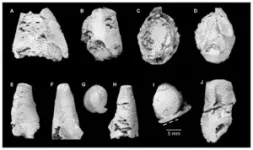
(Press-News.org) A team of researchers led by Alexander Pohle has unveiled a treasure trove of ancient fossils from Queensland's Black Mountain. The findings, published in PeerJ Life & Environment, shed new light on the complex three-dimensional siphuncle morphology of Plectronoceratids, a pivotal group of molluscs from the latest Cambrian period.
The study surpasses the entirety of previously documented Plectronoceratid fossils, presenting over 200 well-preserved specimens. These fossils, meticulously collected by the late Mary Wade and her team during the 1970s and 1980s, offer unprecedented insights into the intricate structures of these ancient creatures.
Pohle's team focused on specimens from the lower Ninmaroo Formation at Black Mountain, meticulously examining the three-dimensional morphology of the siphuncle. This comprehensive analysis revealed a remarkably intricate siphuncular structure, challenging previous interpretations based on longitudinal sections and prompting a major revision of the taxonomic classification within the order Plectronoceratida.
Of particular note is the discovery of Sinoeremoceras marywadeae sp. nov., a new species named in honor of Mary Wade. This species, characterized by its highly oblique siphuncular segments and elongated septal neck, represents a significant addition to the cephalopod evolutionary tree. Moreover, the study advocates for a revised taxonomy, consolidating multiple species, genera, families and even one order under the Plectronoceratida.
Pohle expressed his gratitude to Mary Wade, whose dedication to specimen collection and preparation paved the way for this groundbreaking research. "Would it not be for her, these faunas would still largely be unknown," said Pohle. The team hopes that their work honors Wade's legacy, acknowledging the invaluable contributions she made to paleontological science.
As the scientific community delves deeper into the origins of cephalopods, Pohle's team emphasizes the significance of further exploration and advanced imaging techniques. They advocate for the use of 3D reconstructions, such as µCT scans or serial grinding tomography, to unlock new dimensions of understanding in research on Palaeozoic cephalopds.
The publication of this groundbreaking study marks a pivotal moment in our quest to unravel the mysteries of ancient marine life. With each fossil unearthed, we inch closer to a comprehensive understanding of Earth's prehistoric past.
END
Black mountain unveils fossil trove
New revelations poised to reshape our understanding of early cephalopod evolution
2024-02-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
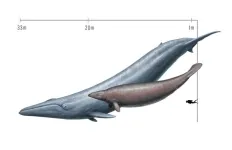
Slimming down a colossal fossil whale
2024-02-29
A 30 million year-old fossil whale may not be the heaviest animal of all time after all, according to a new analysis by paleontologists at UC Davis and the Smithsonian Institution. The new analysis puts Perucetus colossus back in the same weight range as modern whales and smaller than the largest blue whales ever recorded. The work is published Feb. 29 in PeerJ.
A fossil skeleton of Perucetus was discovered in Peru and described in a paper in Nature last year. The animal lived about 39 million years ago and belonged to an extinct group of early whales called ...
Better neutron mirrors can reveal the inner secrets of matter
2024-02-29
Improved neutron mirrors can increase the efficiency of material analysis in neutron sources such as the ESS, which is being built outside Lund, Sweden. The improved mirror has been developed by researchers at Linköping University by coating a silicon plate with extremely thin layers of iron and silicon mixed with boron carbide. Their study has been published in the journal Science Advances.
“Instead of increasing the power on the neutron source, which is extremely expensive, it’s better to focus on improving optics,” says Fredrik Eriksson, researcher at the Thin Film Physics Division at Linköping University.
Together with protons, neutrons ...
Astronomers reveal a new link between water and planet formation
2024-02-29
Researchers have found water vapour in the disc around a young star exactly where planets may be forming.
Water is a key ingredient for life on Earth and is also thought to play a significant role in planet formation, yet, until now, astronomers have never been able to map how water is distributed in a stable, cool disc — the type of disc that offers the most favourable conditions for planets to form around stars.
For the first time, astronomers have weighed the amount of water vapour around a typical planet-forming star.
The new findings were made possible thanks to the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) - a collection of telescopes ...
Plant biologists identify promising new fungicides
2024-02-29
A promising new fungicide to fight devastating crop diseases has been identified by researchers at the University of California, Davis. The chemical, ebselen, prevented fungal infections in apples, grapes, strawberries, tomatoes and roses and improved symptoms of pre-existing fungal infection in rice.
Fungal pathogens account for almost a quarter of global crop losses. In the United States, these losses amount to around $150 billion per year. However, fungicide development has been slow for the past 50 years, largely because researchers have had difficulty identifying molecular pathways to target. In a new study published Feb. 29 in ...
Researchers uncover a potential genetic marker associated with better survival outcomes in patients with head and neck cancer
2024-02-29
FINDINGS
Researchers from the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center show for the first time that a gene usually linked to giant axonal neuropathy, a rare and severe neurological condition, also plays a role in inhibiting aggressive tumor cell growth in head and neck cancers.
The team found when the specific genetic variant (GAN gene exon 8 SNP T allele) of the GAN gene isn't present, it leads to the production of certain proteins that make cancer cells more likely to spread and become resistant to treatment.
These findings suggest that the presence of the genetic variant and higher expression of the GAN gene product gigaxonin may contribute ...
European Society for Endocrinology’s European Journal of Endocrinology announces “Rising Stars” in endocrine research for 2024-26
2024-02-29
Thirteen exceptional endocrine researchers from across Europe and the US have been selected as the 2024-26 cohort of the EJE Rising Star Editorial Board by the European Journal of Endocrinology (EJE), a journal published by the European Society of Endocrinology (ESE).
This prestigious opportunity is given to individuals selected by EJE Editors who show promise, achievement and trajectory as leading clinical and translational researchers in endocrinology, with high potential to serve as future editors of EJE.
Through the Rising Stars Programme, awardees are granted the following:
membership ...
Hai-quan Huang's research team at Southwest Forestry University has revealed the cellular and molecular basis of the spur development in Impatiens uliginosa
2024-02-29
As an important reproductive organ of angiosperms, flowers have clear purposefulness and adaptive significance in their various characteristics. As a typical floral evolutionary feature, the floral spur is a tubular structure extending from the petal, which has undergone several independent evolutions in angiosperms (e.g., Impatiens, Aquilegia, Linaria, etc.). Meanwhile, it plays a vital role in the pollination process because of its properties of secreting and storing nectar. In addition, the morphology (length, diameter, degree of distortion), ...
New research reveals that lockdowns had an impact on gut microbes and allergies in newborns
2024-02-29
29 February 2024: Lockdowns imposed during the COVID-19 pandemic had an impact on the gut microbiome development of babies born during these periods according to new research from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, Children’s Health Ireland and APC Microbiome Ireland (APC), a world leading SFI Research Centre, based in University College Cork.
Our gut microbiome, an ecosystem of microbes that live in our digestive tract, plays an essential role in human health. The study published in Allergy is the first to specifically explore the gut health of newborns in the pandemic. ...
Seeing the wood for the trees: how archaeologists use hazelnuts to reconstruct ancient woodlands
2024-02-29
If we could stand in a landscape that our Mesolithic ancestors called home, what would we see around us? Scientists have devised a method of analyzing preserved hazelnut shells to tell us whether the microhabitats around archaeological sites were heavily forested or open and pasture-like. This could help us understand not only what a local environment looked like thousands of years ago, but how humans have impacted their habitats over time.
“By analyzing the carbon in hazelnuts recovered from archaeological sites in southern Sweden, from Mesolithic hunter-gatherer ...
EU-funded Biodiversity Community Integrated Knowledge Library (BiCIKL) project sums up outcomes and future prospects at a Final GA in Cambridge
2024-02-29
The city of Cambridge and the Wellcome Campus hosted the Final General Assembly of the EU-funded project BiCIKL (acronym for Biodiversity Community Integrated Knowledge Library): a 36-month endeavour that saw 14 member institutions and 15 research infrastructures representing diverse actors from the biodiversity data realm come together to improve bi-directional links between different platforms, standards, formats and scientific fields. Consortium members who could not attend the meeting in Cambridge joined the meeting remotely.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Black mountain unveils fossil troveNew revelations poised to reshape our understanding of early cephalopod evolution