(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 3, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – People who experience sleep apnea may be more likely to also have memory or thinking problems, according to a preliminary study released today, March 3, 2024, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 76th Annual Meeting taking place April 13–18, 2024, in person in Denver and online. The study shows a positive association but did not determine whether sleep apnea causes cognitive decline.
Sleep apnea is when people stop and restart breathing repeatedly during sleep which can lower oxygen levels in the blood. Symptoms include snorting, gasping and breathing pauses. People with the disorder may also experience morning headaches or have trouble focusing on tasks.
“Sleep apnea is a common disorder that is often underdiagnosed, yet treatments are available,” said study author Dominique Low, MD, MPH, of Boston Medical Center in Massachusetts, and a member of the American Academy of Neurology. “Our study found participants who had sleep apnea symptoms had greater odds of having memory or thinking problems.”
The study involved 4,257 people. Participants completed a questionnaire asking about sleep quality as well as memory and thinking problems. For sleep, participants were asked about snorting, gasping or breathing pauses in their sleep. For memory and thinking, participants were asked questions related to difficulty remembering, periods of confusion, difficulty concentrating or problems with decision making.
Of all participants, 1,079 reported symptoms of sleep apnea. Of those with symptoms, 357 people, or 33%, reported memory or thinking problems compared to 628 people, or 20% of people without sleep apnea symptoms.
After adjusting for other factors that could affect memory and thinking problems, such as age, race, gender and education, researchers found that people who reported sleep apnea symptoms were about 50% more likely to also report having memory or thinking problems compared to people who did not have sleep apnea symptoms.
“These findings highlight the importance of early screening for sleep apnea,” said Low. “Effective treatments like continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are readily available. Quality sleep, along with eating a healthy diet, regular exercise, social engagement and cognitive stimulation, may ultimately reduce a person’s risk of thinking and memory problems, improving their quality of life.”
Limitations of the study include that the data was sourced from one survey and participants reported their symptoms instead of being assessed by medical professionals. Additional studies are needed following people’s sleep apnea, memory and thinking symptoms over time.
Learn more about sleep apnea at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, X and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the American Academy of Neurology’s Annual Meeting hashtag #AANAM.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, X, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
Sleep apnea symptoms linked to memory and thinking problems
2024-03-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nanoscale topcoat can turbocharge supported gold nanoparticle catalysts
2024-03-02
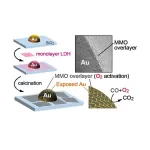
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to add single nanosheets of mixed metal oxide to gold nanoparticles supported on silica to enhance their catalytic activity. Converting carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide, they found that the temperature required for the reaction was greatly reduced, with significant improvements over existing methods for coating gold/silica structures. The method paves the way for the development of a wide range of new high-performance catalysts.
Gold nanoparticles, particles less than five nanometers in diameter, are known to be excellent catalysts ...
Beyond the ink: Painting with physics
2024-03-02
Falling from the tip of a brush suspended in mid-air, an ink droplet touches a painted surface and blossoms into a masterpiece of ever-changing beauty. It weaves a tapestry of intricate, evolving patterns. Some of them resemble branching snowflakes, thunderbolts or neurons, whispering the unique expression of the artist's vision.
Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) researchers set out to analyse the physical principles of this fascinating technique, known as dendritic painting. They took inspiration from the artwork ...
Only 9 percent of older Americans were vaccinated against RSV before the disease hit this fall and winter
2024-03-02
A new study from the Texas A&M University School of Public Health found that only 9 percent of older Americans had been vaccinated against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) prior to this fall and winter, despite the threat of increased rates of hospitalization and deaths nationwide from the virus.
“RSV—along with COVID-19 and influenza—form the current ‘tripledemic’ found across the United States this fall and winter,” said Simon Haeder, PhD, the study’s author. “While the elderly, as well as the very young and those with chronic health conditions, typically are affected ...
Evolution-capable AI promotes green hydrogen production using more abundant chemical elements
2024-03-02
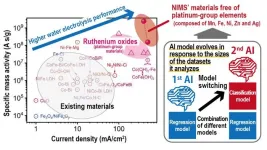
1. A NIMS research team has developed an AI technique capable of expediting the identification of materials with desirable characteristics. Using this technique, the team was able to discover high-performance water electrolyzer electrode materials free of platinum-group elements—substances previously thought to be indispensable in water electrolysis. These materials may be used to reduce the cost of large-scale production of green hydrogen—a next-generation energy source.
2. Large-scale production of green ...
In wake of powerful cyclone, remarkable recovery of Pacific island’s forests
2024-03-01
After one of the most intense cyclones in world history tore through the Pacific island of Tanna in Vanuatu, new research led by the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa showed the resilience of the island’s forests.
In the Pacific islands, climate change is expected to increase the intensity and frequency of cyclones, causing huge potential risks to forests and the people who depend on them. In March 2015, Cyclone Pam touched down on the island of Tanna as the strongest Pacific island cyclone in history ...
PSU study sheds light on 2020 extreme weather event that brought fires and snow to western US
2024-03-01
The same weather system that led to the spread of the devastating Labor Day wildfires in 2020 brought record-breaking cold and early-season snowfall to parts of the Rocky Mountains. Now, new research from Portland State is shedding light on the meteorology behind what happened and the impacts of such an extreme weather event.
“It’s really interesting to see such an amplified pattern result in opposing extremes in the Pacific Northwest and the Rocky Mountains,” said Emma Russell, a master’s student in geography ...
Rice physicist earns NSF CAREER Award to revolutionize quantum technology
2024-03-01
HOUSTON – (March 1, 2024) – Yonglong Xie, assistant professor of physics at Rice University, has been awarded a Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF). The $888,555 grant over five years will support Xie’s research into harnessing magnons, quantum mechanical wavelike objects in magnetic materials, to create synthetic matter and develop next-generation quantum devices and sensors.
The CAREER program offers NSF’s most prestigious awards in support of early career faculty who have the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education. Xie’s project focuses ...
Mining the treasures locked away in produced water
2024-03-01
In an ironic twist, a treasure trove of critical minerals is dumped out with water considered too polluted and expensive to clean.
Texas A&M University researcher Dr. Hamidreza Samouei is investigating the components of produced water and says this waste byproduct of oil and gas operations contains nearly every element in the periodic table, including those of significant interest to national economies.
His goal is to treat the water using unwanted carbon dioxide (CO2) in stages to recover these valuable elements and ultimately produce fresh water for agricultural use once the processes are complete.
“Recognizing the latent value ...
Minoritized groups face high anxiety when taking part in research experiments
2024-03-01
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- When participating in research studies, moderately anxious or highly anxious children from minoritized groups are likely to be hypervigilant to threat, further compounding the effects of their general state of anxiety, a research study led by a University of California, Riverside, psychologist reports.
The study, which involved the participation of 46 Inland Southern California preadolescent Latina girls (8–13 years), has implications also for children from families with low socioeconomic status.
“Psychological research is often conducted in white, educated, and affluent communities,” said Kalina Michalska, ...
Orcas demonstrating they no longer need to hunt in packs to take down the great white shark
2024-03-01
An orca (killer whale) has been observed, for the first-ever time, individually consuming a great white shark – and within just two minutes.
“The astonishing predation, off the coast of Mossel Bay, South Africa, represents unprecedented behavior underscoring the exceptional proficiency of the killer whale”, remarks Dr. Alison Towner from Rhodes University, who led an international research team into the discovery.
Their findings are published today in the peer-reviewed African Journal of Marine Science.
The groundbreaking insight is the latest from Dr. Towner and the team, who, in 2022 in the same journal, ...