(Press-News.org)
“[...] our findings support the hypothesis that the intrauterine environment, particularly essential and non-essential metals, affect epigenetic aging biomarkers across the life course.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 12, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 4, entitled, “Associations of prenatal one-carbon metabolism nutrients and metals with epigenetic aging biomarkers at birth and in childhood in a US cohort.”
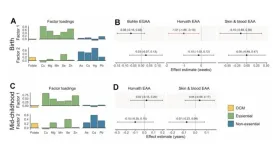
Epigenetic gestational age acceleration (EGAA) at birth and epigenetic age acceleration (EAA) in childhood may be biomarkers of the intrauterine environment. In this new study, researchers Anne K. Bozack, Sheryl L. Rifas-Shiman, Andrea A. Baccarelli, Robert O. Wright, Diane R. Gold, Emily Oken, Marie-France Hivert, and Andres Cardenas from Stanford University School of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Columbia University, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai investigated the extent to which first-trimester folate, B12, 5 essential and 7 non-essential metals in maternal circulation are associated with EGAA and EAA in early life.
“[...] we hypothesized that OCM [one-carbon metabolism] nutrients and essential metals would be positively associated with EGAA and non-essential metals would be negatively associated with EGAA. We also investigated nonlinear associations and associations with mixtures of micronutrients and metals.”
Bohlin EGAA and Horvath pan-tissue and skin and blood EAA were calculated using DNA methylation measured in cord blood (N=351) and mid-childhood blood (N=326; median age = 7.7 years) in the Project Viva pre-birth cohort. A one standard deviation increase in individual essential metals (copper, manganese, and zinc) was associated with 0.94-1.2 weeks lower Horvath EAA at birth, and patterns of exposures identified by exploratory factor analysis suggested that a common source of essential metals was associated with Horvath EAA. The researchers also observed evidence of nonlinear associations of zinc with Bohlin EGAA, magnesium and lead with Horvath EAA, and cesium with skin and blood EAA at birth. Overall, associations at birth did not persist in mid-childhood; however, arsenic was associated with greater EAA at birth and in childhood.
“Prenatal metals, including essential metals and arsenic, are associated with epigenetic aging in early life, which might be associated with future health.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205602
Corresponding Author: Andres Cardenas
Corresponding Email: andres.cardenas@stanford.edu
Keywords: epigenetic age acceleration, metals, folate, B12, prenatal exposures
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X, formerly Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Gun manufacturers are appealing to women as “serious students” of firearms in their advertising – a shift in strategy over the last two decades that may be contributing to increased gun sales, a new study shows.
From 2007 through 2022, women’s gun ownership rose from 16% to 22%, while the rate for men stayed roughly steady at 43%. And more than half of new gun owners in the United States between 2019 and 2021 were women.
“Those trends in gun ownership ...
Adults 65 and older, who were hospitalized for a variety of medical conditions, had highly satisfying conversations about whether they wanted CPR, regardless of whether doctors used the terms “allow a natural death” or “do not resuscitate” for indicating no CPR, according to a pilot study by Rutgers Health researchers.
The study, published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, sought to determine the best language doctors could use when discussing a patient’s code ...
Building on its more than 70 years pioneering the study of fusion energy, the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has added a new field to its research portfolio — quantum information science.
On March 11, PPPL opened its new Quantum Diamond Lab (QDL), a space devoted to studying and refining the processes involved in using plasma, the electrically charged fourth state of matter, to create high-quality diamond material for quantum information science applications. Scientists around the ...
People with depression face an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD); however, more women experience CVD following a depression diagnosis than men, according to a new study published today in JACC: Asia. The study investigates the connection between depression and CVD, shedding light on potential mechanisms that contribute to its sex-based differences and underscoring the importance of tailoring CVD prevention and management strategies according to sex-specific factors.
Depression is the third leading cause of morbidity worldwide. Prior research shows that it is associated with a heightened risk of cardiovascular events, ...
Oak Brook, IL (March 12, 2024) – The Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening (SLAS) is pleased to announce Lan Mi, Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemistry from the University of Massachusetts Amherst (Amherst, Massachusetts, USA), as the 2024 SLAS Graduate Education Fellowship Grant recipient.
The SLAS grant will support Mi's research regarding the synthesis and applications of fluorogenic RNA aptamers for extensive in vitro and in vivo investigations. It will also support her work in developing and assessing fluorogenic RNA-based sensors, employing high-throughput ...
A Texas A&M AgriLife animal nutritionist believes precision livestock management — utilizing an extra set of eyes and ears and a little artificial intelligence — can go a long way toward making today’s livestock operations more efficient.
Computer monitors and cameras, along with artificial intelligence, are part of a precision livestock management system being researched by Luis Tedeschi, Ph.D., in the Texas A&M Department of Animal Science. (Michael Miller/Texas A&M AgriLife)
Luis Tedeschi, Ph.D., Texas A&M AgriLife Research Fellow and Chancellor EDGES Fellow in the Texas A&M ...
(Toronto, March 12, 2024) JMIR Publications is pleased to announce a new theme issue titled “Diversity in Dermatology” in JMIR Dermatology. The premier, peer-reviewed journal is indexed in Sherpa Romeo, Scopus, DOAJ, CABI, and PubMed Central/PubMed and is the official journal of the International Society of Digital Health in Dermatology (ISDHD).
Diversity plays a significant role in dermatology, influencing various aspects of health care delivery in community health. Current research consistently highlights the advantages of diversity in the health care sector in patient outcomes and dermatological research. JMIR Dermatology places a special emphasis on exchanging ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- More than 20 million Americans undergo colonoscopy screenings every year, and in many of those cases, doctors end up removing polyps that are 2 cm or larger and require additional care. This procedure has greatly reduced the overall incidence of colon cancer, but not without complications, as patients may experience gastrointestinal bleeding both during and after the procedure.
In hopes of preventing those complications from occurring, researchers at MIT have developed a new gel, GastroShield, that can be sprayed onto the surgical sites through an endoscope. This gel forms a tough but flexible protective layer that ...
New study identifies ten key components that will promote the development and implementation of sustainable, equitable, climate-smart ocean planning initiatives around the globe.
In a paper published March 12 in npj Ocean Sustainability, the researchers outlined guidelines to support marine managers and planners on how to develop climate-smart ocean plans and put them into action. Led by Catarina Frazão Santos, researcher and professor at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Ciências ULisboa) and honorary research associate at the University of Oxford, the team ...
Irvine, Calif., March 12, 2024 — Scientists know relatively little about particles released into the air when a vehicle driver brakes, though evidence suggests those particles may be more harmful to health than particles exiting the tailpipe.
In a new study in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, University of California, Irvine researchers show how most of these particles emitted during light braking carry an electric charge – something that could potentially be ...