(Press-News.org) In a study published on January 18, 2024 in the journal Physics of Fluids, researchers from Tohoku University theoretically linked ignition and deflagration in a combustion system, unlocking new configurations for stable, efficient combustion engines due to the possible existence of any number of steady-state solutions.
"This research directly tackles the challenge of reducing carbon dioxide emissions by enhancing the efficiency of combustion engines, a significant source of these emissions," said Youhi Morii from the Institute of Fluid Science at Tohoku University.
"A better understanding of combustion dynamics will also support the development of safer, more sustainable engineering solutions," said Kaoru Maruta, also from the Institute of Fluid Science.
Combustion dynamics involves complex coupled fluid and chemical reactions. Researchers use computational fluid dynamics to help them better understand and control the process.
If a system that operates stably in a steady state and has a certain tolerance range for small perturbations can be utilized, it would simplify the structure and control of combustors, and increase the feasibility of commercializing new combustor designs.
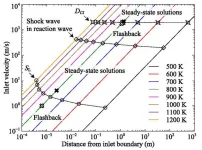
To explore this concept, the Tohoku University researchers considered a simple, one-dimensional reactive flow system, where unburned premixed gas enters a combustion chamber from the left inlet boundary, while burned gas, or deflagration wave, exits from the right outlet boundary.
The working theory up to this point held that a steady-state solution exists only when the inlet velocity matches either the velocity of the deflagration wave (which travels at subsonic speeds) or the velocity of the detonation wave - a shock reaction where the exiting flames travel at supersonic speeds.
However, this conventional wisdom is predicated on the assumption that chemical reactions in the preheating zone are negligible. Recent studies emphasize the significance of what's called "autoignition-assisted flames," wherein a deflagration propagating in a hot unburned premixed gas mixture has a faster propagation speed with the help of chemical reactions in front of the flame. This suggests that there are any number of steady-state solutions, which affect the amount of residence time gas stays in front of the deflagration.
Building on these findings, the Tohoku University researchers designed a theory that successfully bridged the gap between ignition and deflagration waves, revealing the existence of additional steady-state solutions that are possible when they considered the "autoignitive reaction wave" - a wave that is affected by ignition in the preheat zone but behaves like a deflagration wave.
"Contrary to the prevailing view that only a single steady-state solution exists for deflagration waves in subsonic one-dimensional systems, our approach posits an infinite number of such solutions as autoignitive reaction waves, asserting that ignition and flame are intrinsically linked," Morii said.
This means that steady-state solutions exist not merely at the two points where the inlet velocity matches the velocities of the deflagration or detonation waves, but also in a broader region if autoignitive conditions are considered.
The team further extended the theory to scenarios involving supersonic inlet velocities. In the supersonic regime, the conventional understanding is that a steady-state solution is possible only when the inlet velocity matches the detonation wave velocity. However, given that the autoignitive reaction wave originates from zero-dimensional ignition, the researchers argued that it should be independent of the inlet velocity.
"We propose that an infinite number of steady-state solutions exist for the autoignitive reaction wave, even in supersonic conditions," Morii said.
By theoretically linking ignition and flame, the engine can now be considered from a new perspective. Accounting for ignition phenomena offers the possibility of more stable combustion, leading to the idea of a new concept of engine that is more efficient than the conventional one.
"This work on stabilizing autoignitive reaction waves marks a fundamental breakthrough, potentially revolutionizing the design of combustion systems, especially in the realm of supersonic combustion," Morii said.
While theoretical and numerical results have provided a new engine concept, it has not yet been experimentally verified. The team, therefore, plans to apply the research findings to an actual engine through further experimental verification through joint research.
END
A theory linking ignition with flame provides roadmap to better combustion engines
2024-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Doping engineering in halide perovskite, an efficient synthesis method of white LEDs
2024-03-15
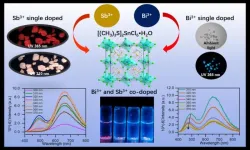
In 1879, Edison invented the incandescent lamp, which brought light to the night. In 1969, the first red light emitting diodes (LEDs) lamp came out. However, as the key to making white light bulbs, high-energy blue light has not been successfully commercialized. Until 1998, the Japan’s Nakamura Shoji made white LEDs, which marked the official entry of LEDs into the lighting era. LEDs have the advantages of high efficiency, environmental protection and energy saving. Metal halide perovskites (MHPs) have become a powerful candidate for new LEDs ...
Parallel physical random bit generation towards rates of order 100 Tb/s
2024-03-15
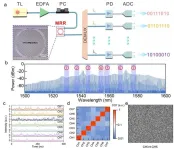
In our digital networked society, random bit generators (RBGs) are vital for services and state-of-the-art technologies such as cryptographically secured communication, blockchain technologies, and quantum key distribution. An ever-increasing demand to improve the security of digital information has shifted the generation of random bits from sole reliance on pseudorandom algorithms to the use of physical entropy sources. Shannon’s theorem establishes that it is required for the ultimate security to achieve bit rate matching that of the true RBGs with that of the communication systems. For this purpose, optical chaos has been widely studied in the past decades as a means for the ...
The Lancet Neurology: Neurological conditions now leading cause of ill health and disability globally, affecting 3.4 billion people worldwide
2024-03-15
Peer-reviewed / Modelling study / People
Embargoed access to the paper and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
Most comprehensive study to date finds the burden of nervous system (neurological) conditions is much greater than previously understood, with this diverse group of conditions affecting 43% of the world’s population (3.4 billion individuals) in 2021.
Neurological conditions were responsible for 443 million years of healthy life lost due to illness, disability, and premature death (disability-adjusted life years) in 2021, making them the ...
Study of long-term student engagement challenges “one great teacher” narrative of education
2024-03-15
A positive relationship with a teacher at an early age may help children to feel more engaged with school, but not necessarily in the long term, new research shows.
The finding comes from a University of Cambridge study of more than 3,600 young people in Australia, using data gathered at several points between the ages of eight and 15. The students’ levels of school engagement – meaning their interest in school and willingness to learn – fluctuated during this period, especially during the ...
UChicago Medicine helps bring first-of-its-kind drug for metabolic liver disease to the clinic
2024-03-15
Liver disease specialists at the University of Chicago Medicine will soon begin prescribing a first-of-its-kind drug for treating advanced metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) — formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Resmetirom (to be sold under the brand name Rezdiffra), received FDA approval on March 14, 2024. It is the first medication approved for treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), a more advanced stage of MASLD characterized by liver inflammation and scarring known as fibrosis.
“Until now, liver disease has ...
Long COVID ‘indistinguishable’ from other post-viral syndromes a year after infection
2024-03-14
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
Long COVID appears to manifest as a post-viral syndrome indistinguishable from seasonal influenza and other respiratory illnesses, with no evidence of increased moderate-to-severe functional limitations a year after infection, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2024) in ...
Improved neuromonitoring could prevent brain injuries for patients on ECMO life support
2024-03-14
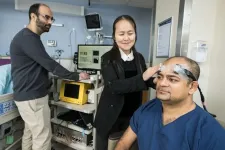
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) can be a life-saving therapy for patients with acute heart or lung failure. During ECMO therapy, a patient’s blood flows out of their veins through tubes and into a machine that does both the actions of the heart and lungs. The oxygenated blood is then returned to the body allowing the heart and lungs to rest.
While ECMO can stabilize a critically ill patient in an intensive care unit, the procedure carries significant risks, including brain injury. Often these patients are comatose, and current neuromonitoring techniques are too risky and invasive to perform routinely. Now, researchers at the University ...
Kurdish uprisings have led to new ways for communities to claim Kurdish identity, study shows
2024-03-14
Kurdish uprisings have become a way for people to assert their identity and challenge their historical and structural erasure in modern Iran, a new study shows.
Protests following the death of Jina (Mahsa) Amini in police custody in Iran led to “remarkable” acts of resistance built on decades of activism, according to the research.
The study, published in the International Journal of Middle East Studies, outlines how the growing resistance that up to “Jîna's uprising” had been largely unnoticed by many Iranians.
Dr ...
Infections from these bacteria are on the rise. New blood test cuts diagnosis time from months to hours
2024-03-14
Inhaling nontuberculous mycobacteria is common for most people. The bacteria are found in water systems, soil and dust worldwide and, for many, cause no harm.
For those with underlying conditions, nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) can infect the lungs, causing symptoms similar to tuberculosis. Inflammation can cause a chronic and sometimes bloody cough as well as scarring, which can make respiratory infections like bronchitis and pneumonia more common. Due to the slow growth of the bacteria, proper diagnosis and treatment can take months.
In a new study, Tulane University researchers have developed a CRISPR-based platform for diagnosing NTM infections where blood testing ...
Researchers prove fundamental limits of electromagnetic energy absorption
2024-03-14
Electrical engineers at Duke University have determined the theoretical fundamental limit for how much electromagnetic energy a transparent material with a given thickness can absorb. The finding will help engineers optimize devices designed to block certain frequencies of radiation while allowing others to pass through, for applications such as stealth or wireless communications.
“Much of the physics of the known universe already have fundamental solutions or are too complex to get an exact answer,” said Willie Padilla, professor of electrical and computer engineering at Duke. “In any field, finding a truly novel, fundamental, exact ...