Eating habits, physical activity practice and clinical prognosis of colorectal cancer patients with overweight/obesity
2024-03-07
(Press-News.org) Background and objectives
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease associated with the development of several other diseases, including cancer. The present study aims to evaluate the eating habits, physical activity, and clinical profiles of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with overweight/obesity.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with data collected from the medical records of patients diagnosed with CRC (n = 41) from June 2019 to June 2022. Additionally, a questionnaire (n = 35) was applied to gather information on eating habits and physical activity. The data were subdivided into two groups of CRC patients: eutrophic and overweight/obesity. The results were presented as frequency distribution in percentage (%), mean ± standard deviation, or median and interquartile range.
Results
All patients presented adenocarcinoma-type; most were in stages 3 and 4 and underwent surgery and chemotherapy. The overweight/obesity group showed a higher prevalence of metastasis, recurrence, and death compared to the eutrophic group. Ninety-six percent of patients demonstrated the need to reevaluate their eating habits, and the overweight/obesity group presented a significantly lower consumption of vegetables. Walking was the most commonly practiced physical activity both before and after diagnosis. However, both groups experienced a reduction in physical activity after CRC diagnosis, especially in the overweight/obesity group, in which both the frequency (p = 0.001) and duration of physical activity (p = 0.0005) significantly decreased.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study revealed that a majority of patients diagnosed with CRC were male, overweight/obese, ∼48 years old, Hispanic, married, and living in the city of Sinop-MT. All patients were diagnosed with adenocarcinoma type, with most presenting tumor stages 3 and 4. The overweight/obesity group presented higher percentages of metastasis and deaths, although no statistical difference was observed.
The majority of patients did not exhibit healthy eating habits and did not engage in physical activity regularly, which is essential to prevent tumor development. Both groups exhibited similar eating habits, with the majority indicating a need to improve their eating quality, adopt healthier habits, or pay more attention to consumption. Furthermore, the overweight/obesity group reported consuming fewer vegetables daily. Only 57% of patients reported practicing physical activity before their CRC diagnosis. Subsequently, after the diagnosis, both the frequency and duration of these activities decreased, and these variables were significantly different in the overweight/obesity group.
All these results highlight the important and urgent need to improve eating habits, encourage physical activity, and control body weight to prevent tumor development, especially in those with CRC. Such interventions hold the potential to improve the prognosis and quality of life of patients.
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2835-3315/CSP-2023-00009S
The study was recently published in the Cancer Screening and Prevention.
Cancer Screening and Prevention (CSP) publishes high-quality research and review articles related to cancer screening and prevention. It aims to provide a platform for studies that develop innovative and creative strategies and precise models for screening, early detection, and prevention of various cancers. Studies on the integration of precision cancer prevention multiomics where cancer screening, early detection and prevention regimens can precisely reflect the risk of cancer from dissected genomic and environmental parameters are particularly welcome.
Follow us on X: https://twitter.com/xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/xia&he-publishing-inc/
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-07
Endometriosis is a chronic condition affecting women, often resulting in painful symptoms such as menstrual cramps and pelvic pain. Pain caused by endometriosis significantly lowers the quality of life and reproductive health of affected women, with around one-third of women still experiencing pain and discomfort despite treatment. While hormonal therapies and surgeries are common treatments, they often do not result in complete alleviation of symptoms. Effectively managing pain is, therefore, crucial for managing ...
2024-03-07
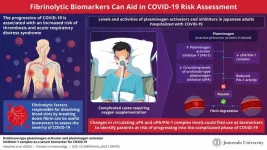
The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare systems has been significant. The sudden surge in infected cases overwhelmed hospitals and disrupted routine healthcare services, thus further worsening public health. Managing patients, too, has been challenging due to the variation of COVID-19 symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, that require medical intervention.
To help hospitals prioritize patients in need of care, researchers have been looking into various biological markers that can determine the risk of the disease becoming more severe. Among these, proteins in the blood related to blood clot formation, increased inflammation, and ...
2024-03-07
Spintronics is a field that deals with electronics that exploit the intrinsic spin of electrons and their associated magnetic moment for applications such as quantum computing and memory storage devices. Owing to its spin and magnetism exhibited in its insulator-metal phase transition, the strongly correlated electron systems of nickel oxide (NiO) have been thoroughly explored for over eight decades. Interest in its unique antiferromagnetic (AF) and spin properties has seen a revival lately, since NiO is a potential material for ultrafast spintronics devices.
Despite this rise in popularity, exploration of its surface magnetic properties using ...
2024-03-07
As role models and mentors for the youth, teachers play an important role in guiding children into well-rounded adults. However, excessive workloads and high skill expectations have allegedly led to teacher shortages in Japan. In 2022, the Ministry of Education Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) reported a record low in applicants for primary school teaching positions, and a survey from the same year revealed that 65.8% of 924 full-time educators expressed a desire to quit due to overwhelming demands.
To address the teacher shortage, Associate Professor Akihiro Saito from ...
2024-03-07
The James Webb Space Telescope makes one of the most unexpected findings within its first year of service: A high number of faint little red dots in the distant Universe could change the way we understand the genesis of supermassive black holes. The research, led by Jorryt Matthee, Assistant Professor in astrophysics at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), is now published in The Astrophysical Journal.
A bunch of little red dots found in a tiny region of our night sky might be an unexpected breakthrough for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) within its first year of service. These objects were indistinguishable from normal galaxies through the ...
2024-03-07
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Los Alamos National Laboratory have used machine learning to create a model that can simulate reactive processes in a diverse set of organic materials and conditions.
"It's a tool that can be used to investigate more reactions in this field," said Shuhao Zhang, a graduate student in Carnegie Mellon University's Department of Chemistry. "We can offer a full simulation of the reaction mechanisms."
Zhang is the first author on the paper that explains the creation and results of this new machine learning model, ...
2024-03-07
Common inherited genetic factors that predict cancer risk in the general population may also predict elevated risk of new cancers among childhood cancer survivors, according to a study led by researchers at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health. The findings, published March 7, 2024, in Nature Medicine, provide additional evidence that genetics may play an important role in the development of subsequent cancers in survivors of childhood cancer and suggest that common inherited variants could potentially inform screening and long-term ...
2024-03-07
[Vienna, March 5 2024] — The world population is aging at an increasing pace. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2023, one in six people were over 60 years old. By 2050, the number of people over 60 is expected to double to 2.1 billion.
“As age increases, the risk of multiple, often chronic diseases occurring simultaneously—known as multimorbidity—significantly rises,” explains Elma Dervic from the Complexity Science Hub (CSH). Given the demographic shift we are facing, this poses several challenges. On one hand, multimorbidity diminishes ...
2024-03-07
LOS ANGELES — A pioneering Phase 1 CAR T cell therapy trial for the treatment of glioblastoma at City of Hope, one of the largest cancer treatment and research organizations in the United States, demonstrates promising clinical activity against incurable brain tumors, according to research published today in Nature Medicine.
The study, which is the largest reported trial to date of CAR T therapy for solid tumors, evaluated CAR T cells engineered to target the tumor-associated antigen interleukin-13 receptor alpha 2 (IL13Rα2), a product invented at City of Hope and exclusively licensed by Mustang Bio Inc. (Nasdaq: MBIO), a Fortress Biotech Inc. (Nasdaq: ...
2024-03-07
The findings reveal a troubling surge in cases of syphilis, gonorrhoea, and chlamydia, indicating a pressing need for heightened awareness of STI transmission, and the need to enhance robust prevention, access to testing, and effective treatment to address this public health challenge.
In 2022, the number of reported cases saw a significant increase compared to the previous year, with gonorrhoea cases rising by 48%, syphilis cases by 34%, and chlamydia cases by 16%. In addition, cases of lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) and congenital syphilis (caused by transmission from mother to fetus) have also substantially increased.
These trends underscore the urgent need for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Eating habits, physical activity practice and clinical prognosis of colorectal cancer patients with overweight/obesity