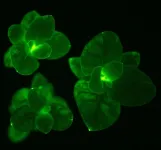
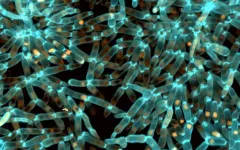
(Press-News.org) New research from Oregon Health & Science University describes the science behind a promising technique to treat infertility by turning a skin cell into an egg that is capable of producing viable embryos.
Researchers at OHSU documented in vitro gametogenesis, or IVG, in a mouse model through the preliminary steps of a technique that relies upon transferring the nucleus of a skin cell into a donated egg whose nucleus has been removed. Experimenting in mice, researchers coaxed the skin cell’s nucleus into reducing its chromosomes by half, so that it could then be fertilized by a sperm cell to create a viable embryo.
The study published today in the journal Science Advances.
“The goal is to produce eggs for patients who don’t have their own eggs,” said senior author Shoukhrat Mitalipov, Ph.D., director of the OHSU Center for Embryonic Cell and Gene Therapy.
The technique could be used by women of advanced maternal age or for those who are unable to produce viable eggs due to previous treatment for cancer or other causes. It also raises the possibility of men in same-sex relationships having children who are genetically related to both parents.
Rather than attempting to differentiate induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPSCs, into sperm or egg cells, OHSU researchers are focused on a technique based on somatic cell nuclear transfer, in which a skin cell nucleus is transplanted into a donor egg stripped of its nucleus. In 1996, researchers famously used this technique to clone a sheep in Scotland named Dolly.
In that case, researchers created a clone of one parent.
In contrast, the OHSU study described the result of a technique that resulted in embryos with chromosomes contributed from both parents. The process involves three steps:
Researchers transplant the nucleus of a mouse skin cell into a mouse egg that is stripped of its own nucleus.
Prompted by cytoplasm — liquid that fills cells — within the donor egg, the implanted skin cell nucleus discards half of its chromosomes. The process is similar to meiosis, when cells divide to produce mature sperm or egg cells. This is the key step, resulting in a haploid egg with a single set of chromosomes.
Researchers then fertilize the new egg with sperm, a process called in vitro fertilization. This creates a diploid embryo with two sets of chromosomes — which would ultimately result in healthy offspring with equal genetic contributions from both parents.
OHSU researchers previously demonstrated the proof of concept in a study published in January 2022, but the new study goes further by meticulously sequencing the chromosomes.
The researchers found that the skin cell’s nucleus segregated its chromosomes each time it was implanted in the donor egg. In rare cases, this happened perfectly, with one from each pair of matching egg and sperm chromosomes.
“This publication basically shows how we achieved haploidy,” Mitalipov said. “In the next phase of this research, we will determine how we enhance that pairing so each chromosome-pair separates correctly.”
Laboratories around the world are involved in a different technique of IVG that involves a time-intensive process of reprogramming skin cells to become iPSCs, and then differentiating them to become egg or sperm cells.
“We’re skipping that whole step of cell reprogramming,” said co-author Paula Amato, M.D., professor of obstetrics and gynecology in the OHSU School of Medicine. “The advantage of our technique is that it avoids the long culture time it takes to reprogram the cell. Over several months, a lot of deleterious genetic and epigenetic changes can happen.”
Although researchers are also studying the technique in human eggs and early embryos, Amato said it will be years before the technique would be ready for clinical use.
“This gives us a lot of insight,” she said. “But there is still a lot of work that needs to be done to understand how these chromosomes pair and how they faithfully divide to actually reproduce what happens in nature.”
The research was supported by Open Philanthropy; the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health, grant R01AG062459 and Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development of the National Institutes of Health, grant R01HD113562; Shoukhrat Mitalipov, Ph.D., holds an Innovation in Regulatory Science Award from Burroughs Wellcome Fund; and OHSU institutional funding. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
All research involving animal subjects at OHSU must be reviewed and approved by the university’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The IACUC’s priority is to ensure the health and safety of animal research subjects. The IACUC also reviews procedures to ensure the health and safety of the people who work with the animals. No live animal work may be conducted at OHSU without IACUC approval.
END
Research sheds light on new strategy to treat infertility
OHSU research advances technique to turn a skin cell into an egg; could help same-sex couples, others have children genetically related to both parents
2024-03-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The brain builds emotions regardless of the senses
2024-03-08
How much do our emotions depend on our senses? Does our brain and body react in the same way when we hear a fearful scream, see an eerie shadow, or smell a sinister odor? And does hearing an upbeat music or seeing a colorful landascape bring the same joy?
In an innovative study published in Science Advances, researchers have unveiled new insights into the intricate relationship between emotion and perception.
Led by a team of Italian neuroscientists from the IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, and conducted in collaboration with the University of Turin, the research project investigates whether the brain employs sensory-specific or abstract codes to construct ...
Harnessing the mechanisms of fungal bioluminescence to confer autonomous luminescence in plants and animal cells
2024-03-08
In a striking new study published today in Science Advances, a team of synthetic biologists led by Karen Sarkisyan at the MRC Laboratory of Medical Sciences, have reported the discovery of multiple plant enzymes – hispidin synthases – that can perform the most complex reaction of the bioluminescence pathway. This discovery is a significant milestone towards figuring out whether plants can natively produce all the molecules required for light emission. It also means that the glow of bioluminescent plants can now be more closely aligned with their internal biology.
The technology reported in the paper is a hybrid ...
New study discovers how altered protein folding drives multicellular evolution
2024-03-08
Researchers have discovered a mechanism steering the evolution of multicellular life. They identified how altered protein folding drives multicellular evolution.
In a new study led by researchers from the University of Helsinki and the Georgia Institute of Technology, scientists turned to a tool called experimental evolution. In the ongoing Multicellularity Long Term Evolution Experiment (MuLTEE), laboratory yeast are evolving novel multicellular functions, enabling researchers to investigate how they arise.
The study puts the spotlight on the regulation of proteins in understanding evolution.
"By demonstrating the effect of protein-level ...
Socially prescribed creative play boosts parents’ and children’s wellbeing
2024-03-08
University of Leeds news
For immediate release
Socially prescribed creative play boosts parents’ and children’s wellbeing
Socially prescribed creative play helps children and their parents develop new skills and promotes wellbeing, a new study has found.
The University of Leeds-led study evaluated a five-week programme of arts-based play, including singing and music-making, for families of children aged up to three. It found that parents benefited from developing social networks and sharing experiences with each other, as well as learning creative approaches to parenting. ...
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks
2024-03-08
Quantum computers, which can solve several complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers, are expected to improve artificial intelligence (AI) applications deployed in devices like autonomous vehicles; however, just like their predecessors, quantum computers are vulnerable to adversarial attacks.
A team of University of Texas at Dallas researchers and an industry collaborator have developed an approach to give quantum computers an extra layer of protection against such attacks. Their solution, Quantum Noise Injection for Adversarial Defense (QNAD), counteracts the impact of ...
Rogue enzymes cause numerous diseases. A new method could help design drugs to treat them.
2024-03-08
Helicases are enzymes that unwind DNA and RNA. They’re central to cellular life, implicated in a number of cancers and infections—and, alas, extraordinarily difficult to target with drugs.
Now, new research provides a powerful platform for designing covalent inhibitors tailored to target helicases. The paper, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, describes how researchers used this innovative new platform to design molecules that take aim at helicases involved in COVID and certain cancers.
“High-resolution structural and biochemical data alone are not sufficient ...
Study shows how oestrogen protects against fatty liver
2024-03-08
New research from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden shows how oestrogen protects against MASLD, a fatty liver disease that has increased dramatically during the current obesity epidemic. The study, published in Molecular Systems Biology, shows how a new drug under development could become a future treatment for fatty liver disease and liver cancer.
The global obesity epidemic has resulted in a dramatic increase in fatty liver, a disease in which fat that does not fit into fat cells is stored in liver cells instead.
Since last year, fatty liver due to obesity (and not excessive alcohol consumption) is known as MASLD (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease). ...
Limited correlation between canine lymphoma and proximity to environmental toxins in new study
2024-03-08
DENVER/March 8, 2024 – As awareness of the health risks associated with radon and fracking exposure in connection to cancer continues to rise in human medicine, a recent study explored these ties with multicentric lymphoma, a prevalent canine cancer. Surprisingly, the study did not identify significant correlations between living near sources of environmental toxins, such as fracking by-products and radon, and dogs diagnosed with lymphoma.
The results of this study were published on Monday using data from Morris Animal Foundation’s Golden Retriever Lifetime Study, which enrolled dogs with multicentric lymphoma and matched unaffected ...
Bald eagles eat prairie dogs? Researchers underscore relationship between raptors and rodents in the southern plains
2024-03-08
We all know that bald eagles like fish. Few of us, however, picture them soaring over grasslands seeking out prairie dog snacks. In a new paper from the Journal of Raptor Research, lead author Courtney Duchardt and coauthors make the case that prairie dogs are an important resource for at least four species of raptors overwintering in the Southern Great Plains, bald eagles included. Their paper, titled “Overwintering Raptor Abundance and Community Composition in Relation to Prairie Dog Colonies in the Southern Great Plains,” explains the first broad scale look into the relationship between prairie dogs and their aerial predators, and illuminates ...
Facing illegal wildlife trade in the European union: A call for comprehensive measures
2024-03-08
New paper now published in Science proposes three measures the European Union should implement to improve open information, legality and sustainability of wildlife trade in the region.
Wildlife trade affects all kinds of species, from insects and fungi to large plants and mammals. The global trade of numerous species poses a significant threat to their survival, increasing their risk of extinction. The European Union is a major global hub for the illegal and unsustainable trade of those species whose international trade is not regulated by the Convention on International Trade in Endangered ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
[Press-News.org] Research sheds light on new strategy to treat infertilityOHSU research advances technique to turn a skin cell into an egg; could help same-sex couples, others have children genetically related to both parents