Single type of light creates multi-types of particles
2024-03-13
(Press-News.org)
Laser direct writing (LDW) current researches mostly generate single type of materials for sensing layers or electrodes, while the sensor with different types of materials by LDW method is lacked. Researchers led by Prof. Gao Yang from East China University of Science and Technology (ECUST), China, are interested in expanded the application of LDW method, where can utilize the photo-thermal conversion, to synthesize materials and then engrave them with the desired morphologies and structures.
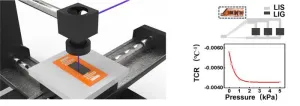
Focusing on the functionality of materials, the researchers use all-LDW method to generate laser induced silver (LIS) as electrodes and laser induced graphene (LIG) as temperature sensing layer without any assistant supporting. They investigate the relationship between LDW photothermal conversion and the morphology and structure of LIG and LIS by finite element analysis. Moreover, for regulating the sensing units with high sensitivity and electrodes with high stability, the anti-interfere strategy with the temperature and mechanical sensing is considered. By introducing a correction factor, a revised temperature calculation formula is carried out for smaller measurement deviations. The work entitled “All-laser direct writing process for temperature sensor based on graphene and silver” is published on Frontiers of Optoelectronics (published on Feb. 5, 2024).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-13
More than 80% of patients with tuberculosis, the world’s most deadly infection, do not have a persistent cough, despite this being seen as a key symptom of the disease. The infection is predominantly transmitted by coughing, but probably also through simply breathing. Research, led by Amsterdam UMC and the Amsterdam Institute for Global Heath and Development, analysed data on more than 600,000 individuals in Africa and Asia and found that 82.8% of those with tuberculosis had no persistent cough and 62.5% had no cough at all. These results ...
2024-03-13
Women with a short cervix around 20 weeks of pregnancy have an increased risk of preterm birth. Preventing preterm birth in pregnant women with a short cervix is a crucial step in protecting the health of the child. Research from Amsterdam UMC now shows that, in pregnant women with a short cervix around 20 weeks, Progesterone (a hormone) is better than a cervical pessary at reducing the risk of severe preterm birth. This study was published today in the BMJ.
"This is an important improvement that can contribute to the reduction of preterm births and the associated complications, such as an increased risk of infant mortality and long-term health problems for the child," says ...
2024-03-13
Girls with obesity are more likely to experience pain in their bones, joints, muscles, ligaments or tendons compared with children with a healthy weight, according to research by Queen Mary University of London. The same did not apply to boys.
Queen Mary researchers hope their findings will raise awareness that obesity may contribute to musculoskeletal problems in children.
In the study, published today in Archives of Disease in Childhood, researchers analysed anonymised information on 120,000 children, linking data from the National Child Measurement Programme with GP records. They found that girls with obesity were 1.7 times more likely than those ...
2024-03-13
A new analysis led by researchers at the University of Oxford and funded by the Nuffield Foundation has found that virtually all care homes forced to close in England by the Care Quality Commission are run on a for-profit basis. The results, published today in The Lancet Healthy Longevity, raise questions about the role of the private sector in exacerbating the care sector’s ongoing crisis.
The study assessed the number of care homes which had been forced to close by the independent regulator of health and social care in England, the Care Quality Commission ...
2024-03-13
Cancer patients who received specialized mental health support as part of their treatment plan are more likely to see improvements in their quality of life and reductions in pain, depression and fatigue, according to a study led by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
In addition to lasting improvements in patients’ quality of life, researchers observed lower risk of cardiovascular disease in family caregivers, as well as substantial cost savings to the healthcare system. The findings from a Phase III clinical trial were published today in The Lancet.
“The ...
2024-03-13
There is a high burden of typhoid fever in sub-Saharan African countries, according to a new study published today in The Lancet Global Health. This high burden combined with the threat of typhoid strains resistant to antibiotic treatment calls for stronger prevention strategies, including the use and implementation of typhoid conjugate vaccines (TCVs) in endemic settings along with improvements in access to safe water, sanitation, and hygiene.
The findings from this 4-year study, the Severe Typhoid ...
2024-03-13
HOUSTON – (March 13, 2024) – Rice University’s Naomi Halas has been selected as the 2024 recipient of the C.E.K. Mees Medal by Optica for “her design, fabrication, and demonstration of nanoparticles with specific optical and physical properties, the widespread application of which enables advances in fields including cancer therapy, water security, and light-driven chemistry.”
Halas’ groundbreaking work in nanotechnology has enabled the creation of metal nanoparticles possessing structural ...
2024-03-13
UCL Press Release
Under embargo until Wednesday 13 March 2024, 00:01 UK Time
Imported giant sequoia trees are well adapted to the UK, growing at rates close to their native ranges and capturing large amounts of carbon during their long lives, finds a new study led by UCL researchers with colleagues at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
The new research, published in Royal Society Open Science, found that the most massive species of redwood trees, Sequoiadendron giganteum, known as the giant sequoia, can potentially pull an average of 85 kilograms of carbon out ...
2024-03-13
We all know that the early bird gets the worm, but new research shows they turn to something far more nutritious for their breakfast.
Poo – either their own, or from other birds – provides them with essential nutrients, energy, and helps them adapt to new environments and seasonal variations, especially when they are developing.
New research led by the University of South Australia and published in Biological Reviews explains how eating faeces (known as coprophagy) shapes wild birds’ digestive tracts (gut biota), enabling them to absorb lost or deficient nutrients and adjust to seasonal variations in food sources.
This ...
2024-03-13
The fertility of both female and male tsetse flies is affected by a single burst of hot weather, researchers at the University of Bristol and Stellenbosch University in South Africa have found.
The effects of a single heatwave were even felt in the offspring of heat exposed parents, with more daughters being born than sons.
The study, published today in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, helps explain why tsetse are declining in some parts of their range in Africa and has important implications for the disease they spread, particularly sleeping sickness in humans and nagana in cattle.
Lead author ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Single type of light creates multi-types of particles