Innovative domain-adaptive method enables 3D face reconstruction from single depth images
2024-03-01
(Press-News.org)
Reconstructing a 3D face from visuals is crucial for digital face modeling and manipulation. Traditional methods predominantly depend on RGB images, which are susceptible to lighting variations and offer only 2D information. In contrast, depth images, resistant to lighting changes, directly capture 3D data, offering a potential solution for robust reconstructions. Recent studies have turned to deep learning for more robust reconstruction from depth data; however, the scarcity of real depth images with accurate 3D facial labels has hindered the training process. Attempts to use auto-synthesized data for training have met limitations in generalizing to real-world scenarios due to domain disparities.
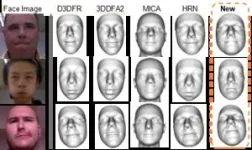
In their efforts to address these challenges, a research team, led by Xiaoxu Cai, unveiled their latest findings on 15 Feb 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature. Their research introduces a novel domain-adaptive reconstruction method, utilizing deep learning alongside a fusion of auto-labeled synthetic and unlabeled real data. This approach facilitates the reconstruction of 3D faces from individual depth images captured in the real world. Their method implements domain-adaptive neural networks dedicated to predicting head pose and facial shape, respectively. Each network is trained using specific strategies tailored to its component. The head pose network is trained using a straightforward fine-tuning method, whereas a more robust adversarial domain adaptation approach is applied to train the facial shape network. The initial step of preprocessing involves converting pixel values from the depth image into 3D point coordinates within the camera space. This process allows the utilization of 2D convolutions in the reconstruction network for processing 3D geometric information. The network output employs 3D vertex offsets, establishing a more focused target distribution to facilitate the learning process.
The method is thoroughly evaluated on challenging real-world datasets, demonstrating its competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art techniques.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-3541-7
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-01
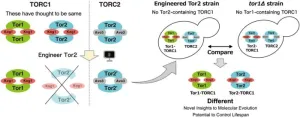
Assistant Professor Takahiro Kosugi of Institute for Molecular Science, assistant Professor Yoshiaki Kamada at National Institute for Basic Biology, and colleagues have developed an advanced molecular cell biology approach by integrating computational redesigning of protein complexes based on the predicted three-dimensional structure into yeast genetics. They revealed that two types of protein complexes in yeast, which were thought to have the same function, play distinct roles in cellular environmental response and lifespan. Furthermore, ...
2024-03-01
Fiber, as the wearable material with the longest application in the history of humankind, is currently an ideal substrate for wearable devices due to its excellent breathability, flexibility, and ability to adapt perfectly to the 3D irregular shape of the human body. As a means of visualization in the field of functional fibers, light-emitting fiber breaks the rigidity of the traditional display interface and is expected to become an emerging interaction interface. The current commercial light-emitting fibers are polymer optical fibers and Corning® Fibrance® light-diffusing fibers. These fibers ...
2024-03-01
The General Medical Council (GMC) should revise its terminology regarding international medical graduates (IMGs) in the UK, argues a new commentary published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine (JRSM).
The existing terminology used by the GMC fails to encompass the full spectrum of doctors facing challenges in the UK medical workforce, according to the paper’s author, Professor Mo Al-Haddad of Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, Glasgow.
Notably, he says, the GMC's definition of IMGs overlooks ...
2024-03-01
A new study from experts at the University of Exeter has found that a widely used test for prostate cancer may leave black men at increased risk of overdiagnosis.
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing is routinely used as the first step in the UK to investigate men with urinary symptoms such as blood in urine or urinating very frequently. Men aged over 50 years without symptoms are also able to request the blood test from their GP.
The new study, published in BMC Medicine, sought to investigate the performance of the PSA test in identifying prostate cancer among men ...
2024-03-01
Niigata, Japan –Dialysis patients often develop dialysis-related amyloidosis and exhibit bone and joint disorders that impair their activity of daily living (Figure 1). Blood purification devices consisting of hexadecyl-immobilized cellulose beads aimed at removing the precursor protein, β2- microglobulin (β2-m), are used in the treatment of dialysis-related amyloidosis. Dr. Yamamoto et al. investigated that comprehensive analysis of proteins adsorbed onto blood purification devices revealed the identification of 200 types of proteins, including β2-m. ...
2024-03-01
Magnetite, a tiny particle found in air pollution, can induce signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, new research suggests.
Alzheimer’s disease, a type of dementia, leads to memory loss, cognitive decline, and a marked reduction in quality of life. It impacts millions globally and is a leading cause of death in older individuals.
The study, Neurodegenerative effects of air pollutant particles: Biological mechanisms implicated for early-onset Alzheimer’s disease, led by Associate Professor Cindy Gunawan and Associate Professor Kristine McGrath from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) was recently published in Environment ...
2024-03-01
A patient with gastrointestinal problems pays his doctor a visit. The doctor orders a stool test that will measure fecal bile acids, compounds made by the liver that can also be modified by the intestinal microbiome and are known for facilitating digestion and absorption of lipids or fats in the small intestine.
Bile acid profiles are altered in several gastrointestinal conditions, including irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn’s disease, and several forms of diarrhea, colitis and some bacterial ...
2024-03-01
The loneliness often experienced by older people in our society has a negative effect on their physical health, according to researchers from Amsterdam UMC and the University of Glasgow. Emiel Hoogendijk, epidemiologist at Amsterdam Public Health, analysed research results from more than 130 studies and found that loneliness led to an increase in physical frailty, which in turn increases the risk of adverse health outcomes such as depression, falls and cognitive decline. These results are published today in The Lancet Healthy Longevity.
"Recently, ...
2024-03-01
The Lancet: More than one billion people in the world are now living with obesity, global analysis suggests
Obesity rates among children and adolescents worldwide increased four times from 1990 to 2022, while obesity rates among adults have more than doubled.
Over the same period, rates of underweight fell among children, adolescents and adults, leading to obesity becoming the most common form of malnutrition in many countries.
Countries with the highest combined ...
2024-03-01
Every year, millions of older Americans spend money and time to try to look younger than they are. They color graying hair, buy anti-balding products, use teeth whiteners and wrinkle fillers, and much more.
Now, a new study looks at what this kind of effort means for older adults’ experiences with the ageism that pervades American society. The study also explores how a person’s perception of how old they look relates to both their positive and negative age-related experiences, and their physical and mental health.
In all, 59% of adults age 50 to 80 say they think they look younger than other people their age. The percentage was ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Innovative domain-adaptive method enables 3D face reconstruction from single depth images