Regulatory-standard sensors are wildly expensive to deploy and maintain, resulting in sparse coverage in regions infamous for poor air quality, such as the greater Salt Lake City metropolitan area in Utah.
A University of Utah-led study found that the AethLabs ...
UC Irvine advances stem cell research with $4 million CIRM grant for shared resources lab
2024-02-26
Irvine, Calif., Feb. 26, 2024 — The University of California, Irvine has received a five-year, $4 million grant from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine to establish a shared resources lab in the Sue & Bill Gross Stem Cell Research Center. The facility will offer essential technologies and training for the development of novel in vitro stem cell-based modeling that will serve researchers across the campus and the state.
“Stem cells possess the potential to transform into particular cell types, offering promising avenues for rejuvenating and restoring tissues harmed by injury or affected ...
New discovery suggests significant glacial retreat in West Antarctica began in 1940s
2024-02-26
Among the vast expanse of Antarctica lies the Thwaites Glacier, the world’s widest glacier measuring about 80 miles on the western edge of the continent. Despite its size, the massive landform is losing about 50 billion tons of ice more than it is receiving in snowfall, which places it in a precarious position in respect to its stability.
Accelerating ice loss has been observed since the 1970s, but it is unclear when this significant melting initiated – until now. A new study published in the journal PNAS, led by researchers ...
Butterflies mimic each other’s flight behaviour to avoid predators
2024-02-26
Researchers have shown that inedible species of butterfly that mimic each others’ colour patterns have also evolved similar flight behaviours to warn predators and avoid being eaten.
It is well known that many inedible species of butterfly have evolved near identical colour patterns, which act as warning signals to predators so the butterflies avoid being eaten.
Researchers have now shown that these butterflies have not only evolved similar colour patterns, but that they have also evolved similar ...
What math tells us about social dilemmas
2024-02-26
Human coexistence depends on cooperation. Individuals have different motivations and reasons to collaborate, resulting in social dilemmas, such as the well-known prisoner's dilemma. Scientists from the Chatterjee group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now present a new mathematical principle that helps to understand the cooperation of individuals with different characteristics. The results, published in PNAS, can be applied to economics or behavioral studies.
A group of neighbors shares a driveway. Following a heavy snowstorm, the entire driveway is covered in snow, requiring clearance for daily activities. ...