Making sense of Mendelian randomization
2024-03-01
(Press-News.org) Mendelian randomization, a powerful tool in medical research, helps us understand whether certain factors truly cause disease. This technique uses genetic variations as "natural experiments" to reveal cause-and-effect relationships. However, choosing the proper genetic variations is crucial for accurate results.
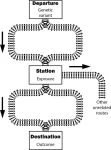
Think of a train network where the genetic variation is the starting point, the exposure is a station, and the disease is the destination. The train must pass through the exposure station en route to the disease. This represents the critical assumption of Mendelian randomization: the genetic variation affects the exposure, which then influences the disease.
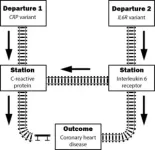
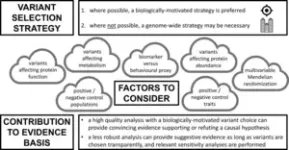
Biologically motivated approaches are preferred for selecting these genetic variations. They focus on genes directly linked to the exposure, like using variations within a protein-coding gene to understand the protein's impact on disease. This approach is more reliable as it minimizes "off-track" influences on the disease.
Genome-wide analyses, while tempting due to their vast data, can be misleading. They often introduce noise and weaken the signal, leading to unreliable conclusions. Just like having trains going in different directions, these analyses lack the focused direction of biologically motivated approaches.
However, genome-wide analyses can still be helpful as supporting evidence. Imagine having multiple trains starting from different stations but all converging at the exposure station. If these trains consistently reach the disease destination, it strengthens the evidence for a causal link.
The key takeaway? Prioritize biologically motivated approaches whenever possible. While not always feasible, they offer more precise insights. Genome-wide analyses can be used cautiously for additional support, but their limitations must be considered.
Combining biological understanding with statistical expertise is essential for drawing accurate causal conclusions from Mendelian randomization. This collaboration across disciplines ensures we stay on the right track in understanding the true causes of disease.
See the article:
Burgess S, Cronjé HT. Incorporating biological and clinical insights into variant choice for Mendelian randomisation: examples and principles. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100042. doi:10.1136/egastro-2023-100042
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-01
Penn Engineers have developed a new means of targeting the lungs with lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the miniscule capsules used by the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines to deliver mRNA, opening the door to novel treatments for pulmonary diseases like cystic fibrosis.
In a paper in Nature Communications, Michael J. Mitchell, Associate Professor in the Department of Bioengineering, demonstrates a new method for efficiently determining which LNPs are likely to bind to the lungs, rather than the liver. “The way the liver is designed,” says Mitchell, “LNPs tend to filter into hepatic cells, and struggle ...
2024-03-01
The question of where the boundary between classical and quantum physics lies is one of the longest-standing pursuits of modern scientific research and in new research published today, scientists demonstrate a novel platform that could help us find an answer.
The laws of quantum physics govern the behaviour of particles at miniscule scales, leading to phenomena such as quantum entanglement, where the properties of entangled particles become inextricably linked in ways that cannot be explained by classical physics.
Research in quantum physics ...
2024-03-01
New findings reveal that the body undergoes significant, systematic changes across multiple organs during prolonged periods of fasting. The results demonstrate evidence of health benefits beyond weight loss, but also show that any potentially health-altering changes appear to occur only after three days without food.
The study, published today in Nature Metabolism, advances our understanding of what’s happening across the body after prolonged periods without food.
By identifying the potential health benefits from fasting ...
2024-03-01
The microbiome can identify those who benefit from combination immunotherapy across multiple different cancers, including rare gynaecological cancers, biliary tract cancers and melanoma.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute in Australia, and collaborators, have identified specific strains of bacteria that are linked with a positive response to combination immunotherapy in the largest study of its kind.
The study, published today (1 March) in Nature Medicine, details a signature collection of microorganisms in an individual’s gut bacteria that may help identify those who would benefit from combination immunotherapy and ...
2024-03-01
A study published today in Nature Nanotechnology shows that similarly charged particles can sometimes attract, rather than repel.
The team found that like-charged particles suspended in liquids can attract one another at long-range, depending on the solvent and the sign of the charge.
The study has immediate implications for processes that involve interactions in solution across various length-scales, including self-assembly, crystallisation, and phase separation.
‘Opposites charges attract; like charges repel’ is a fundamental principle of basic physics. But a new study from Oxford University, published today in Nature Nanotechnology, has demonstrated that similarly ...
2024-03-01
In this study, we determined nine genomes of Japanese wolves and 11 genomes of modern Japanese dogs at high coverage and analyzed with one hundred dog and wolf genomes in the public database. The analyses showed that 1) the Japanese wolf was a unique subspecies of the gray wolf that is genetically distinct from both extant and ancient gray wolves known to date, 2) the Japanese wolf is most closely related to the monophyletic group of dogs. Furthermore, 3) Japanese wolf ancestry has introgressed into the ancestor of East Eurasian dogs at an early stage of the dog’s history ...
2024-03-01
Brown bears foraging for food in the Shiretoko Peninsula of Hokkaido, Japan, have been disrupting tree growth in artificial conifer forests, according to a new study. Researchers compared soil and tree samples from human-forested plots with samples from natural forests. They found that the bears’ digging for cicada nymphs damaged tree roots and altered the nitrogen content of the soil, which in turn limited the diameter growth of trees. The phenomena of bears digging for cicadas, an unusual food source, appears to be restricted to human-planted conifer forest; diversely vegetated natural forest ...
2024-03-01
Reconstructing a 3D face from visuals is crucial for digital face modeling and manipulation. Traditional methods predominantly depend on RGB images, which are susceptible to lighting variations and offer only 2D information. In contrast, depth images, resistant to lighting changes, directly capture 3D data, offering a potential solution for robust reconstructions. Recent studies have turned to deep learning for more robust reconstruction from depth data; however, the scarcity of real depth images with accurate 3D facial labels has hindered the training process. Attempts to use auto-synthesized data for training have met limitations ...
2024-03-01
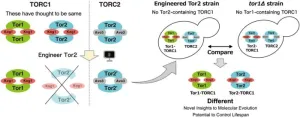
Assistant Professor Takahiro Kosugi of Institute for Molecular Science, assistant Professor Yoshiaki Kamada at National Institute for Basic Biology, and colleagues have developed an advanced molecular cell biology approach by integrating computational redesigning of protein complexes based on the predicted three-dimensional structure into yeast genetics. They revealed that two types of protein complexes in yeast, which were thought to have the same function, play distinct roles in cellular environmental response and lifespan. Furthermore, ...
2024-03-01
Fiber, as the wearable material with the longest application in the history of humankind, is currently an ideal substrate for wearable devices due to its excellent breathability, flexibility, and ability to adapt perfectly to the 3D irregular shape of the human body. As a means of visualization in the field of functional fibers, light-emitting fiber breaks the rigidity of the traditional display interface and is expected to become an emerging interaction interface. The current commercial light-emitting fibers are polymer optical fibers and Corning® Fibrance® light-diffusing fibers. These fibers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Making sense of Mendelian randomization