Discovery of proteins associated with the progression of dialysis-related amyloidosis
2024-03-01
(Press-News.org)
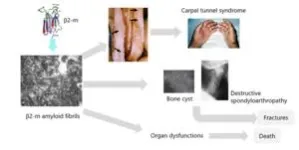
Niigata, Japan –Dialysis patients often develop dialysis-related amyloidosis and exhibit bone and joint disorders that impair their activity of daily living (Figure 1). Blood purification devices consisting of hexadecyl-immobilized cellulose beads aimed at removing the precursor protein, β2- microglobulin (β2-m), are used in the treatment of dialysis-related amyloidosis. Dr. Yamamoto et al. investigated that comprehensive analysis of proteins adsorbed onto blood purification devices revealed the identification of 200 types of proteins, including β2-m. Among these, several molecules, such as lysozyme, were shown to be involved in amyloid fibril formation (Figure 2).
I. Background of the Study
Patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) require kidney replacement therapy, such as hemodialysis, to manage their condition. Hemodialysis patients often experience various symptoms, leading to a compromised quality of life and reduced activity levels.
Itching is a common symptom frequently observed in hemodialysis patients. Although its exact causes remain unclear, a survey conducted in Japan in 2000 found that itching was present in 73% of hemodialysis patients, and it was associated with elevated levels of β2-microglobulin, calcium, phosphorus, or parathyroid hormone in the blood. Subsequently, improvements in hemodialysis therapy and pharmacological treatments have led to changes in the severity of itching and its associated factors in hemodialysis patients.
Uremic toxins are a group of molecules whose concentrations increase in the blood due to kidney disease. Those molecules are associated with systemic diseases and prognosis in patients with end-stage kidney disease. Among them, molecules with high protein-bound properties, called PBUTs, such as indoxyl sulfate, are difficult to remove by dialysis therapy and have been reported to be associated with various pathologies. However, there have been no reports regarding their association with itching. in hemodialysis patients.
Therefore, Dr. Yamamoto et al. conducted a study to investigate the details of itching and factors associated with it, particularly focusing on PBUTs in hemodialysis patients.
II. Overview of the Study
In this study, Yamamoto et al. extracted adsorbed proteins from β2-m adsorption columns on hemodialysis patients with dialysis-related amyloidosis, and analyzed them through mass spectrometry (Figure). As a result, 200 types of proteins, including β2-m, were detected.
Among them, four proteins (lysozyme, angiogenin, matrix Gla protein, and complement factor D) were identified, which are present in amyloid tissue and highly adsorbed by the β2-m adsorption column. When β2-m was reacted with those proteins in vitro, those proteins acted β2-m amyloid fibril formation.
III. Publication of Research Findings
The research findings were published in the scientific journal Amyloid: Journal of Protein Folding Disorders on February 11, 2024.
Paper Title: Mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of proteins adsorbed by hexadecyl-immobilized cellulose bead column for the treatment of dialysis-related amyloidosis
Authors: Suguru Yamamoto, Keiko Yamamoto, Yoshitoshi Hirao, Keiichi Yamaguchi, Kichitaro Nakajima, Mami Sato, Miho Kawachi, Mio Domon, Kei Goto, Kentaro Omori, Noriaki Iino, Hisaki Shimada, Ryuzi Aoyagi, Isei Ei, Shin Goto, Yuji Goto, Fumitake Gejyo, Tadashi Yamamoto, Ichiei Narita
doi: 10.1080/13506129.2024.2315148
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-01
Magnetite, a tiny particle found in air pollution, can induce signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, new research suggests.
Alzheimer’s disease, a type of dementia, leads to memory loss, cognitive decline, and a marked reduction in quality of life. It impacts millions globally and is a leading cause of death in older individuals.
The study, Neurodegenerative effects of air pollutant particles: Biological mechanisms implicated for early-onset Alzheimer’s disease, led by Associate Professor Cindy Gunawan and Associate Professor Kristine McGrath from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) was recently published in Environment ...
2024-03-01
A patient with gastrointestinal problems pays his doctor a visit. The doctor orders a stool test that will measure fecal bile acids, compounds made by the liver that can also be modified by the intestinal microbiome and are known for facilitating digestion and absorption of lipids or fats in the small intestine.
Bile acid profiles are altered in several gastrointestinal conditions, including irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn’s disease, and several forms of diarrhea, colitis and some bacterial ...
2024-03-01
The loneliness often experienced by older people in our society has a negative effect on their physical health, according to researchers from Amsterdam UMC and the University of Glasgow. Emiel Hoogendijk, epidemiologist at Amsterdam Public Health, analysed research results from more than 130 studies and found that loneliness led to an increase in physical frailty, which in turn increases the risk of adverse health outcomes such as depression, falls and cognitive decline. These results are published today in The Lancet Healthy Longevity.
"Recently, ...
2024-03-01
The Lancet: More than one billion people in the world are now living with obesity, global analysis suggests
Obesity rates among children and adolescents worldwide increased four times from 1990 to 2022, while obesity rates among adults have more than doubled.
Over the same period, rates of underweight fell among children, adolescents and adults, leading to obesity becoming the most common form of malnutrition in many countries.
Countries with the highest combined ...
2024-03-01
Every year, millions of older Americans spend money and time to try to look younger than they are. They color graying hair, buy anti-balding products, use teeth whiteners and wrinkle fillers, and much more.
Now, a new study looks at what this kind of effort means for older adults’ experiences with the ageism that pervades American society. The study also explores how a person’s perception of how old they look relates to both their positive and negative age-related experiences, and their physical and mental health.
In all, 59% of adults age 50 to 80 say they think they look younger than other people their age. The percentage was ...
2024-02-29
URBANA, Ill. – Leafy green vegetables are important sources of dietary fiber and nutrients, but they can harbor harmful pathogens. In particular, lettuce has often been involved in outbreaks of foodborne illness across the U.S. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign examines factors that affect E. coli contamination on five different leafy greens – romaine lettuce, green-leaf lettuce, spinach, kale, and collards.
“We are seeing a lot of outbreaks on lettuce, but not so much on kale and other brassica vegetables. We wanted to learn more about the susceptibility of different leafy greens,” said lead author Mengyi Dong, now a postdoctoral ...
2024-02-29
Individuals with mild cognitive impairment, especially of the “amnestic subtype” (aMCI), are at increased risk for dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease relative to cognitively healthy older adults. Now, a study co-authored by researchers from MIT, Cornell University, and Massachusetts General Hospital has identified a key deficit in people with aMCI, which relates to producing complex language.
This deficit is independent of the memory deficit that characterizes this group and may provide an additional “cognitive biomarker” to aid in early detection — the time when treatments, ...
2024-02-29
A new study by a team of University of Notre Dame researchers makes a significant contribution to understanding the factors that influence how young elementary school students respond to reading interventions in fragile and low-income contexts.
The study, published in the Comparative Education Review, evaluated an early-grade literacy intervention in Catholic schools in Haiti. The study has important implications for addressing educational inequities and improving learning outcomes to create opportunity and lift millions of children globally out of poverty.
“This ...
2024-02-29
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — The crucial role of social emotions in our lives and in society cannot be overstated. Empathy, guilt, embarrassment, pride and other feelings we experience in the context of other people govern and motivate how we act, interact and the countless decisions we make. Which is why a more holistic approach, one that integrates the various ways these emotions are studied, is necessary to gain insight and address gaps in knowledge. That’s according to researchers from UC Santa Barbara, New York University School ...
2024-02-29
Nearly every massive galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole at its center. When two galaxies merge, their black holes can form a binary pair, meaning they are in a bound orbit with one another. It’s hypothesized that these binaries are fated to eventually merge, but this has never been observed [1]. The question of whether such an event is possible has been a topic of discussion amongst astronomers for decades. In a recently published paper in The Astrophysical Journal, a team of astronomers have presented new insight into this question.
The team used data from the Gemini North telescope in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Discovery of proteins associated with the progression of dialysis-related amyloidosis