(Press-News.org) BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Anoles are the scuba-diving champions of the lizard world, able to stay underwater for more than 16 minutes. For animals whose body temperature depends on the environment, time spent in a cool running stream can have some tradeoffs, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
A recent study by Binghamton University doctoral candidate Alexandra M. Martin, Christopher K. Boccia of Queens University in Canada, and Binghamton University Assistant Research Professor of Biological Sciences Lindsey Swierk explores the balance between behavioral needs and physiological costs. “Diving behavior in semi-aquatic Anolis lizards results in heat loss with sex-specific cooling tolerance” recently appeared in Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
The three worked together on a 2021 paper in Current Biology, which established that the small South American lizards form a bubble of air over their noses as they dive and use it to breathe underwater. While their first line of defense is to run away on land, they will dive underwater to evade continued pursuit against predators — or researchers, said Martin, the lead author of the most recent article.
On average, the researchers discovered that male anoles stayed underwater for 20 fewer seconds than females. However, actual dive times and sex differences could be greater in the field, given the stress of predation and the cool temperatures of the flowing water in their habitat.
“This may not sound like very much, but biologically, 20 seconds could easily be the difference between life and death,” Martin pointed out. “A hungry bird may decide that searching for an extra 20 seconds simply isn’t worth the energy it might cost and would rather search for better luck downstream.”
Diving, however, comes at a cost: up to a 6°C drop in body temperature. Reptiles are ectotherms which rely on their external environment to maintain body temperature. Remaining in cool water can potentially affect a range of bodily functions, including muscle function — critical for escaping predation.
Recouping body heat isn’t easy for anoles, either. Temperatures are mild at the researchers’ higher-elevation study sites in Costa Rica, with an average day at around 70 degrees Fahrenheit.
“Semi-aquatic anoles seem to have evolved a sex-specific tradeoff between finding safety underwater and retaining body heat on land. This represents what behavioral ecologists call an ‘optimization problem,’ where animals have to balance the costs and benefits of performing particular behaviors,” Swierk said.
In their study, the researchers didn’t find any evidence of sex differences in oxygen consumption, which suggests that other factors drive the sex difference in dive times, Swierk said.
In species such as Anolis aquaticus, males are the showier sex while females are the choosier sex, Martin explained. Females invest more energy in producing offspring, whereas males spend more on courtship and mating. By shortening their dives, males conserve body heat and physiological capacity, which may minimize the “time out” period, as their muscles recover from the cool water.
Longer dives, however, mean that it’s less likely for a predator to be waiting once the anole returns to the surface. Females appear to trade the physiological cost of cool water for that extra safety, since they don’t face the same pressure as males to look for eligible mates or defend territory.
Like little scuba divers, anoles maintain a “dry suit” of air underwater, which may help them retain some heat. The researchers plan to explore the function and mechanisms of this trait and others more fully in future research, Swierk said.
“The ways that animals can adapt to environmental pressures are astounding and have continued to inspire humans to push the boundaries of bio-inspired design,” Swierk said. “We are curious and excited to explore these ideas in the future.”
END
Research explores the cooling effects of ‘scuba-diving’ in lizards
Strategy to hide from predators can cause up to a 6°C drop in body temperature, representing an ‘optimization problem’ for diving lizards
2024-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gender gap on Wikipedia
2024-03-05
Since it was created in 2001, Wikipedia has become a key element of the modern public sphere, which has revolutionized the way we create and share information. However, it has defects when it comes to its decentralization and flexibility, specially regarding inclusion and diversity.
Some gender biases that stand out are shown in its content and its editorial participation. It has a low percentage of women’s biographies and an unequal representation in editing. Also, there are gaps in the gender representation regarding its content, biases in editing and participation, as well as imbalances in readership.
These ...
Scientists to study real-world eating behaviors using wearable sensors and artificial intelligence
2024-03-05
A pedometer measures your steps, but what if you had a similar automated device to measure your eating behavior? Evidence from nutritional studies has long shown that the speed, timing and duration of an individual’s eating behavior are strongly related to obesity and other health issues. While eating behaviors can be accurately measured in a controlled laboratory setting, a blind spot exists when researchers attempt to study how participants actually eat “in the wild.”
A new National Institutes ...
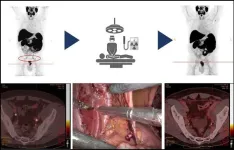
Radioguided surgery accurately detects and removes metastatic lymph nodes in newly diagnosed prostate cancer patients
2024-03-05
Reston, VA — Radioguided surgery can detect and remove metastatic pelvic lymph nodes in patients newly diagnosed with prostate cancer, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Targeting the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), which is overexpressed in most prostate cancer patients, radioguided surgery can improve nodal staging to guide treatment recommendations for this important patient population.
In newly diagnosed prostate cancer patients, nodal involvement correlates with recurrence, and determining if lymph node metastases are present and where they ...
Aluminum nanoparticles make tunable green catalysts
2024-03-05
HOUSTON – (March 5, 2024) – Catalysts unlock pathways for chemical reactions to unfold at faster and more efficient rates, and the development of new catalytic technologies is a critical part of the green energy transition.
The Rice University lab of nanotechnology pioneer Naomi Halas has uncovered a transformative approach to harnessing the catalytic power of aluminum nanoparticles by annealing them in various gas atmospheres at high temperatures.
According to a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Rice ...
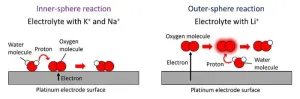
Electrolyte cation types control electrochemical reactions on an electrode surface
2024-03-05
1. An international research group consisting of NIMS and the Finnish University of Jyväskylä has discovered through its electrode-electrolyte system research that electron and proton (i.e., hydrogen ion) transfer mechanisms during oxygen reduction reactions (ORRs) on electrode surfaces vary depending on the types of cations dissolved in the electrolytic solution. These results suggest that the energy conversion efficiencies and selectivity of electrochemical systems (e.g., fuel cells and water electrolysis hydrogen production systems) can be improved by selecting optimal reaction pathways and that this could be achieved without using expensive electrode ...
The dangers of misaligned product co-development contracts—and how they can derail innovation in high-tech firms
2024-03-05
Researchers from Mansoura University and University of Guelph published a new Journal of Marketing study that examines how misaligned contracts can erode innovation outcomes of high-tech firms.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Collaborating to Innovate: Balancing Strategy Dividend and Transactional Efficiencies” and is authored by Nehal Elhelaly and Sourav Ray.
When a giant multinational like Unilever partners with one of its major suppliers, such as the industrial enzyme-producer Novozyme, the collaboration can fast-track ...
New publication highlights urgency of parasitic wasp release to save native bird
2024-03-05
DENVER/March 5, 2024 – Researchers with the University of Minnesota, funded by Morris Animal Foundation, hope to release highly-specialized parasitic wasps to serve as a biological control method to save Darwin’s finches from a dire threat: the invasive avian vampire fly, Philornis downsi.
This species has been devastating finch populations on the Galapagos Islands by laying eggs in their nests, with the emerging larvae harming the nestlings.
To protect these iconic birds and other endemic species impacted by the fly, ...
Tiny worms tolerate chornobyl radiation
2024-03-05
The 1986 disaster at the Chornobyl nuclear power plant transformed the surrounding area into the most radioactive landscape on Earth. Humans were evacuated, but many plants and animals continue to live in the region, despite the high levels of radiation that persist nearly four decades later.
A new study led by researchers at New York University finds that exposure to chronic radiation from Chornobyl has not damaged the genomes of microscopic worms living there today—which doesn’t mean that the region is safe, the scientists caution, but suggests that these worms are exceptionally resilient.
In ...
Restoration of degraded areas in semi-arid region contributes to ‘return’ of soil microorganisms, study shows
2024-03-05
Strategies deployed for the restoration of degraded land have had promising results in Brazil’s semi-arid region, improving the microbial properties of the soil and contributing to a return of native ecosystem services. The techniques include removal of cattle or restriction of their access to specific areas of pasture; cultivation of cover crops; and terracing to control erosion. Recovery of soil microbial properties maintains biodiversity and raises crop yields, contributing to agricultural ...
New research details negative consumer impacts of BLM support on major companies and brands
2024-03-05
INFORMS Journal Marketing Science New Study Key Takeaways:
Brands that supported BLM on social media during the height of the movement suffered negative impacts on social media.
Negative impacts were felt from both Democratic and Republican consumers.
The ‘bandwagon effect’ was one of the more significant factors.
Some brands with more historical prosocial posting on social media and socially oriented missions suffer less from the negative effects and may even benefit from supporting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Research explores the cooling effects of ‘scuba-diving’ in lizardsStrategy to hide from predators can cause up to a 6°C drop in body temperature, representing an ‘optimization problem’ for diving lizards