(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Tumors can carry mutations in hundreds of different genes, and each of those genes may be mutated in different ways — some mutations simply replace one DNA nucleotide with another, while others insert or delete larger sections of DNA.
Until now, there has been no way to quickly and easily screen each of those mutations in their natural setting to see what role they may play in the development, progression, and treatment response of a tumor. Using a variant of CRISPR genome-editing known as prime editing, MIT researchers have now come up with a way to screen those mutations much more easily.
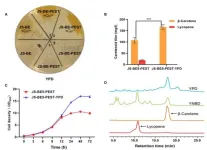
The researchers demonstrated their technique by screening cells with more than 1,000 different mutations of the tumor suppressor gene p53, all of which have been seen in cancer patients. This method, which is easier and faster than any existing approach, and edits the genome rather than introducing an artificial version of the mutant gene, revealed that some p53 mutations are more harmful than previously thought.
This technique could also be applied to many other cancer genes, the researchers say, and could eventually be used for precision medicine, to determine how an individual patient’s tumor will respond to a particular treatment.
“In one experiment, you can generate thousands of genotypes that are seen in cancer patients, and immediately test whether one or more of those genotypes are sensitive or resistant to any type of therapy that you’re interested in using,” says Francisco Sanchez-Rivera, an MIT assistant professor of biology, a member of the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, and the senior author of the study.
MIT graduate student Samuel Gould is the lead author of the paper, which appears today in Nature Biotechnology.
Editing cells
The new technique builds on research that Sanchez-Rivera began 10 years ago as an MIT graduate student. At that time, working with Tyler Jacks, the David H. Koch Professor of Biology, and then-postdoc Thales Papagiannakopoulos, Sanchez-Rivera developed a way to use CRISPR genome-editing to introduce into mice genetic mutations linked to lung cancer.
In that study, the researchers showed that they could delete genes that are often lost in lung tumor cells, and the resulting tumors were similar to naturally arising tumors with those mutations. However, this technique did not allow for the creation of point mutations (substitutions of one nucleotide for another) or insertions.
“While some cancer patients have deletions in certain genes, the vast majority of mutations that cancer patients have in their tumors also include point mutations or small insertions,” Sanchez-Rivera says.
Since then, David Liu, a professor in the Harvard University Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology and a core institute member of the Broad Institute, has developed new CRISPR-based genome editing technologies that can generate additional types of mutations more easily. With base editing, developed in 2016, researchers can engineer point mutations, but not all possible point mutations. In 2019, Liu, who is also an author of the Nature Biotechnology study, developed a technique called prime editing, which enables any kind of point mutation to be introduced, as well as insertions and deletions.
“Prime editing in theory solves one of the major challenges with earlier forms of CRISPR-based editing, which is that it allows you to engineer virtually any type of mutation,” Sanchez-Rivera says.
When they began working on this project, Sanchez-Rivera and Gould calculated that if performed successfully, prime editing could be used to generate more than 99 percent of all small mutations seen in cancer patients.
However, to achieve that, they needed to find a way to optimize the editing efficiency of the CRISPR-based system. The prime editing guide RNAs (pegRNAs) used to direct CRISPR enzymes to cut the genome in certain spots have varying levels of efficiency, which leads to “noise” in the data from pegRNAs that simply aren’t generating the correct target mutation. The MIT team devised a way to reduce that noise by using synthetic target sites to help them calculate how efficiently each guide RNA that they tested was working.
“We can design multiple prime-editing guide RNAs with different design properties, and then we get an empirical measurement of how efficient each of those pegRNAs is. It tells us what percentage of the time each pegRNA is actually introducing the correct edit,” Gould says.
Analyzing mutations
The researchers demonstrated their technique using p53, a gene that is mutated in more than half of all cancer patients. From a dataset that includes sequencing information from more than 40,000 patients, the researchers identified more than 1,000 different mutations that can occur in p53.
“We wanted to focus on p53 because it’s the most commonly mutated gene in human cancers, but only the most frequent variants in p53 have really been deeply studied. There are many variants in p53 that remain understudied,” Gould says.
Using their new method, the researchers introduced p53 mutations in human lung adenocarcinoma cells, then measured the survival rates of these cells, allowing them to determine each mutation’s effect on cell fitness.
Among their findings, they showed that some p53 mutations promoted cell growth more than had been previously thought. These mutations, which prevent the p53 protein from forming a tetramer — an assembly of four p53 proteins — had been studied before, using a technique that involves inserting artificial copies of a mutated p53 gene into a cell.
Those studies found that these mutations did not confer any survival advantage to cancer cells. However, when the MIT team introduced those same mutations using the new prime editing technique, they found that the mutation prevented the tetramer from forming, allowing the cells to survive. Based on the studies done using overexpression of artificial p53 DNA, those mutations would have been classified as benign, while the new work shows that under more natural circumstances, they are not.
“This is a case where you could only observe these variant-induced phenotypes if you're engineering the variants in their natural context and not with these more artificial systems,” Gould says. “This is just one example, but it speaks to a broader principle that we’re going to be able to access novel biology using these new genome-editing technologies.”
Because it is difficult to reactivate tumor suppressor genes, there are few drugs that target p53, but the researchers now plan to investigate mutations found in other cancer-linked genes, in hopes of discovering potential cancer therapies that could target those mutations. They also hope that the technique could one day enable personalized approaches to treating tumors.
“With the advent of sequencing technologies in the clinic, we'll be able to use this genetic information to tailor therapies for patients suffering from tumors that have a defined genetic makeup,” Sanchez-Rivera says. “This approach based on prime editing has the potential to change everything.”
###
The research was funded, in part, by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, an MIT School of Science Fellowship in Cancer Research, a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Hanna Gray Fellowship, the V Foundation for Cancer Research, a National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant, the Ludwig Center at MIT, a Koch Institute Frontier Award, the MIT Research Support Committee, and the Koch Institute Support (core) Grant from the National Cancer Institute.
END
Scientists develop a rapid gene-editing screen to find effects of cancer mutations
With the new technique, MIT researchers hope to identify mutations that could be targeted with new cancer therapies
2024-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rainforest's next generation of trees threatened 30 years after logging
2024-03-12
Rainforest seedlings are more likely to survive in natural forests than in places where logging has happened – even if tree restoration projects have taken place, new research shows.
Scientists monitored over 5,000 seedlings for a year and a half in North Borneo.
They studied a landscape containing both natural forest and areas logged 30 years ago – some of which were recovering naturally, while some had been restored by methods including tree planting.
A drought had triggered “mast fruiting” across ...
Expertly engineered saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strain in the optimized production of carotenoids
2024-03-12
More than 90% of the commercially available carotenoids are synthetically produced using chemicals. To meet the increasing demand for cost-effective natural compounds in carotenoid synthesis, researchers at Xiamen University, China, have developed an engineered S. cerevisiae yeast strain capable of selectively overproducing carotenoids. They redesigned the genomic sequence and critical pathways to optimize carotenoid production. This novel and successful research approach can be extended to other model ...
Beer byproduct behind Marmite could help us recycle metal waste
2024-03-12
When we recycle electronic devices we can no longer use, we expect to make the most out of the precious natural resources that went into building them. But electronic waste is notoriously difficult to recycle, because it’s hard to separate the different metals in the waste from each other. Scientists have now found a way of selectively capturing metals from a waste stream using spent brewer’s yeast, the same beer byproduct that goes into Marmite. Not only that: the yeast can be reused, making the process even more eco-friendly.
“Electronic waste is difficult to recycle because it is very heterogeneous,” said Dr Klemens Kremser ...
Guessing game: Response may bias understanding of future scenarios
2024-03-12
Does previous experience bias a person in future estimations? Yes, Osaka Metropolitan University researchers in Japan report, but only if the person engages higher processing powers by responding, as opposed to simply observing.
They made their findings through experiments involving participants estimating the number of dots flashed on a screen. Participants either had to input their estimate before making another estimate on a new set of dots or were not prompted to do anything but observe. The researchers found ...
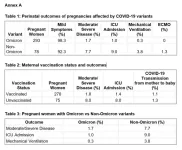
KKH-led study reveals low COVID-19 transmission rate from mothers to newborns
2024-03-12
11 March 2024, Singapore – A study[1] by KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital (KKH), Singapore General Hospital (SGH) and National University Hospital (NUH) has revealed that COVID-19 transmission from mothers to their newborns is low.
The study involving 371 women who had COVID-19 infection during pregnancy and their newborns found that only four infants or 1.1 per cent of the babies were diagnosed with COVID-19 after birth, of which three (1.1 per cent) were from mothers who were COVID-19 vaccinated and one infant (1.3 per cent) was from a mother who was not vaccinated.
Senior Author of the study, Dr Yeo Kee Thai, Senior Consultant, Department of Neonatology, KKH ...
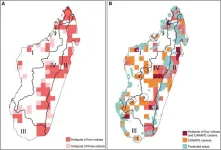
Scientists identify biodiversity conservation gaps in Madagascar
2024-03-12
Despite the importance of biodiversity and the urgency to conserve it, assessing what aspect of biodiversity requires the highest priority has proven complex, especially when conservation resources are limited. A new study published in Current Biology sheds light on this question.
Prof. CHEN Zhiduan's team from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IBCAS) and international collaborators have identified the spatial heterogeneity of biodiversity hotspots and endemism centers. With ...
Sting operation out of gas
2024-03-12
Kyoto, Japan -- Cells possess an innate immune system that defends against invasive pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. Previous studies have mapped out the cytoplasmic cGAS-STING pathway in the cytoplasm, known for responding to foreign nucleic acids, such as double-stranded DNA.
Micronuclei -- or MN, abnormal intracellular structures containing the cell's DNA -- have also been suspected of triggering the pathway. However, no conclusive evidence exists of pathway activation by MN-induced cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, or cGAS.
Now, Kyoto University and the AIRC Institute of Molecular Oncology, or IFOM, have ...
Have metalenses expanded their reach into the ultraviolet region?
2024-03-12
Ultraviolet rays find diverse applications in medical and healthcare, serving purposes such as disinfection, sterilization, and therapy. They are also used in the semiconductor industry for creating microcircuits and patterns. A metalens fabrication process, developed by a team of researchers at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), enables control over the optical properties of these UV rays. This innovation has garnered significant attention across industries, sparking interest in potential advancements.
A collaborative research team, comprising Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and the Department of Chemical Engineering ...
Key protein linked to immune disorders
2024-03-12
A new study highlights a potential therapeutic target for immune-related disorders, such as multiple sclerosis and asthma.
A new study has shed light on the importance of the protein STAP-1 in activating certain immune cells. Understanding the role of STAP-1 in these cells could give researchers a better glimpse into immune-related disorders and ways to treat them.
The researchers found that STAP-1 plays an important role in the activation of T cells, which are white blood cells that play a critical role in defending the body against infections and maintaining overall health. T cells are adept at recognizing foreign molecules that ...
COVID-19 had greater impact on life expectancy than previously known, but child mortality rates continued to decline during the pandemic
2024-03-12
**Embargo: 23:30 UK, 7:30 p.m. ET March 11, 2024**
***Please note the unusual embargo time for the United States due to daylight savings time***
Global Burden of Disease
COVID-19 had greater impact on life expectancy than previously known,
but child mortality rates continued to decline during the pandemic
A new study published in The Lancet reveals never-before-seen details about staggeringly high mortality from the COVID-19 pandemic within and across countries. Places such as Mexico City, Peru, and Bolivia had some of the largest drops in life expectancy from 2019 to 2021. The research, which presents updated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
[Press-News.org] Scientists develop a rapid gene-editing screen to find effects of cancer mutationsWith the new technique, MIT researchers hope to identify mutations that could be targeted with new cancer therapies