(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 28, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – For children and teens, irregular meals such as skipped breakfasts are linked to an increased risk of frequent headaches, according to a new study published in the February 28, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study also found that for those ages 12 to 17, substance use and exposure, specifically electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), were associated with frequent headaches.
For the study, frequent headaches were defined as occurring more than once per week.
“It is not uncommon for children and teens to have headaches, and while medications are used to stop and sometimes prevent headaches, lifestyle changes may also offer an effective route to relief by preventing headaches from happening and improving quality of life,” said study author Serena L. Orr, MD, MSc, of the University of Calgary in Canada and a member of the American Academy of Neurology.
The study included nearly 5 million children and teens, ages five to 17, who were enrolled in a large Canadian health survey. They were asked if they had experienced headaches over the previous six months and how often. Approximately 6% of participants had headaches more than once a week.
The survey asked about several lifestyle factors including screen time, sleep hours and meals. Anxiety and mood disorders were assessed. Participants ages 12 to 17 were also asked about substance use and exposure.
For meals, participants reported how many times over the past week they ate breakfast and how often they sat down to eat dinner with their family, for a total of 14 possible meals. Those who experienced frequent headaches had an average of nine such meals compared to an average of 12 meals for kids who had one or fewer headaches a week.
After adjusting for factors such as age, sex, household income and the other lifestyle factors, researchers found that participants who regularly ate breakfast as well as dinners with their family had an 8% lower risk of frequent headaches than those who did not eat regular meals.
Participants ages 12 to 17 were also asked how often they used substances like alcohol, cigarettes, e-cigarettes and cannabis. E-cigarettes were used daily by 8% of participants with frequent headaches compared to 3% of participants with one or fewer headaches per week. Also, 79% of participants with frequent headaches had not used e-cigarettes in the past month compared to 88% of those who did not have frequent headaches.
After adjustments for age, sex, household income, and the other lifestyle factors, researchers found those who used e-cigarettes daily had double the odds of frequent headaches compared to those who never used e-cigarettes.
After similar adjustments, researchers did not find links to headaches for sleep, screen time and other substance use.
Participants with anxiety and mood disorders had twice the risk of frequent headaches as those without.
“We assessed anxiety and mood disorders because they have been linked to headaches and may impact lifestyle behaviors,” said Orr. “It is possible regular family meals may lead to greater connectedness and communication within the family, and better mental health outcomes, which in turn may impact headache frequency.”
Orr added, “Our findings suggest that asking about lifestyle factors such as substance abuse may help medical professionals identify lifestyle interventions that may be helpful to young people and may help to reduce frequent headaches.”
A limitation of the study was it did not include children and teens living in foster homes, institutions or on First Nation reserves and other Indigenous settlements in Canada.
Learn more about headache at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
For young people, irregular meals, e-cigarette use linked to frequent headaches
Study Also Found Increased Risk for Those with Anxiety, Mood Disorders
2024-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study finds link between health care disparities and stroke treatment
2024-02-28
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 28, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – For people with stroke, social factors such as education, neighborhood and employment, may be linked to whether they receive treatment with clot-busting drugs according to a preliminary study released today, February 28, 2024, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 76th Annual Meeting taking place April 13–18, 2024, in person in Denver and online. The study looked at people with ischemic stroke, which ...
Prognostic model development and molecular subtypes identification in bladder urothelial cancer
2024-02-28
“Our study introduces an oxidative stress-based prognostic model for bladder cancer, offering insights into personalized therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 28, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “Prognostic model development and molecular subtypes identification in bladder urothelial cancer by oxidative stress signatures.”
Mounting studies indicate that oxidative stress (OS) significantly ...
Study proposes streamlined approach to developing cancer drugs
2024-02-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. — Drug discovery can be a frustrating process of trial and error.
Scientists using fragment-based drug discovery link fragments of different molecules together to create a more potent drug but may not know whether a compound works until millions of dollars in research and development have already been spent.
New University at Buffalo research may offer a more streamlined approach, allowing drug makers to determine the viability of a fragment-based design earlier in the process.
While developing a fragment-based drug to treat lung cancer, a team co-led by UB found that where they linked fragments together had a large effect on potency.
“Despite ...
New study finds high-dose inhaled nitric oxide decreases the risk of death among critically ill Black patients with COVID-19
2024-02-28
In a first-of-its-kind study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, physician-scientists from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine discovered that high-dose inhaled nitric oxide therapy may improve oxygenation and reduce the risk of mortality among critically ill Black patients with COVID-19.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS, is a condition that most commonly occurs in the setting of a lung infection such as COVID-19.
“In ARDS, the barrier between the blood vessels and air sacs in the lungs is disrupted leading to the accumulation of fluid ...
Ochsner Digital Medicine Partners with Humana Healthy Horizons
2024-02-28
New Orleans, LA. – Ochsner Digital Medicine has partnered with Humana Healthy Horizons to provide digital medicine services to its members. This agreement was effective February 1, 2024, with member enrollment in digital programs available immediately after.
Humana Healthy Horizons is Humana’s Medicaid plan for Louisiana, covering thousands of members throughout the state. Through this partnership, Ochsner Digital Medicine will offer Humana Healthy Horizons members who have been diagnosed with Hypertension and Type 2 diabetes remote programs designed to manage and control their conditions.
The programs use remote patient management through digital devices and personalized ...
Vision Zero road safety projects in Seattle are unlikely to have negative impacts on local business sales, UW study finds
2024-02-28
Seattle is routinely listed as one of the most walkable and bike-friendly cities in the nation. The city government has committed to Vision Zero, which aims to completely eliminate traffic deaths and serious injuries by 2030, and embarked on a slew of infrastructure projects: expanding the city’s bike network, redesigning high-crash intersections and enhancing crosswalks to protect pedestrians.
Such safety projects sometimes meet opposition from local business owners, who worry that reduced parking and disruption ...
African great apes predicted to see frequent extreme climate events in the next 30 years
2024-02-28
African apes are already being exposed to climate change impacts, and will experience extreme events such as wildfires, heatwaves and flooding more frequently in the next 30 years, according to a study publishing February 28 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Razak Kiribou at Haramaya University in Ethiopia and colleagues.
To better understand how African great apes will be affected by climate change, researchers investigated past and future climate for 363 sites across Africa. They estimated temperature and rainfall at each site between 1981 and 2010. Using two climate change scenarios, they projected how frequently apes would be exposed to climate change impacts in the near ...
EU countries have seen a decade of progress towards their 2030 sustainable energy goal
2024-02-28
Countries in the European Union (EU) have made progress over the past decade toward Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7), which calls for “access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all” by 2030, according to a study published February 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marek Walesiak from Wroclaw University of Economics and Business, Poland, and Grażyna Dehnel from Poznań University of Economics and Business, Poland.
In 2015, the United Nations developed 17 global Sustainable Development Goals to be achieved by 2030. Tenets of SDG 7 include universal access to affordable energy; increased renewable energy ...
Climate change threatens thousands of archaeological sites in coastal Georgia
2024-02-28
Thousands of historic and archaeological sites in Georgia are at risk from tropical storm surges, and that number will increase with climate change, according to a study published February 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Matthew D. Howland and Victor D. Thompson of Wichita State University and the University of Georgia.
Anthropogenic climate change poses a major risk to coastlines due to rising sea level and increasingly severe tropical storms. This threatens not only living populations but also historic and archaeological sites. Mitigating damage requires accurate assessments of risks, but most predictive models focus on projected ...
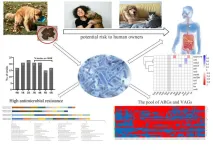
Pet dogs with diarrhea may be shedding multi-drug resistant E.coli in 5 in 10 cases, with potential risks to their human owners
2024-02-28
Pet dogs with diarrhea may be shedding multi-drug resistant E.coli in 5 in 10 cases, with potential risks to their human owners
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0298053
Article Title: Characteristics of MDR E. coli strains isolated from Pet Dogs with clinic diarrhea: A pool of antibiotic resistance genes and virulence-associated genes
Author Countries: China
Funding: This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0500900, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
[Press-News.org] For young people, irregular meals, e-cigarette use linked to frequent headachesStudy Also Found Increased Risk for Those with Anxiety, Mood Disorders