(Press-News.org)
“[...] we posit that the majority of results in biology of aging may be irrelevant to the fundamental aim of this field and must be acknowledged appropriately.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 5, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 4, entitled, “On standardization of controls in lifespan studies.”
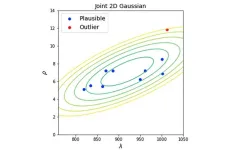
In this new paper, researchers Olga Spiridonova, Dmitrii Kriukov, Nikolai Nemirovich-Danchenko, and Leonid Peshkin from Harvard Medical School's Department of Systems Biology discuss the burgeoning field of the search for interventions to slow down, and even reverse, aging. Currently available literature cites hundreds of supposedly beneficial pharmacological and genetic interventions in model organisms: mice, rats, flies, and worms, where research into physiology is routinely accompanied by lifespan data. However, when experimental animals from one article live as long as controls from another article, comparing the results of interventions across studies can yield misleading outcomes.
“Theoretically, all lifespan data are ripe for re-analysis: we could contrast the molecular targets and pathways across studies and help focus the further search for interventions.”
Alas, the results of most longevity studies are difficult to compare. This is in part because there are no clear, universally accepted standards for conducting such experiments or even for reporting such data. The situation is worsened by the fact that the authors often do not describe experimental conditions completely. As a result, works on longevity make up a set of precedents, each of which might be interesting in its own right, yet incoherent and incomparable at least for the reason that in a general context, it may indicate, for example, not prolonging the life of an average organism, but compensating for any genetic abnormalities of a particular sample or inappropriate living conditions.
“Here we point out specific issues and propose solutions for quality control by checking both inter- and intra-study consistency of lifespan data.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205604
Corresponding Author: Leonid Peshkin
Corresponding Email: pesha@hms.harvard.edu
Keywords: animal disease models, survival modeling, aging, data standardization
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X, formerly Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
When biologist Elizabeth Carlen pulled up in her 2007 Subaru for her first look around St. Louis, she was already checking for the squirrels. Arriving as a newcomer from New York City, Carlen had scrolled through maps and lists of recent sightings in a digital application called iNaturalist. This app is a popular tool for reporting and sharing sightings of animals and plants.
People often start using apps like iNaturalist and eBird when they get interested in a contributory science project (also sometimes called a citizen science project). Armed with cellphones equipped with cameras and GPS, app-wielding volunteers can submit geolocated data that iNaturalist then translates into user-friendly ...
HOUSTON – (March 5, 2024) – Nai-Hui Chia, an assistant professor of computer science at Rice University, has won a National Science Foundation CAREER Award to develop a new theoretical framework to facilitate the development of efficient quantum algorithms for a range of problems in quantum physics and computer science as well as enhance the security of quantum cryptography.
The highly competitive grants are awarded each year to a selective cohort of about 500 early career faculty across all disciplines engaged in pathbreaking research and committed to growing their field through outreach and education.
“Quantum computing holds immense ...
WHAT:
The monthly dapivirine vaginal ring and daily oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine were each found to be safe for HIV prevention among cisgender women who started using one of them in their second trimester of pregnancy, according to findings presented today at the 2024 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Denver. Pregnant people are estimated to be three times more likely to acquire HIV through sexual intercourse than similarly aged people who ...
Michelson Medical Research Foundation (MMRF) and Human Immunome Project (HIP) have awarded Dr. Siyuan Ding (Washington University in St. Louis), Dr. Claire Otero (Weill Cornell Medicine), and Dr. Dennis Schaefer-Babajew (Rockefeller University) the Michelson Prizes: Next Generation Grants, the organizations announced today.
The $150,000 research grants are awarded annually to support early-career scientists advancing human immunology, vaccine discovery, and immunotherapy research for major global ...
Since more than a decade it has been possible for physicists to accurately measure the location of individual atoms to a precision of smaller than one thousandth of a millimeter using a special type of microscope. However, this method has so far only provided the x and y coordinates. Information on the vertical position of the atom – i.e., the distance between the atom and the microscope objective – is lacking. A new method has now been developed that can determine all three spatial coordinates of an atom with one single image. This method – developed by the University of Bonn and University of Bristol ...
CLEVELAND – New Cleveland Clinic-led research points to sildenafil (Viagra) as a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. The study provides evidence from computational models, insurance claims data and observations from brain cells in Alzheimer’s patients.
Sildenafil is the main component of drugs used to treat erectile dysfunction (Viagra) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (Revatio).
“Our findings provide further weight to re-purposing this existing FDA-approved drug as a novel treatment for Alzheimer’s, which is in great need of new therapies,” ...
Antarctic researchers hitched a lift on a cruise ship, and recommend this eco-friendly, collaborative approach to remote ocean science.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000348
Article Title: New methods of undertaking marine science in Antarctica using tourism vessels
Contact: Matthew Mulrennan; matt@kolossal.org
Author Countries: Canada, United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
March 5, 2024, Mountain View, CA – The moon lander Odysseus, known as Odie, touched down on the Moon's surface on February 22, becoming the first time the U.S. has landed on the Moon in more than 50 years and the first commercial moon lander to successfully land on the Moon. Along with its science payload, the spacecraft also brought along a fusion of art and space exploration, SETI Institute's Artist in Residence (SETI AIR), Felipe Pérez Santiago's Earthling Project, a collection of global musical compositions representing Earth's cultural ...
Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology researchers Jonathan Sweedler, a professor of chemistry, and Fan Lam, a professor of bioengineering, outlined how spatial omics technologies can reveal the molecular intricacy of the brain at different scales.
Their research appeared this month in Nature Methods.
The researchers and their colleagues used a biochemical imaging framework integrated with deep learning to create 3D molecular maps with cell specificity to better understand how the brain functions in health and disease. Their research is supported by a $3 million grant from ...
WHAT:
A weekly injection of semaglutide was safe and reduced the amount of fat in the liver by 31% in people with HIV and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), according to a presentation today at the 2024 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Denver. This is the first clinical trial of semaglutide for MASLD in people with HIV. The research was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and conducted in the United States and Brazil by ACTG, a global clinical trials network focused on HIV and other infectious diseases. ...