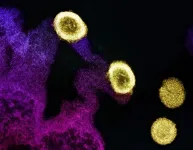
(Press-News.org) Antarctic researchers hitched a lift on a cruise ship, and recommend this eco-friendly, collaborative approach to remote ocean science.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000348
Article Title: New methods of undertaking marine science in Antarctica using tourism vessels
Contact: Matthew Mulrennan; matt@kolossal.org
Author Countries: Canada, United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
Antarctic researchers hitched a lift on a cruise ship, and recommend this eco-friendly, collaborative approach to remote ocean science
2024-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Odysseus has a new home and brings the Earthling Project along for the ride
2024-03-05
March 5, 2024, Mountain View, CA – The moon lander Odysseus, known as Odie, touched down on the Moon's surface on February 22, becoming the first time the U.S. has landed on the Moon in more than 50 years and the first commercial moon lander to successfully land on the Moon. Along with its science payload, the spacecraft also brought along a fusion of art and space exploration, SETI Institute's Artist in Residence (SETI AIR), Felipe Pérez Santiago's Earthling Project, a collection of global musical compositions representing Earth's cultural ...
Painting a molecular portrait of the brain with mass spectrometry and deep learning
2024-03-05
Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology researchers Jonathan Sweedler, a professor of chemistry, and Fan Lam, a professor of bioengineering, outlined how spatial omics technologies can reveal the molecular intricacy of the brain at different scales.
Their research appeared this month in Nature Methods.
The researchers and their colleagues used a biochemical imaging framework integrated with deep learning to create 3D molecular maps with cell specificity to better understand how the brain functions in health and disease. Their research is supported by a $3 million grant from ...
Semaglutide reduces severity of common liver disease in people with HIV
2024-03-05
WHAT:
A weekly injection of semaglutide was safe and reduced the amount of fat in the liver by 31% in people with HIV and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), according to a presentation today at the 2024 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Denver. This is the first clinical trial of semaglutide for MASLD in people with HIV. The research was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and conducted in the United States and Brazil by ACTG, a global clinical trials network focused on HIV and other infectious diseases. ...
The Lancet: Experts warn about the overmedicalisation of menopause and call for a new approach to how society views menopause and supports women as they age
2024-03-05
The Lancet: Experts warn about the overmedicalisation of menopause and call for a new approach to how society views menopause and supports women as they age
Menopause is a life stage for half the world’s population and is generally depicted in a negative way. However, women’s experiences of menopause are unique and vary hugely.
The Lancet 2024 Series on menopause argues that an over-simplified narrative of menopause as a health problem to be solved by replacing hormones is not based on evidence and deflects attention from the need for substantial societal shifts in how menopause, and midlife/older women in general, are viewed and treated around the world.
The ...
Researchers show that menopause does not always impact mental health
2024-03-05
A new review paper from authors at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and collaborators concludes that menopause does not uniformly elevate the risk of depression and other mental health conditions.
Menopause has long been thought to cause psychological distress, but a new review suggests that this is not always the case. The review, written by experts from Brigham Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, and international collaborators, is the third in a series of menopause-themed papers published in The ...
Evolving hydrogen-storage technology: guidelines developed for the design of anti-evaporation catalysts
2024-03-05
1. A research team consisting of NIMS and the Tokyo Institute of Technology has identified materials capable of catalyzing the conversion of ortho-hydrogen to para-hydrogen. These catalysts should be essential to the spread of mass-transportation/storage of liquid hydrogen.
2. Hydrogen is becoming widely accepted as an alternative energy source to fossil fuels. Its liquefaction (at temperatures below -253°C under pressures higher than one atmosphere) can dramatically reduce its volume, making it suitable for transportation and storage. Hydrogen molecules (H2)—each composed of two hydrogen atoms—exist in two isomeric forms: ortho- and para-H2. Under normal conditions, ...
Early retirement impacts mental health of blue-collar women more than white-collar peers
2024-03-05
Retirement is a major transition that can have a significant impact on a person’s life.
For some, retirement evokes thoughts of slowing down, relaxing, and enjoying more of what life has to offer. For others, ending a regular work schedule can create stress and uncertainties about being able to pay necessary bills and maintain adequate medical care.
A new study by researchers at the Yale School of Public Health examines how retirement affects mental health and related inpatient mental health care among female workers in China, ...
A smart molecule beats the mutation behind most pancreatic cancer
2024-03-05
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Media Contact: LEVI GADYE (628) 399-1046
Levi.Gadye@ucsf.edu
Subscribe to UCSF News
A Smart Molecule Beats the Mutation Behind Most Pancreatic Cancer
Scientists discover a new way to disarm a deadly protein that also appears in cancers of the lung, breast and colon.
UC San Francisco researchers have designed a candidate drug that could help make pancreatic cancer, which is almost always fatal, a treatable, perhaps even curable, condition.
The new molecule permanently modifies a wily cancer-causing ...
Using light to precisely control single-molecule devices
2024-03-05
In a new Nature Communications study, Columbia Engineering researchers report that they have built highly conductive, tunable single-molecule devices in which the molecule is attached to leads by using direct metal-metal contacts. Their novel approach uses light to control the electronic properties of the devices and opens the door to broader use of metal-metal contacts that could facilitate electron transport across the single-molecule device.
The challenge
As devices continue to shrink, their electronic ...
Boston College researchers use electrocatalysis for site-specific protein modification
2024-03-05
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (03/05/2024) – Boston College researchers used a mild charge of electricity to precisely modify proteins, a new tool that can be used to develop novel biotherapeutics and protein-based research tools, the team reported recently in the journal Nature Chemistry.
The team, led by BC professors of chemistry Abhishek Chatterjee and Eranthie Weerapana, developed and optimized a novel electrochemical protein labeling reaction called "eCLIC", that enables precise modification of site-specifically incorporated 5-hydroxytryptophan (5HTP) residues on many different proteins including full-length therapeutic antibodies.
“We used this strategy to generate ...