(Press-News.org) Researchers at Cima Universidad de Navarra have discovered that a ribonucleic acid that does not contain information to make proteins (long non-coding RNA) plays a crucial role in signalling and repairing errors in DNA replication during cell division. This finding could lead to the development of new anti-tumour therapies.
Scientists have identified an RNA that they named 'lncREST' (long non-coding RNA REplication STress) and uncovered its role in triggering an effective response to the stress induced by rapid cell division. "LncREST localises to chromatin (the structure in which DNA is organised in the cell). Its main function is to facilitate the localisation of key proteins in the process of DNA replication and DNA damage repair where they are needed. In fact, the absence of lncREST has been shown to cause impaired stress signalling, leading to the accumulation of severe DNA defects and, ultimately, cell death", explains Luisa Statello PhD, first and co-corresponding author of the study.
"We have discovered that lncREST - controlled by the tumour suppressor p53 - acts as a functional sensor. It ensures that the necessary proteins are in the right place at the right time and, that genome replication does not fail", says Maite Huarte, leader of the study and principal investigator of the Non-Coding RNA and Cancer Genome Group at Cima Universidad de Navarra.
The work, published in the journal Nature Communications, has not only revealed IncREST as a critical component of the stress response, but could also be an effective therapeutic target in the fight against various types of cancer. "This discovery is an important step towards a better understanding of how our cells deal with stress during cell division. In addition, it could open up a new avenue for studies to develop new therapies against cancer cells, or improve existing ones, using lncREST as a therapeutic target," argues Statello.
The researchers, who carried out the study in colorectal cancer cells and in mouse tumour models, also highlight the promising scenario that may result from combining known inhibitors with lncREST inhibitors to achieve a greater therapeutic effect. "The findings may lead to a combination therapy to use fewer drugs and reduce toxicity to the patient. By using two inhibitors at the same time, the chances of tumour cells developing resistance to treatment are reduced," suggests Huarte.
New cutting-edge method
In this study, the Cima researchers have reformulated an existing technology to detect RNA molecules in the replication process. "We have developed a methodology called iROND, which allows us to identify RNAs that are located specifically at the sites where DNA is replicating. In fact, that is how we detected lncREST associated with replication sites under stress conditions," reveals Luisa Statello.
This research was carried out by a team of scientists with public and private funding from the Worldwide Cancer Research Foundation, the Spanish State Research Agency, the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, the European Research Council (ERC) and a Marie Skłodowska Curie European grant.
END
Discovered a RNA molecule that helps prevent DNA replication errors
Cima researchers identify a ribonucleic acid that could be used as a therapeutic target against cancer cells
2024-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Small and overlooked: Amount of repetitive DNA in blood hints at cancer early
2024-03-04
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
People with cancer have different amounts of a type of repetitive DNA — called Alu elements — than people without cancer. Now, machine learning can measure that from a blood draw. Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center have used this finding to improve a test that detects cancer early, validating and reproducing the results by starting with a sample size tenfold larger than typical of such types of studies.
The research was published Jan. 24 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Alu ...
Study determines the original orientations of rocks drilled on Mars
2024-03-04
As it trundles around an ancient lakebed on Mars, NASA’s Perseverance rover is assembling a one-of-a-kind rock collection. The car-sized explorer is methodically drilling into the Red Planet’s surface and pulling out cores of bedrock that it’s storing in sturdy titanium tubes. Scientists hope to one day return the tubes to Earth and analyze their contents for traces of embedded microbial life.
Since it touched down on the surface of Mars in 2021, the rover has filled 20 of its 43 tubes with cores of bedrock. Now, MIT geologists have remotely determined a crucial property of the rocks collected to date, which will help scientists answer key questions about the planet’s ...
Illinois study: Supporting disease-challenged broiler chickens through nutrition
2024-03-04
URBANA, Ill. — When broiler chickens are busy fighting the parasitic infection coccidiosis, they can’t absorb nutrients efficiently or put energy toward growth. With consumer sentiment pitted against antimicrobials and other drugs, producers still have some options to ensure optimal growth during inevitable outbreaks. New research from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign suggests diet changes might help.
“Vaccines and anticoccidials are the traditional ways to prevent this disease. Nutrition can't replace all of the pharmaceuticals, but it can be supportive in providing care,” said senior study author Ryan Dilger, ...
Communities severed by roads and traffic experience a larger number of collisions in New York City
2024-03-04
March 4, 2024- New York City neighborhoods with disrupted community connections, due to traffic, roads, and transport infrastructure, are experiencing an increase in traffic collisions. This increase is seen both in total collisions and for those in which pedestrians or cyclists are injured or killed, according to a new study from Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The findings are reported in the journal Environment International.
“Despite recent remarkable progress, road safety remains an urgent urban issue in New York and other U.S. cities. It is important to understand how the spatial configuration of the city enhances ...
Study shows new class of antivirals that works against SARS-CoV-2
2024-03-04
EDMONTON — A University of Alberta research team has uncovered a new class of drugs with the potential to prevent or treat infections in a future viral outbreak.
In the paper, published this week in Nature, the team reports that SARS-CoV-2 — the virus that causes COVID-19 — activates a pathway in cells that stops the production of peroxisomes and interferon, key parts of the normal immune response. The team successfully tested a new class of antiviral drugs that stimulate interferon production to reverse that effect.
Tom ...
Cost of direct air carbon capture to remain higher than hoped
2024-03-04
Switzerland plans to reduce its net carbon emissions to zero by no later than 2050. To achieve this, it will need to drastically reduce its greenhouse gas emissions. In its climate strategy, the Swiss government acknowledges that some of these emissions, particularly in agriculture and industry, are difficult or impossible to avoid. Swiss climate policy therefore envisages actively removing 5 million tonnes of CO2 from the air and permanently storing it underground. By way of comparison, the Intergovernmental ...
Unraveling the mystery of chiton visual systems
2024-03-04
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — You’d probably walk past a chiton without even seeing it. These creatures often look like nothing more than another speck of seaweed on the crusty intertidal rocks. But it sees you. At least, if it’s one of the species with eyes dotting its platemail shell.
A team of scientists — led by Rebecca Varney at UC Santa Barbara’s Department of Ecology, Evolution, and Marine Biology (EEMB) — discovered that some of these tough mollusks sport the most recently evolved eyes with a lens. What’s more, the ...
Case Western Reserve University-led research team discovers new method to test for oral cancer
2024-03-04
CLEVELAND—Oral cancers and precancerous mouth lesions are considered especially difficult to diagnose early and accurately.
For one, biopsies are expensive, invasive, stressful for the patient and can lead to complications. They’re also not feasible if repeated screenings of the same lesion are required.
But a team of researchers, led by a clinician scientist at the Case Western Reserve University School of Dental Medicine, has discovered a noninvasive, low-cost test to detect oral cancer, monitor precancerous lesions and determine when a biopsy is warranted.
Their findings, published ...
Firearm access and gun violence exposure are common in Black and native communities
2024-03-04
A New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center study is the first to provide nationally representative data on gun use, storage and violence within Black and American Indian/Alaskan Native (AIAN) families.
Both Black and native communities have seen increasingly elevated rates of gun violence victimization, including homicide and suicide, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. In recent years, minorities have become more represented among new firearm owners. Despite this, research on firearm access, storage and use has focused on samples of white adults. This prevents understanding the access Black and native individuals have to firearms, whether they are stored ...
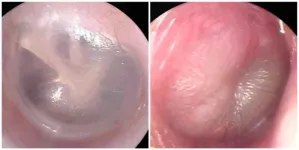
New AI smartphone tool accurately diagnoses ear infections
2024-03-04
A new cellphone app developed by physician-scientists at UPMC and the University of Pittsburgh, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to accurately diagnose ear infections, or acute otitis media (AOM), could help decrease unnecessary antibiotic use in young children, according to new research published today in JAMA Pediatrics.
AOM is one of the most common childhood infections for which antibiotics are prescribed but can be difficult to discern from other ear conditions without intensive training. The new AI tool, which makes a diagnosis by assessing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
Flagging claims about cancer treatment on social media as potentially false might help reduce spreading of misinformation, per online experiment with 1,051 US adults
Yawns in healthy fetuses might indicate mild distress
Conservation agriculture, including no-dig, crop-rotation and mulching methods, reduces water runoff and soil loss and boosts crop yield by as much as 122%, in Ethiopian trial
Tropical flowers are blooming weeks later than they used to through climate change
Risk of whale entanglement in fishing gear tied to size of cool-water habitat
Climate change could fragment habitat for monarch butterflies, disrupting mass migration
Neurosurgeons are really good at removing brain tumors, and they’re about to get even better
Almost 1-in-3 American adolescents has diabetes or prediabetes, with waist-to-height ratio the strongest independent predictor of prediabetes/diabetes, reveals survey of 1,998 adolescents (10-19 years
Researchers sharpen understanding of how the body responds to energy demands from exercise
New “lock-and-key” chemistry
Benzodiazepine use declines across the U.S., led by reductions in older adults
How recycled sewage could make the moon or Mars suitable for growing crops
Don’t Panic: ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’ has begun
A robust new telecom qubit in silicon
Vertebrate paleontology has a numbers problem. Computer vision can help
Reinforced enzyme expression drives high production of durable lactate-based polyester
In Rett syndrome, leaky brain blood vessels traced to microRNA
Scientists sharpen genetic maps to help pinpoint DNA changes that influence human health traits and disease risk
AI, monkey brains, and the virtue of small thinking
Firearm mortality and equitable access to trauma care in Chicago
Worldwide radiation dose in coronary artery disease diagnostic imaging
Heat and pregnancy
Superagers’ brains have a ‘resilience signature,’ and it’s all about neuron growth
New research sheds light on why eczema so often begins in childhood
Small models, big insights into vision
Finding new ways to kill bacteria
An endangered natural pharmacy hidden in coral reefs
[Press-News.org] Discovered a RNA molecule that helps prevent DNA replication errorsCima researchers identify a ribonucleic acid that could be used as a therapeutic target against cancer cells