Under embargo until Wednesday 13 March 2024, 00:01 UK Time
Imported giant sequoia trees are well adapted to the UK, growing at rates close to their native ranges and capturing large amounts of carbon during their long lives, finds a new study led by UCL researchers with colleagues at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
The new research, published in Royal Society Open Science, found that the most massive species of redwood trees, Sequoiadendron giganteum, known as the giant sequoia, can potentially pull an average of 85 kilograms of carbon out of the atmosphere per year. Though introduced to the UK 160 years ago, this is the first time the trees’ growth rate and resilience in the UK have been analysed.
There are an estimated half a million redwoods in the UK and more are being planted, partly due to their public appeal. In the wild they are endangered with fewer than 80,000 giant sequoias remaining in their native California range.
Lead author Ross Holland, formerly a Master’s student at the UCL Department of Geography and now at East Point Geo, said: “Giant sequoias are some of the most massive organisms on Earth and in their native range make up some of the most carbon dense forests in the world due to their great age. We found that UK redwoods are well adapted to the UK and able to capture a large amount of carbon dioxide. We hope that these findings can help guide decisions on future tree planting and management.”
The researchers emphasise that the most effective way to mitigate climate change is by reducing carbon emissions from burning fossil fuels. Trees can help by absorbing carbon emissions, but they also provide other important climate, ecosystem and wellbeing benefits.
Giant sequoias grow quickly and are also some of the longest-lived organisms in the world, keeping up their rapid growth throughout their 3,000-plus year lives. They can grow up to 90 metres tall, and while not quite the tallest in the world (that title goes to their closely-related cousin the coastal redwood), their wide trunks grow out, giving them the greatest volumes. In addition, they’re fire resistant, able to survive blazes that would wipe out forests of other tree species.
The trees grow best in their native range in California’s Sierra Nevada mountains, so the researchers wanted to gauge how they fare under UK climates, which are milder and with a wider range of rainfall. They compiled the first dedicated map of giant sequoias in the UK, mapping nearly 5,000 individual known trees.
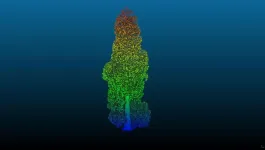
The team visited three groves of trees, located at Wakehurst, the wild botanic garden of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew in Sussex, Havering Country Park in Essex, and Benmore Botanical Garden in Scotland. They set up terrestrial laser scanners to map the trees in 3D, enabling them to measure the heights and volumes very accurately and to create 3D models of 97 representative trees.
Co-author Dr Phil Wilkes, formerly of UCL and now at Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, said: “Using the latest laser scanning technology has allowed us to accurately ‘weigh’ these massive trees without having to cut them down. This means we can measure many more trees as well as revisit them in the future.”
The tallest tree they found measured about 180 feet tall (54.87 metres) – giant compared with most native UK species, but dwarfed by their American counterparts. This is in part because of the UK sequoias’ youth: the oldest giant sequoias in the UK are those at Benmore, the earliest dating to 1863.
Knowing when the trees were planted allowed the team to calculate their average growth rates under the varying climate conditions between the three UK sites. They found that the trees at Kew and Benmore grew at similar rates as their US counterparts, although growing slightly taller and slimmer at Benmore compared to Wakehurst, while at Havering the trees grew more slowly, likely due to less rainfall in the region and competition from dense local woodland.
Though giant sequoia stack up well for sequestering carbon, the researchers caution that planting trees requires long-term commitment, and consideration needs to be given to how well they will thrive in the UK’s changing climate in the next 160 years and beyond.
Senior author, Professor Mat Disney (UCL Geography), said: “These results give us an important baseline for estimating how well giant sequoias are doing in the UK climate. Currently, these trees are probably more important for their aesthetic and historical interest than they are for solving the climate crisis. But as more are planted we need to know how they will grow.
“The history of these trees in Britain is fascinating – initially as symbols of wealth and power, through to now being widely planted in parks and woodlands. They are iconic, but there is almost no work on how fast they grow or how well they will do in the UK's changing climate. I find it amazing to see these giants dotted across the landscape and see how rapidly they are growing.”
This research was funded by NERC National Centre for Earth Observation (NCEO) and in conjunction with the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
Notes to Editors
For more information or to speak to the researchers involved, please contact Michael Lucibella, UCL Media Relations. T: +44 (0)75 3941 0389, E: m.lucibella@ucl.ac.uk
Ross Holland, et al. ‘Giant sequoia (Sequoiadendron giganteum) in the UK: carbon storage potential and growth rates’ will be published in Royal Society Open Science on Wednesday 13 March 2024, 00:01 UK time and is under a strict embargo until this time.
The DOI for this paper will be https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.ttdz08m3n
Additional material
Images available at: https://wwwapps-live.ucl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/dropbox/dropbox.cgi?state=pickup_info&id=138cea42
claim id: 138cea42
passcode: 5f150025
About UCL – London’s Global University
UCL is a diverse global community of world-class academics, students, industry links, external partners, and alumni. Our powerful collective of individuals and institutions work together to explore new possibilities.
Since 1826, we have championed independent thought by attracting and nurturing the world's best minds. Our community of more than 50,000 students from 150 countries and over 16,000 staff pursues academic excellence, breaks boundaries and makes a positive impact on real world problems.
The Times and Sunday Times University of the Year 2024, we are consistently ranked among the top 10 universities in the world and are one of only a handful of institutions rated as having the strongest academic reputation and the broadest research impact.
We have a progressive and integrated approach to our teaching and research – championing innovation, creativity and cross-disciplinary working. We teach our students how to think, not what to think, and see them as partners, collaborators and contributors.
For almost 200 years, we are proud to have opened higher education to students from a wide range of backgrounds and to change the way we create and share knowledge.
We were the first in England to welcome women to university education and that courageous attitude and disruptive spirit is still alive today. We are UCL.
www.ucl.ac.uk | Follow @uclnews on Twitter | Read news at www.ucl.ac.uk/news/ | Listen to UCL podcasts on SoundCloud | View images on Flickr | Find out what’s on at UCL Minds
About Kew Science
Kew Science is the driving force behind RBG Kew’s mission to understand and protect plants and fungi, for the well-being of people and the future of all life on Earth. Over 470 Kew scientists work with partners in more than 100 countries worldwide to halt biodiversity loss, uncover secrets of the natural world, and to conserve and restore the extraordinary diversity of plants and fungi. Kew’s Science Strategy 2021–2025 lays out five scientific priorities to aid these goals: research into the protection of biodiversity through Ecosystem Stewardship, understanding the variety and evolution of traits in plants and fungi through Trait Diversity and Function; digitising and sharing tools to analyse Kew’s scientific collections through Digital Revolution; using new technologies to speed up the naming and characterisation of plants and fungi through Accelerated Taxonomy; and cultivating new scientific and commercial partnerships in the UK and globally through Enhanced Partnerships. One of Kew’s greatest international collaborations is the Millennium Seed Bank Partnership, which has to date stored more than 2.4 billion seeds of over 40,000 wild species of plants across the globe. In 2023, Kew scientists estimated in the State of the World’s Plants and Fungi report that 45% of all known flowering plants are threatened with extinction.
END