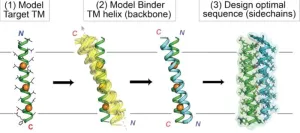
(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA—Hitting targets embedded within the cell membrane has long been difficult for drug developers due to the membrane’s challenging biochemical properties. Now, Scripps Research chemists have demonstrated new custom-designed proteins that can efficiently reach these “intramembrane” targets.
In their study, published March 13, 2024, in Nature Chemical Biology, the researchers used a unique computer-based approach to design novel proteins targeting the membrane-spanning region of the erythropoietin (EPO) receptor, which controls red blood cell production and can go awry in cancers. In addition to these new EPO-targeting molecules, the study yielded a general computational process, or “workflow,” for streamlining the flexible custom design of proteins aimed at intramembrane targets.
The researchers are now using their approach to develop potential new intramembrane-targeting treatments across a wide range of diseases.
“This work opens up many new possibilities for the modulation of targets within the cell membrane, including for therapeutic applications and understanding signaling mechanisms across cell biology,” says study co-corresponding author Marco Mravic, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Integrative Structural and Computational Biology at Scripps Research.
The study’s other co-corresponding authors were Daniel DiMaio, MD, PhD, of the Yale School of Medicine; and William DeGrado, PhD, of the University of California, San Francisco School of Pharmacy, where Mravic was previously a PhD student.
“A major goal of synthetic biology is to design proteins with biological activity—here, we report the design and testing of a small protein that specifically perturbs the activity of a much larger protein receptor involved in blood cell growth and differentiation,” says DiMaio, who is a professor of Genetics and of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, and deputy director of Yale Cancer Center. “We accomplished this by targeting the segment of the receptor that crosses the cell membrane. Because many cell proteins contain structurally conserved membrane-spanning segments, this general approach may be applicable to many other protein targets and provides a new tool to modulate the behavior of cells.”
Hitting intramembrane targets has long been an important goal in biomedicine since many proteins in cells—especially receptor proteins—have functionally important domains inside the membrane. Such proteins have prominent roles in almost every area of health and disease.
Yet intramembrane targets are not ordinary targets. Cell membranes generally are made of two layers of tightly spaced, fat-related “lipid” molecules, which are water-repellent and have other unique and complex properties. This makes the intramembrane space a much harder target for drug designers, compared to the watery zones of cell surfaces or interiors.
“There have been very few successful examples of drugs that target this space inside the membrane,” Mravic says.
Those few successes, which include treatments for low-blood-platelet disorders and cystic fibrosis, have come from blind screenings of large compound libraries or from close mimicry of proteins known to interact with partner proteins within the cell membrane. By contrast, Mravic and colleagues set out to design completely novel proteins—small ones called peptides—to hit intramembrane protein targets in new and diverse ways. To do that, they had to extend the frontier of computational methods, combining “data mining” of known protein-to-protein interactions in membranes with traditional physics-based predictions of protein interactions.
Ultimately, Mravic and his colleagues designed the first proteins that bind the EPO receptor’s membrane-spanning portion in a new way—not seen in nature. The team showed that these proteins very specifically and potently block the receptor’s function, in contrast to prior approaches.
The results may be of most immediate interest to researchers seeking new ways to inhibit the EPO receptor, which is often abnormally activated by tumor cells to maintain their growth and survival. But for Mravic and his colleagues, the study above all represents a proof of principle of a new and more flexible approach to intramembrane targeting.
“We intend to use this approach to target membrane proteins across multiple biological processes and disease areas, including cancers, immune disorders, and pain,” Mravic says.
He also expects the computational workflow he designed for the project to be a general accelerator of membrane-targeting drug design.
“Before, the process basically involved two people in a dark room looking at a computer screen and saying, ‘Yeah, I think this looks better than that,’” Mravic says. “Now, we’ve automated a lot of that molecule design process and decision making in the computer. Being more modular, flexible and streamlined allows the method to be more accessible for a broader range of scientists.”
Mravic and his colleagues have posted their computational tools for public use on Github: https://github.com/mmravic314/CHAMP2023/.
“De Novo Transmembrane Proteins Designed to Bind and Inhibit a Cytokine Receptor” was co-authored by Marco Mravic, Li He, Huong Kratochvil, Hailin Hu, Sarah Nick, Weiya Bai, Anne Edwards, Hyunil Jo, Yibing Wu, Daniel DiMaio and William DeGrado.
Support for the research came from the National Institutes of Health (R35-122603, CA037157, GM68933) and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
About Scripps Research
Scripps Research is an independent, nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation by Nature Index. We are advancing human health through profound discoveries that address pressing medical concerns around the globe. Our drug discovery and development division, Calibr, works hand-in-hand with scientists across disciplines to bring new medicines to patients as quickly and efficiently as possible, while teams at Scripps Research Translational Institute harness genomics, digital medicine and cutting-edge informatics to understand individual health and render more effective healthcare. Scripps Research also trains the next generation of leading scientists at our Skaggs Graduate School, consistently named among the top 10 US programs for chemistry and biological sciences. Learn more at www.scripps.edu.
END
New computational strategy boosts the ability of drug designers to target proteins inside the membrane
Customized-design approach could streamline the design of novel proteins targeting the hard-to-access cell membrane region
2024-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic condition haemochromatosis linked to higher levels of disease in older people
2024-03-13
A largescale new study has found that some people whose genetics are linked to the common iron overload condition haemochromatosis have substantially greater levels of liver, musculoskeletal and brain disease than previously reported, especially at older ages.
Haemochromatosis causes a build-up of iron in the body which can cause harm to joints and organs – although the extent of this harm is unclear, especially in older ages. The new research, led by a team at the University of Exeter and supported by the National Institute for Health and Care ...
Advancing tissue engineering with shape memory hydrogels
2024-03-13
One of the primary goals in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine is the development of artificial scaffolds that can serve as substitutes for damaged tissue. These materials must ideally resemble natural tissue and must have the ability to support cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. When considering scaffold materials, researchers account for the scaffold’s properties, such as its surface roughness, its water content (hydration state), and its flexibility or stiffness (elastic modulus), since these properties are known to affect cell ...
Developing a stem cell therapy to prevent amputations from critical limb ischemia
2024-03-13
Critical limb ischemia is a condition in which the main blood vessels supplying blood to the legs are blocked, causing blood flow to gradually decrease as atherosclerosis progresses in the peripheral arteries. It is a severe form of peripheral artery disease that causes progressive closure of arteries in the lower extremity, leading to the necrosis of the leg tissue and eventual amputation. Current treatments include angioplasty procedures such as stent implantation and anti-thrombotic drugs, but there is a risk of blood vessel damage and recurrence of blood clots, which is why there is a strong interest ...
Good news: the US maternal death rate is stable, not sky rocketing, as reported
2024-03-13
Philadelphia, March 13, 2024 – A new study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, published by Elsevier, challenges the prevailing view on the maternal death rate in the United States. The findings show that the rates of maternal death were stable between 1999-2002 and 2018-2021, instead of the dramatic upward trends previously reported by the National Vital Statistics System (NVSS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Additionally, the study indicates that direct obstetric causes of death declined over the last 20 years.
To determine whether the reported maternal death rates are accurate, a team of researchers took a deep dive into ...
CDC sharply overestimates maternal death rate, new study finds
2024-03-13
Maternal death rates in the United States may be sharply overstated as a result of faulty surveillance techniques, according to an analysis by researchers at Rutgers Health and other universities.
The National Vital Statistics System (NVSS) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that maternal death rates have more than tripled over the last two decades to 32.9 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2021 – substantially more than in any other wealthy nation.
The new study that looked at all deaths in the United States from 1999 to 2021 published in The American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology reports consistent death rates of slightly ...
NIH researchers identify brain connections associated with ADHD in youth
2024-03-13
What: Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered that symptoms of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are tied to atypical interactions between the brain’s frontal cortex and information processing centers deep in the brain. The researchers examined more than 10,000 functional brain images of youth with ADHD and published their results in the American Journal of Psychiatry. The study was led by researchers at NIH’s National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and National Human Genome Research Institute.
Luke Norman, Ph.D., a staff scientist in the NIMH Office of the Clinical Director, and colleagues ...
Single type of light creates multi-types of particles
2024-03-13
Laser direct writing (LDW) current researches mostly generate single type of materials for sensing layers or electrodes, while the sensor with different types of materials by LDW method is lacked. Researchers led by Prof. Gao Yang from East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST), China, are interested in expanded the application of LDW method, where can utilize the photo-thermal conversion, to synthesize materials and then engrave them with the desired morphologies and structures.
Focusing on the functionality of materials, the researchers use all-LDW method to generate laser induced silver (LIS) as electrodes and laser induced graphene ...
No persistent cough in 4 out of 5 with Tuberculosis
2024-03-13
More than 80% of patients with tuberculosis, the world’s most deadly infection, do not have a persistent cough, despite this being seen as a key symptom of the disease. The infection is predominantly transmitted by coughing, but probably also through simply breathing. Research, led by Amsterdam UMC and the Amsterdam Institute for Global Heath and Development, analysed data on more than 600,000 individuals in Africa and Asia and found that 82.8% of those with tuberculosis had no persistent cough and 62.5% had no cough at all. These results ...
Progesterone protects babies from preterm birth
2024-03-13
Women with a short cervix around 20 weeks of pregnancy have an increased risk of preterm birth. Preventing preterm birth in pregnant women with a short cervix is a crucial step in protecting the health of the child. Research from Amsterdam UMC now shows that, in pregnant women with a short cervix around 20 weeks, Progesterone (a hormone) is better than a cervical pessary at reducing the risk of severe preterm birth. This study was published today in the BMJ.
"This is an important improvement that can contribute to the reduction of preterm births and the associated complications, such as an increased risk of infant mortality and long-term health problems for the child," says ...
School-age girls with obesity are more likely to experience joint and muscle pain
2024-03-13
Girls with obesity are more likely to experience pain in their bones, joints, muscles, ligaments or tendons compared with children with a healthy weight, according to research by Queen Mary University of London. The same did not apply to boys.
Queen Mary researchers hope their findings will raise awareness that obesity may contribute to musculoskeletal problems in children.
In the study, published today in Archives of Disease in Childhood, researchers analysed anonymised information on 120,000 children, linking data from the National Child Measurement Programme with GP records. They found that girls with obesity were 1.7 times more likely than those ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] New computational strategy boosts the ability of drug designers to target proteins inside the membraneCustomized-design approach could streamline the design of novel proteins targeting the hard-to-access cell membrane region