An increase in the number of extreme cold days in North China during 2003–2012
2024-03-08
(Press-News.org)
How extreme weather and climate events change is an intriguing issue in the context of global warming. As IPCC AR6 points out, cold extremes have become less frequent and less severe since the 1950s, mainly driven by human-induced climate change. However, cold extremes could also exhibit robust interdecadal changes at regional scale.
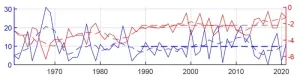
A recent study by researchers from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, presents robust interdecadal changes in the number of extreme cold days in winter over North China during 1989–2021, and the findings have been published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters. Specifically, the number of extreme cold days increased around the year 2003 and then decreased around the year 2013, with a value of 8.7 days per year during 1989–2002, 13.5 during 2003–2012, and 6.6 during 2013–2021.
During 2003–2012, the Siberian–Ural High strengthened and the polar jet stream weakened, which favored frequent cold air intrusion into North China, inducing more extreme cold days. In addition, the intensity of extreme cold days in North China showed no significant difference in the three periods. However, the related cold air could influence a larger area, which was especially the case for the stronger cold air center located to the west of Lake Baikal during 2013–2021.
The increase in the number of extreme cold days in North China in 2003–2012 probably arose from natural decadal variability. However, as pointed out by the corresponding author of this study, Prof. Yali Zhu, “This is still a challenging issue that needs further exploration to quantify the relative contributions of natural variability and human activity to regional extreme events.”
How extreme weather and climate events change is an intriguing issue in the context of global warming. As IPCC AR6 points out, cold extremes have become less frequent and less severe since the 1950s, mainly driven by human-induced climate change. However, cold extremes could also exhibit robust interdecadal changes at regional scale.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-08
This paper's objective is to show that the network of frequent relationships that is established between agents in coworking environments, through weak ties, increases the generation of ideas. Thus, the present work argues that collaborative spaces can expand individuals' creativity, as they constitute a social hub for exchanging experiences and visions between individuals from different social and professional backgrounds [Blagoev et al. (2019)]. Through frequent relationships and weak ties, these social connections allow individuals to access different levels of insights and inspirations that make it possible to ...
2024-03-08
The chance sighting of a dead snake beside a sandy track in remote Western Australia, and the investigation of its stomach contents, has led Curtin University researchers to record the first known instance of a spotted mulga snake consuming a pygmy spiny-tailed skink, raising concerns for a similar-looking, endangered lizard species.
Lead researcher Dr Holly Bradley from Curtin’s School of Molecular and Life Sciences said the discovery of the partially digested pygmy spiny-tailed skink within the snake had implications for the vulnerable western spiny-tailed skink species.
“Found about 300km east ...
2024-03-08
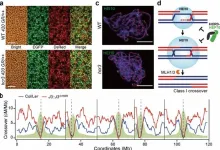
Movies such as ‘X-Men,’ ‘Fantastic Four,’ and ‘The Guardians,’ which showcase vibrant mutant heroes, have captivated global audiences. Recently, a high-throughput genetic screening of meiotic crossover rate mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana garnered the interest of the academic community by unraveling a century-old mystery in the life sciences.
A research team, consisting of Professor Kyuha Choi, Dr. Jaeil Kim, and PhD candidate Heejin Kim from the Department ...
2024-03-08
A University of Colorado Department of Medicine faculty member says she and her colleagues have identified the means in which bacteria in the digestive system can break down tryptophan in the diet into an inflammatory chemical that primes the immune system towards arthritis.
The research was co-authored by Kristine Kuhn, MD, PhD, Scoville Endowed Chair and head of the CU Division of Rheumatology. Several of her division colleagues collaborated on the paper, which was published in February in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid found in many protein-rich foods, including meats, fish, dairy products, and certain seeds and nuts. It has many uses in the ...
2024-03-08
Adults who had amblyopia (‘lazy eye’) in childhood are more likely to experience hypertension, obesity, and metabolic syndrome in adulthood, as well as an increased risk of heart attack, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
In publishing the study in eClinicalMedicine, the authors stress that while they have identified a correlation, their research does not show a causal relationship between amblyopia and ill health in adulthood.
The researchers analysed data from more than 126,000 participants aged 40 to 69 years old from the UK Biobank cohort, who had undergone ocular examination.
Participants ...
2024-03-08
A new psychological treatment for children with epilepsy, developed by a UCL-led team of scientists, has been shown to reduce mental health difficulties compared to standard care, a new study finds.
Mental health problems such as worries, low mood and behaviour problems are more common in children and young people with brain conditions such as epilepsy, than in the general population – with up to 60% of those with epilepsy having associated mental health disorders and many having more than one mental ...
2024-03-08
Is obesity passed down the generations? Individuals are much more likely to be living with obesity in middle age if their parents were living with obesity, Norwegian research finds
Embargo: 2301H UK time Thursday 7 March
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Individuals have six times the odds of living with obesity in middle age if both their parents lived with obesity at that age, ...
2024-03-07
Waltham — February 21, 2024 — African American patients with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) are less likely to receive surgical treatment, reports the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our study shows significant race- and gender-related differences in treatment choices among Medicaid beneficiaries with CTS," comments ASPS Member Surgeon Rachel C. Hooper, MD, of University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. ...
2024-03-07
Waltham — February 21, 2024 — For women undergoing autologous breast reconstruction – reconstruction using the patient's own tissues, rather than implants – the risks of overall and specific complications are increased at higher body mass index (BMI) levels, reports the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our study clarifies the impact of high BMI as a risk factor for adverse outcomes of autologous breast reconstruction," comments senior author Merisa Piper, MD, of ...
2024-03-07
Waltham — March 7, 2024 — In caring for transgender and gender diverse (TGD) people, psychiatrists should focus on alleviating the sequelae of gender minority stress, with the goal of promoting resilience, according to a review published in Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer.
"We envision a role for psychiatry that goes beyond gatekeeping gender-affirming hormone therapy and surgeries," says Alex Keuroghlian, MD, MPH, Michele and Howard J. Kessler Chair and Director of the Division of Public and Community Psychiatry at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] An increase in the number of extreme cold days in North China during 2003–2012