(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO—A multidisciplinary research team at Gladstone Institutes, led by Senior Investigator Katie Pollard, PhD, has received $5 million in funding through a newly launched grant program designed to ignite a fresh wave of cancer discoveries using computational biology and artificial intelligence.
The new Transformative Computational Biology Grant Program from the Biswas Family Foundation, in partnership with the nonpartisan think tank Milken Institute, is providing a total of nearly $14 million to five research groups.
At Gladstone, the grant establishes the Biswas Center for Transformative Computational Cancer Biology, where scientists will fuse powerful machine learning with cutting-edge experimental technologies to help identify and prioritize which research avenues are most likely to lead to success in the area of cancer diagnosis and treatment.
“Our tools and discoveries will be freely shared, fueling a global acceleration of cancer biology research and the development of therapies specialized to each type of cancer mechanism,” says Pollard, who also serves as director of the Gladstone Institute of Data Science and Biotechnology. “This should help patients and their doctors make well-informed decisions about cancer care.”
The new center’s suite of deep learning models is capable of performing trillions of editing experiments to generate and rank testable hypotheses about how changing a cell’s DNA will alter its function and interactions with other cells. Focused initially on colorectal and skin cancers, the group hopes to identify molecular mechanisms overlooked by other researchers and to develop a predictive understanding of how cancer immunotherapies work.
Notably, the Gladstone program is designed to apply equal research emphasis across rare cancer pathways and non-European genetic ancestries, which should generate much-needed information in these understudied areas.
And while the primary focus is cancer biology, the center has potential to advance medicine in many areas.
Sanjit Biswas, co-founder of the Biswas Family Foundation and CEO of Samsara, first crossed paths with Pollard last fall in Washington, D.C., when Pollard delivered an attention-getting presentation on computational biology at a workshop organized by the Milken Institute.
Biswas and his wife, Hope, an infectious disease epidemiologist, had recently established the Biswas Family Foundation and were looking to support scientific research and programs with the potential to improve lives on a global scale. Milken’s leadership thought Pollard’s data science programs meshed with the foundation’s priorities. And indeed, after studying Pollard’s proposal to accelerate cancer research with the aid of a computer framework and deep learning models, the Biswas team was more than intrigued.
“It’s cancer biology but it has the potential to advance medicine in many areas,” says Hope Biswas, PhD. “And, looking at it from a global health perspective, it’s really scalable and likely very cost effective.”
In addition to Pollard’s team at Gladstone, the Biswas Family Foundation awarded grants to research groups from Stanford University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Harvard University.
“The research and health ecosystem has entered an era where vast amounts of data are continuously being generated,” Sanjit Biswas says. “The convergence of powerful computers, big data, and AI is already transforming human health in remarkable ways. And when you amass a lot of smart people in a place like Gladstone, really interesting things are bound to happen.”
The center’s co-Investigators at Gladstone include: Alex Marson, MD, PhD, Barbara Engelhardt, PhD, Catherine Tcheandjieu Gueliatcha, DVM, PhD, Christina Theodoris, MD, PhD, Karin Pelka, PhD, Ryan Corces, PhD, Seth Shipman, PhD, and Vijay Ramani, PhD.
END
$5 million grant bets on computational biology, AI to change the future of cancer
The Biswas Family Foundation and Milken Institute announce funding to establish a center for computational cancer biology at Gladstone Institutes, led by Senior Investigator Katie Pollard
2024-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Integrating renewables and machine learning for improved grid stability
2024-03-12
In the race to achieve a net-zero future based on clean energy, renewable energy sources like solar and wind power have emerged as potential champions in the battle against climate change. However, as traditional synchronous generators are replaced by inverter-based renewable energy resources, the transition creates a low-inertia challenge within the existing power grids leading to stability and reliability concerns.
Xingpeng Li, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Houston, is working on a solution that will allow seamless integration of renewable energy ...
Global ecosystem contribute trillions in its services with key synergies and trade-offs
2024-03-12
Trade-offs and synergies between ecosystem services constitutes an important topic in ecosystem management. The value of each service is substantially influenced by human activities, and changes will affect human decisions. Given the variability in trade-offs and synergies, the simultaneous optimization of multiple ecosystem services presents a considerable challenge.
In a study published in Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, a team from the Chinese Academy of Environmental Planning, which has completed ...
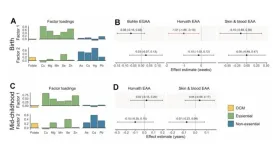
Association of prenatal vitamins and metals with epigenetic aging at birth and in childhood
2024-03-12
“[...] our findings support the hypothesis that the intrauterine environment, particularly essential and non-essential metals, affect epigenetic aging biomarkers across the life course.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 12, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 4, entitled, “Associations of prenatal one-carbon metabolism nutrients and metals with epigenetic aging biomarkers at birth and in childhood in a US cohort.”
Epigenetic gestational age acceleration (EGAA) at birth and epigenetic age acceleration (EAA) in childhood may be biomarkers of ...
Gun manufacturers’ ads appeal to women as ‘serious students’ of firearms to boost sales
2024-03-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Gun manufacturers are appealing to women as “serious students” of firearms in their advertising – a shift in strategy over the last two decades that may be contributing to increased gun sales, a new study shows.
From 2007 through 2022, women’s gun ownership rose from 16% to 22%, while the rate for men stayed roughly steady at 43%. And more than half of new gun owners in the United States between 2019 and 2021 were women.
“Those trends in gun ownership ...
In the resuscitation discussion, do words matter between doctors and patients?
2024-03-12
Adults 65 and older, who were hospitalized for a variety of medical conditions, had highly satisfying conversations about whether they wanted CPR, regardless of whether doctors used the terms “allow a natural death” or “do not resuscitate” for indicating no CPR, according to a pilot study by Rutgers Health researchers.
The study, published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, sought to determine the best language doctors could use when discussing a patient’s code ...
PPPL unveils new laboratory space to advance quantum information science
2024-03-12
Building on its more than 70 years pioneering the study of fusion energy, the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has added a new field to its research portfolio — quantum information science.
On March 11, PPPL opened its new Quantum Diamond Lab (QDL), a space devoted to studying and refining the processes involved in using plasma, the electrically charged fourth state of matter, to create high-quality diamond material for quantum information science applications. Scientists around the ...
Women with depression face higher cardiovascular risk than men
2024-03-12
People with depression face an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD); however, more women experience CVD following a depression diagnosis than men, according to a new study published today in JACC: Asia. The study investigates the connection between depression and CVD, shedding light on potential mechanisms that contribute to its sex-based differences and underscoring the importance of tailoring CVD prevention and management strategies according to sex-specific factors.
Depression is the third leading cause of morbidity worldwide. Prior research shows that it is associated with a heightened risk of cardiovascular events, ...
SLAS announces $100,000 graduate education fellowship grant awarded to Lan Mi of the University of Massachusetts Amherst
2024-03-12
Oak Brook, IL (March 12, 2024) – The Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening (SLAS) is pleased to announce Lan Mi, Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemistry from the University of Massachusetts Amherst (Amherst, Massachusetts, USA), as the 2024 SLAS Graduate Education Fellowship Grant recipient.
The SLAS grant will support Mi's research regarding the synthesis and applications of fluorogenic RNA aptamers for extensive in vitro and in vivo investigations. It will also support her work in developing and assessing fluorogenic RNA-based sensors, employing high-throughput ...
A ‘smart’ examination to improve livestock management efficiency
2024-03-12
A Texas A&M AgriLife animal nutritionist believes precision livestock management — utilizing an extra set of eyes and ears and a little artificial intelligence — can go a long way toward making today’s livestock operations more efficient.
Computer monitors and cameras, along with artificial intelligence, are part of a precision livestock management system being researched by Luis Tedeschi, Ph.D., in the Texas A&M Department of Animal Science. (Michael Miller/Texas A&M AgriLife)
Luis Tedeschi, Ph.D., Texas A&M AgriLife Research Fellow and Chancellor EDGES Fellow in the Texas A&M ...
JMIR Dermatology invites submissions on Diversity in Dermatology
2024-03-12
(Toronto, March 12, 2024) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue titled “Diversity in Dermatology” in JMIR Dermatology. The premier, peer-reviewed journal is indexed in Sherpa Romeo, Scopus, DOAJ, CABI, and PubMed Central/PubMed and is the official journal of the International Society of Digital Health in Dermatology (ISDHD).
Diversity plays a significant role in dermatology, influencing various aspects of health care delivery in community health. Current research consistently highlights the advantages of diversity in the health care sector in patient outcomes and dermatological research. JMIR Dermatology places a special emphasis on exchanging ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
Ancient mind-body practice proven to lower blood pressure in clinical trial
SwRI to create advanced Product Lifecycle Management system for the Air Force
Natural selection operates on multiple levels, comprehensive review of scientific studies shows
Developing a national research program on liquid metals for fusion
AI-powered ECG could help guide lifelong heart monitoring for patients with repaired tetralogy of fallot
Global shark bites return to average in 2025, with a smaller proportion in the United States
Millions are unaware of heart risks that don’t start in the heart
What freezing plants in blocks of ice can tell us about the future of Svalbard’s plant communities
A new vascularized tissueoid-on-a-chip model for liver regeneration and transplant rejection
Augmented reality menus may help restaurants attract more customers, improve brand perceptions
Power grids to epidemics: study shows small patterns trigger systemic failures
[Press-News.org] $5 million grant bets on computational biology, AI to change the future of cancerThe Biswas Family Foundation and Milken Institute announce funding to establish a center for computational cancer biology at Gladstone Institutes, led by Senior Investigator Katie Pollard