(Press-News.org) The quantum systems employed in quantum technologies, for example single atoms, are also very sensitive: any interaction with the environment can induce changes in the quantum system, leading to errors. However, this remarkable sensitivity of quantum systems to environmental factors actually represents a unique advantage. This sensitivity enables quantum sensors to surpass conventional sensors in precision, for example when measuring magnetic or gravitational fields.
Noise cancellation using correlation spectroscopy
The delicate quantum properties needed for sensing can be covered up by noise—rapid interactions between the sensor and the environment that disrupt the information within the sensor, rendering the quantum signal unreadable. In a new paper, physicists led by Christian Roos from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck, together with partners in Israel and the USA, present a method for making this information accessible again using “correlation spectroscopy”. “Here, the key idea is that we do not just use a single sensor, but a network of up to 91 sensors, each consisting of a single atom,” explains Helene Hainzer, the first author of the paper. “Since noise affects all sensors equally, analyzing simultaneous changes in the states of all sensors allows us to effectively subtract the environmental noise and reconstruct the desired information. This allows us to precisely measure magnetic field variations in the environment, as well as determine the distance between the quantum sensors.” Beyond that, the method is applicable for various other sensing tasks and within diverse experimental platforms, reflecting its versatility.
Precision increases with the number of sensors
While correlation spectroscopy has been demonstrated previously with two atomic clocks, allowing for a superior precision in measuring time, “our work marks the first application of this method on such a large number of atoms,” emphasizes ERC award winner Christian Roos. “In order to establish experimental control over so many atoms, we built an entirely new experimental setup over several years.” In their publication, the Innsbruck scientists show that the precision of the sensor measurements increases with the number of particles in the sensor network. Notably, entanglement— conventionally used to enhance quantum sensor precision but hard to create in the laboratory—fails to provide an advantage compared to the multi-sensor network.
The work has been published in the journal Physical Review X and was financially supported by the Austrian Science Fund FWF, the Austrian Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Research, the European Union and the Federation of Austrian Industries Tyrol, among others.
Publication: Correlation spectroscopy with multiqubit-enhanced phase estimation. Phys. Rev. X. H. Hainzer, D. Kiesenhofer, T. Ollikainen, M. Bock, F. Kranzl, M. K. Joshi, G. Yoeli, R. Blatt, T. Gefen, and C. F. Roos. Phys. Rev. X 2024 DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.14.011033
END
Network of quantum sensors boosts precision
Successful demonstration of noise cancellation using correlation spectroscopy
2024-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robotic hip exoskeleton shows promise for helping stroke patients regain their stride
2024-03-04
Robotic Hip Exoskeleton Shows Promise for Helping Stroke Patients Regain Their Stride
A portable robotic device created by UMass Amherst researchers provides new avenue for making state-of-the-art gait rehabilitation methods more effective and accessible
AMHERST, Mass. – More than 80% of stroke survivors experience walking difficulty, significantly impacting their daily lives, independence, and overall quality of life. Now, new research from the University of Massachusetts Amherst pushes forward the bounds of stroke recovery ...
Conservation value of field research stations grossly misunderstood and underfunded according to 173 conservation scientists in new study
2024-03-04
SAN DIEGO – Funding of field conservation research stations worldwide has been drastically reduced since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, raising the alarm of more than 170 conservation researchers representing 157 field stations in 56 countries in a new paper published in Conservation Letters. The authors contend that field research stations have a high return on investment and are essential and highly effective tools for biodiversity conservation.
Trillions of U.S. dollars were mobilized in economic recovery following the pandemic, yet the authors raise concerns ...
Study underscores social factors of low breast cancer screening in the US
2024-03-04
There is a pressing need to explore and understand which social determinants of health (SDOH) and health inequities act as significant influential factors that contribute to low breast cancer screening behaviors in the United States.
Health disparities have been consistently associated with delayed screening, which then contributes to higher mortality rates among both Hispanic and Black populations. Moreover, poverty, lack of education, neighborhood disadvantage, residential segregation, racial discrimination, lack of social support and social isolation ...
Nanomedicine research aims to transform treatment of aortic aneurysms
2024-03-04
Aortic aneurysms are bulges in the aorta, the largest blood vessel that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, or injury can all increase the risk of aneurysms, which tend to occur more often in Caucasian male smokers over the age of 65.
“The soft tissues that make up blood vessels act essentially like rubber bands, and it’s the elastic fibers within these tissues that allow them to stretch and snap back,” says Professor Anand Ramamurthi, chair of the Department of Bioengineering in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering ...
HIV medication can be used safely with gender-affirming hormone therapy
2024-03-04
New research definitively shows that HIV antiretrovirals can be taken together with gender-affirming hormone therapy without changing how well either drug works. The study findings can help healthcare providers address potential patient concerns that one drug will counteract the other.
“This study is the first head-to-head pharmacokinetic analysis of two common HIV medications and long-term feminizing hormone therapy use,” says Walter Kraft, MD, director of the Division of Clinical ...
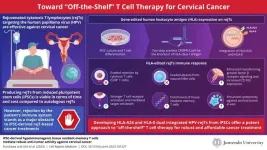
Gene-edited lymphocytes and the path toward ‘off-the-shelf’ therapy against cervical cancer
2024-03-04
Cervical cancer is among the most common malignancies affecting women worldwide. In 2020 alone, approximately 600,000 women were diagnosed with this disease, and over 314,000 died from it. In 99% of the cases, cervical cancer cells harbor human papilloma virus (HPV), and thus, HPV vaccines are an effective way to mitigate the risk of developing this disease. Unfortunately, such preventive measures are useless against established cancers, which are generally incurable once they become metastatic or relapsing.
Fortunately, scientists have made substantial progress in developing a promising ...
Humans have driven the Earth’s freshwater cycle out of its stable state
2024-03-04
A new analysis of freshwater resources across the globe shows that human activity has pushed variation in the planet’s freshwater cycle well outside of its pre-industrial range. The study shows that the updated planetary boundary for freshwater change was surpassed by the mid-twentieth century. In other words, for the past century, humans have been pushing the Earth’s freshwater system far beyond the stable conditions that prevailed before industrialization.
This is the first time that global water cycle change has been assessed over such a long timescale with an appropriate reference baseline. The findings, published in Nature Water, show that human ...
Exposure to different kinds of music influences how the brain interprets rhythm
2024-03-04
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When listening to music, the human brain appears to be biased toward hearing and producing rhythms composed of simple integer ratios — for example, a series of four beats separated by equal time intervals (forming a 1:1:1 ratio).
However, the favored ratios can vary greatly between different societies, according to a large-scale study led by researchers at MIT and the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics and carried out in 15 countries. The study included 39 groups of participants, many of whom came from societies ...
Study shows differences in how patients with impulse control disorder process consequences
2024-03-04
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – March 4, 2024 – Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that affects movement and muscle control. One characteristic of the disease is the deficiency of dopamine, a neurotransmitter or brain chemical that plays a role in movement and can impact how people think and feel.
Dopaminergic medicines can help alleviate the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. However, in some patients, the medications can cause impulse control disorder (ICD), characterized by risky behavior such as excessive gambling, shopping, ...
Improving access to early-stage lung cancer care in Europe
2024-03-04
There are stark differences between European countries when it comes to both the reimbursement of, and access to, new treatments for patients with early-stage lung cancer. There are also differences in reimbursement times and indications between the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Researchers from Amsterdam UMC Cancer Center Amsterdam analysed the landscape, and their results are published today in The Lancet Regional Health Europe as part of a series on the latest developments in the treatment of this lung cancer.
"Tackling inequalities in access to care must be a common European priority," ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Network of quantum sensors boosts precisionSuccessful demonstration of noise cancellation using correlation spectroscopy