Scientists unravel mystery of drug response in small cell lung cancer
2024-03-13
(Press-News.org)
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive tumour of the lung that occurs especially in heavy smokers. Due to the rapid spread of this tumour type, most patients can only be treated with chemotherapy with remarkable initial anti-tumour efficacy. However, relapse often occurs over the course of time. A research team at the University of Cologne led by Professor Dr Roman Thomas, director of the Department of Translational Genomics and speaker of the Collaborative Research Center 1399 (CRC 1399, Mechanisms of Drug Sensitivity and Resistance in Small Cell Lung Cancer), has now identified the mechanisms governing this phenomenon for the first time: Due to predominant cell populations of treatment-sensitive cancer cells at the time of diagnosis, therapy is typically efficacious at the beginning. Furthermore, the team shows that these large sensitive cell populations hide other numerous and very different cancer cells. These cells usually originate from early precursors of the original cells, are resistant to treatment and can multiply unchecked after successful treatment. The study ‘Evolutionary Trajectories of Small Cell Lung Cancer under Therapy’ was published in Nature.
Understanding development for targeted treatment
“It is a major challenge and an important goal to understand the exact development of tumours in individual patients during the course of treatment and relapse. Our analysis reveals mechanisms that are likely to be relevant for many advanced cancers,” said Professor Dr Julie George, lead author and co-speaker of the CRC 1399.
For example, the return of the tumour – which occurs in almost all patients – usually revealed a different dominant cell population. In further treatments during the course of therapy, for example with radiation, the cancer cells exhibited characteristics of the genetic damage caused by the first chemotherapy. In addition, the researchers were able to detect individual genetic characteristics in the tumour cells, which are associated with a particular resistance to chemotherapy.
The findings of the study suggest that the potential success of further therapy developments could always be limited by the large number of therapy-resistant tumour cells. One therapeutic approach would therefore be to provide the most intensive initial treatment possible in order to minimize the number of cancer cells from which resistance can develop later.
“We have taken a decisive step forward in understanding this disease, and we very much hope that it will enable us developing new treatment strategies that will lead to longer survival of the affected patients,” said Professor Dr Roman Thomas. “Although the results are somewhat sobering on the one hand, they offer the hope of new treatment options in the future on the other hand.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-13
Jackson School of Geosciences Professor Peter Flemings is the recipient of the 2024 Robert R. Berg Outstanding Research Award, a top honor bestowed by the American Association of Petroleum Geologists, a worldwide professional association.
Over the course of his career, Flemings has worked to apply his academic research to effect real-world breakthroughs. His work analyzing how pressure within Earth’s crust is controlled by geology and fluid flow, for example, shaped how oil companies now safely search for hydrocarbons.
Flemings and his students explored how the evolution of rock layers controls the flow of fluids within them and the distribution ...
2024-03-13
Findings from a new study conducted by a team of researchers at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine and published in the journal mBio, reflect the important role that the gut microbiome (communities of bacteria) plays in the airway health of persons with cystic fibrosis.
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease that causes sticky, thick mucus to build up in the lungs and other organs, causing persistent infections that can be deadly. Until relatively recently, CF microbiology research has largely ...
2024-03-13
Scientists have long suspected nematodes, commonly known as roundworms, inhabit Utah’s Great Salt Lake sediments, but until recently, no one had actually recovered any there.
It took a University of Utah postdoc with a hammer and loads of field experience to solve the puzzle. Along with biology professor Michael Werner, postdoctoral researcher Julie Jung announced in a study published March 13 that they discovered thousands of tiny worms in the lake’s microbialites, those reef-like structures that cover about a fifth of the lakebed.
Their initial attempts failed to find nematodes in lakebed sediments, prompting Jung to take a hammer to samples ...
2024-03-13
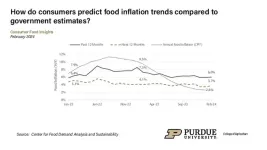
Most U.S. consumers surveyed in February 2024 predicted that they would see an increase in food prices over the next 12 months. Sixty-four percent of respondents predict food prices to rise in the next year, and the average predicted increase is 3.7%, according to the February Consumer Food Insights Report.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, consumer satisfaction and values, support of agricultural and food policies and trust in information sources. Purdue experts conducted and evaluated the survey, which ...
2024-03-13
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Three peer-reviewed journals have recently published research papers by Penn State’s Hammel Family Human Rights Initiative. The papers illustrate how the initiative’s programs help K-12 educators address difficult issues such as racism.
The three journals that published the initiative papers are School-University Partnerships, Journal of Practitioner Research and Journal of Teacher Education. JTE, as it’s known, is widely considered the top-ranked research journal in the field of teacher education. Some of the scholars who independently ...
2024-03-13
Oil and gas operations across the United States are emitting more than 6 million tons per year of methane, the main component of natural gas and the most abundant greenhouse gas after carbon dioxide, according to Stanford-led research published March 13 in Nature.
These emissions, which result from both intentional vents and unintentional leaks, amount to $1 billion in lost commercial value for energy producers. The annual cost rises to $10 billion when researchers account for harm to the economy and human well-being caused by adding this amount of heat-trapping methane ...
2024-03-13
Images
Physicists often turn to the Rayleigh-Taylor instability to explain why fluid structures form in plasmas, but that may not be the full story when it comes to the ring of hydrogen clumps around supernova 1987A, research from the University of Michigan suggests.
In a study published in Physical Review Letters, the team argues that the Crow instability does a better job of explaining the "string of pearls" encircling the remnant of the star, shedding light on a longstanding astrophysical mystery.
"The fascinating ...
2024-03-13
NEWPORT, Ore. – Marine heat waves in the northeast Pacific Ocean create ongoing and complex disruptions of the ocean food web that may benefit some species but threaten the future of many others, a new study has shown.
The study, just published in the journal Nature Communications, is the first of its kind to examine the impacts of marine heat waves on the entire ocean ecosystem in the northern California Current, the span of waters along the West Coast from Washington to Northern California.
The researchers found that the biggest beneficiary of marine heat waves is gelatinous zooplankton – predominantly ...
2024-03-13
The International Society of Microbiota (ISM) announces its 11th World Congress, "Targeting Microbiota 2024", scheduled for October 14-15 at the Corinthia Palace in Malta. This event is set to highlight the latest research and developments in microbiotal medicine, emphasizing its impact on human health and its potential in shaping future medical treatment approaches.
Detailed Workshop: Probiotic Prescribing Practices dedicated to Medical Professionals
The congress will feature a critical workshop on October 15, titled “Probiotic Prescribing Practices: Empowering Medical Doctors for Improved Patient Health.” ...
2024-03-13
Engineering Biology for Climate & Sustainability is the fifth technical roadmap developed by the Engineering Biology Research Consortium (EBRC) and represents the first dedicated to innovations and opportunities towards overcoming a significant global challenge. The roadmap targets and challenges are aligned and were drawn from existing climate and sustainability literature, particularly those focused on long-term impacts and opportunities, including reports from the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
The roadmap consists of six themes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists unravel mystery of drug response in small cell lung cancer