(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 28, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – For people with stroke, social factors such as education, neighborhood and employment, may be linked to whether they receive treatment with clot-busting drugs according to a preliminary study released today, February 28, 2024, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 76th Annual Meeting taking place April 13–18, 2024, in person in Denver and online. The study looked at people with ischemic stroke, which is caused by a blockage of blood flow to the brain and is the most common type of stroke.
“Any barriers that prevent people with stroke from receiving clot-busting drugs, known as thrombolytic therapy, can result in devastating consequences,” said study author Chanaka Nadeeshan Kahathuduwa, MD, PhD, MPhil, of Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center in Lubbock and a member of the American Academy of Neurology. “Our study found that a number of factors like race, insurance status, where a person lives, and other social determinants of health impacted whether a person received this crucial treatment.”
The study involved 63,983 people with ischemic stroke identified through public health records in Texas. For race and ethnicity, 67% of participants were white, 18% were Black and 27% were Hispanic, with some participants having more than one race and ethnicity.
Researchers determined that 7,198, or 11%, received clot-busting drugs.
Researchers then looked at social factors that may impact a person’s health, such as income, education, housing, and access to health services. To rank participants based on these factors, they used U.S. Census data and applied a measure called the Social Vulnerability Index. They divided participants into four groups.
Among the 7,930 people in the group identified as having the least disadvantage, 1,037 received clot-busting drugs. Among the 7,966 people in the group identified as having the most disadvantage, 964 received clot-busting drugs.
After adjusting for age, sex and education, researchers found that those with the least disadvantage were 13% more likely to receive clot-busting drugs than those in the other groups.
When looking specifically at race and ethnicity, Black people were 10% less likely to receive this therapy than white people. Hispanic people were 7% less likely to receive this therapy than non-Hispanic people.
When looking at insurance coverage, researchers found that those who were on Medicare, Medicaid or Veterans Assistance and those who were uninsured were 23% and 10%, respectively, less likely to receive clot-busting drugs than those with private insurance.
After looking at location, researchers found that participants who lived in rural areas were 40% less likely to receive the treatment than those living in urban areas.
“Our results are concerning and shed light on health care disparities,” said Kahathuduwa. “This study demonstrates how social disadvantages may translate to worse stroke care. Further studies are needed to investigate this connection between society, the health care system, and stroke outcomes. Finding new approaches to address these social factors is imperative for improving equity in stroke care and recovery.”
Kahathuduwa noted that clot-busting drugs must be administered within a few hours after the onset of stroke symptoms. A limitation of the study was that it is unknown how many of participants were seen at the hospital within that timeframe and thus eligible to receive the treatment.
Learn more about stroke at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, X and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the American Academy of Neurology’s Annual Meeting hashtag #AANAM.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, X, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
New study finds link between health care disparities and stroke treatment
2024-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Prognostic model development and molecular subtypes identification in bladder urothelial cancer
2024-02-28
“Our study introduces an oxidative stress-based prognostic model for bladder cancer, offering insights into personalized therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 28, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 3, entitled, “Prognostic model development and molecular subtypes identification in bladder urothelial cancer by oxidative stress signatures.”
Mounting studies indicate that oxidative stress (OS) significantly ...
Study proposes streamlined approach to developing cancer drugs
2024-02-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. — Drug discovery can be a frustrating process of trial and error.
Scientists using fragment-based drug discovery link fragments of different molecules together to create a more potent drug but may not know whether a compound works until millions of dollars in research and development have already been spent.
New University at Buffalo research may offer a more streamlined approach, allowing drug makers to determine the viability of a fragment-based design earlier in the process.
While developing a fragment-based drug to treat lung cancer, a team co-led by UB found that where they linked fragments together had a large effect on potency.
“Despite ...
New study finds high-dose inhaled nitric oxide decreases the risk of death among critically ill Black patients with COVID-19
2024-02-28
In a first-of-its-kind study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, physician-scientists from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine discovered that high-dose inhaled nitric oxide therapy may improve oxygenation and reduce the risk of mortality among critically ill Black patients with COVID-19.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome, or ARDS, is a condition that most commonly occurs in the setting of a lung infection such as COVID-19.
“In ARDS, the barrier between the blood vessels and air sacs in the lungs is disrupted leading to the accumulation of fluid ...
Ochsner Digital Medicine Partners with Humana Healthy Horizons
2024-02-28
New Orleans, LA. – Ochsner Digital Medicine has partnered with Humana Healthy Horizons to provide digital medicine services to its members. This agreement was effective February 1, 2024, with member enrollment in digital programs available immediately after.
Humana Healthy Horizons is Humana’s Medicaid plan for Louisiana, covering thousands of members throughout the state. Through this partnership, Ochsner Digital Medicine will offer Humana Healthy Horizons members who have been diagnosed with Hypertension and Type 2 diabetes remote programs designed to manage and control their conditions.
The programs use remote patient management through digital devices and personalized ...
Vision Zero road safety projects in Seattle are unlikely to have negative impacts on local business sales, UW study finds
2024-02-28
Seattle is routinely listed as one of the most walkable and bike-friendly cities in the nation. The city government has committed to Vision Zero, which aims to completely eliminate traffic deaths and serious injuries by 2030, and embarked on a slew of infrastructure projects: expanding the city’s bike network, redesigning high-crash intersections and enhancing crosswalks to protect pedestrians.
Such safety projects sometimes meet opposition from local business owners, who worry that reduced parking and disruption ...
African great apes predicted to see frequent extreme climate events in the next 30 years
2024-02-28
African apes are already being exposed to climate change impacts, and will experience extreme events such as wildfires, heatwaves and flooding more frequently in the next 30 years, according to a study publishing February 28 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Razak Kiribou at Haramaya University in Ethiopia and colleagues.
To better understand how African great apes will be affected by climate change, researchers investigated past and future climate for 363 sites across Africa. They estimated temperature and rainfall at each site between 1981 and 2010. Using two climate change scenarios, they projected how frequently apes would be exposed to climate change impacts in the near ...
EU countries have seen a decade of progress towards their 2030 sustainable energy goal
2024-02-28
Countries in the European Union (EU) have made progress over the past decade toward Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7), which calls for “access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all” by 2030, according to a study published February 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marek Walesiak from Wroclaw University of Economics and Business, Poland, and Grażyna Dehnel from Poznań University of Economics and Business, Poland.
In 2015, the United Nations developed 17 global Sustainable Development Goals to be achieved by 2030. Tenets of SDG 7 include universal access to affordable energy; increased renewable energy ...
Climate change threatens thousands of archaeological sites in coastal Georgia
2024-02-28
Thousands of historic and archaeological sites in Georgia are at risk from tropical storm surges, and that number will increase with climate change, according to a study published February 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Matthew D. Howland and Victor D. Thompson of Wichita State University and the University of Georgia.
Anthropogenic climate change poses a major risk to coastlines due to rising sea level and increasingly severe tropical storms. This threatens not only living populations but also historic and archaeological sites. Mitigating damage requires accurate assessments of risks, but most predictive models focus on projected ...
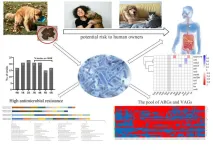
Pet dogs with diarrhea may be shedding multi-drug resistant E.coli in 5 in 10 cases, with potential risks to their human owners
2024-02-28
Pet dogs with diarrhea may be shedding multi-drug resistant E.coli in 5 in 10 cases, with potential risks to their human owners
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0298053
Article Title: Characteristics of MDR E. coli strains isolated from Pet Dogs with clinic diarrhea: A pool of antibiotic resistance genes and virulence-associated genes
Author Countries: China
Funding: This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0500900, ...
Harassment on public transport negatively impacts women's health and welfare, with existing measures being largely ineffective, per systematic review
2024-02-28
Harassment on public transport negatively impacts women's health and welfare, with existing measures being largely ineffective, per systematic review
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0296830
Article Title: Invasion of privacy or structural violence? Harassment against women in public transport environments: A systematic review
Author Countries: Spain
Funding: This study has been supported by the research grant ACIF/2020/035 from the "Generalitat Valenciana". The funding entity did not contribute to the study design or data collection, analysis, interpretation, or writing the manuscript. There was no additional ...