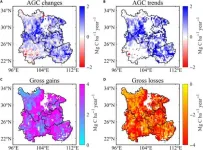
(Press-News.org) A new study reveals a significant increase in aboveground carbon (AGC) in Southwest China from 2013 to 2021, defying the adverse effects of extreme droughts. This achievement underscores the region's pivotal role as a carbon sink, attributed to extensive ecological projects and innovative remote sensing techniques.
Over the past four decades, Southwest China has been a major carbon sink, significantly mitigating anthropogenic CO2 emissions. However, recent severe droughts, especially from 2009-2013 and in 2022, have drastically reduced its carbon absorption capacity by affecting vegetation and biomass. This illustrates the region's susceptibility to climate-induced stressors, emphasizing the critical need for protective measures against environmental fluctuations.
In a new study (doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0113) published in the Journal of Remote Sensing on March 4, 2024, scientists have harnessed satellite and ground-based observations to uncover the significant impact of drought on carbon loss in Southwest China. This research marks a pivotal step in understanding the complex interactions between climate events and the carbon cycle, an essential component for maintaining the balance of our planet's climate.
The study utilized an innovative combination of satellite imagery and ground observations to meticulously analyze the effects of drought on the carbon dynamics within Southwest China. By integrating data from multiple sources, the researchers were able to observe and quantify the extent of carbon loss attributed to drought conditions. This approach not only highlights the vulnerability of the region's carbon stocks to climate variability but also sets a new benchmark in utilizing technology to monitor and understand ecological changes. The findings underscore the importance of satellite data in providing a comprehensive and accurate picture of how natural disasters like droughts can alter the carbon balance, potentially leading to long-term shifts in the ecosystem and climate system. This research highlights the significant impact of ecological initiatives on improving carbon sequestration, offering a strategic model for addressing climate change. The achievements in Southwest China stand as a prominent example for worldwide environmental restoration endeavors.
Dr. Lei Fan, the study's lead researcher, emphasizes, "Our findings illuminate the resilience and potential of Southwest China's ecosystems to act as a substantial carbon sink, highlighting the success of government-led ecological restoration efforts."
By conducting a thorough analysis, the study illuminates the complex interactions within our planet's carbon cycle in response to environmental challenges. This provides essential knowledge for advancing climate science and devising effective management approaches.
###
References
DOI
10.34133/remotesensing.0113
Original Source URL
https://doi. org/10.34133/remotesensing.0113
Funding information
This study is supported in part by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42322103, 42171339, and 41830648).
About Journal of Remote Sensing
The Journal of Remote Sensing, an online-only Open Access journal published in association with AIR-CAS, promotes the theory, science, and technology of remote sensing, as well as interdisciplinary research within earth and information science.
END
Revealing nature's secrets from space: satellite data unlocks drought's impact on Southwest China's carbon cycle
2024-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Health and economic value of eliminating socioeconomic disparities in U.S. youth physical activity
2024-03-15
About The Study: This study quantified the potential savings from eliminating or reducing physical activity disparities, which can help policymakers, health care systems, schools, funders, sports organizations, and other businesses better prioritize investments toward addressing these disparities.
Authors: Bruce Y. Lee, M.D., M.B.A., of Public Health Informatics, Computational, and Operations Research (PHICOR), CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy in New York, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Pain exposure and brain connectivity in preterm infants
2024-03-15
About The Study: Greater exposure to early-life pain was associated with altered maturation of neonatal structural connectivity, particularly in female infants in this study of 150 very preterm infants. Alterations in structural connectivity were associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes, with potential regional specificities.
Authors: Steven P. Miller, M.D.C.M., M.A.S., of the BC Children’s Hospital Research Institute and University of British Columbia in Vancouver, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Eliminating socioeconomic disparities in youth physical activity can save over $15 billion
2024-03-15
What would happen if the existing disparities in physical activity levels between youth of lower and higher socioeconomic statuses were eliminated? Previous studies have shown that those between 6-17 years of age in lower socioeconomic groups get on average 10-15% less physical activity than those of higher socioeconomic groups. A new study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum on Mar. 15 shows that eliminating such disparities could end up saving society over $15 billion in direct medical costs and productivity losses. This in turn could end up benefiting all taxpayers, anyone who pays insurance ...
Shark-bitten orcas in the Northeastern Pacific could be a new population of killer whale
2024-03-15
UBC researchers believe a group of killer whales observed hunting marine mammals including sperm whales, as well as a sea turtle, in the open ocean off California and Oregon could be a new population.
Based on available evidence, the researchers posit in a new study published in Aquatic Mammals that the 49 orcas could belong to a subpopulation of transient killer whales or a unique oceanic population found in waters off the coast of California and Oregon.
“The open ocean is the largest habitat on our planet and observations of killer whales in ...
New research in March: colorectal cancer, kidney health, OR supply costs, and more
2024-03-15
CHICAGO: The March issue of the Journal of the American College of Surgeons (JACS), which includes research presented at the Southern Surgical Association 135th Annual Meeting, features new research on topics ranging from colorectal cancer and social vulnerability to operating room supply costs, the rise in school shootings since 1970, and the impact of permitless open carry laws on suicide rates, among others.
Read highlights from the issue below. The full issue is available on the JACS website.
Social Vulnerability Index and Survivorship after Colorectal Cancer Resection
Researchers analyzed whether data from the Social Vulnerability Index (SVI) can help predict complications ...
Do school grades influence parental support?
2024-03-15
The Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) has researched parents' support behavior in relation to school grades. The study shows that low-income families support their children equally regardless of grades, while parents from higher income groups tend to give more support to children with lower grades. It also raises the question of whether these patterns contribute to low social mobility, as parents of high-achieving children from lower social classes do not have the same resources and strategies at their disposal as parents of low-achieving ...
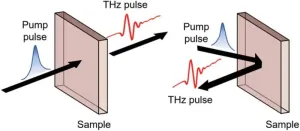
Exploring the frontier of quantum materials through terahertz emission spectroscopy: a comprehensive review
2024-03-15
Researchers at the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, have published a review article on the terahertz (THz) radiation in quantum materials. The work, led by Surui Yang, Liang Cheng, and Jingbo Qi, offers a comprehensive exploration of the time-dependent photocurrents, shedding light on the up-to-date understanding of the physical processes involved.
The investigation, conducted at the forefront of ultrafast science, delves into the potential of THz radiation in unraveling the fundamental physics of quantum materials, with implications for the development of novel technologies. The review focuses on recent advancements in revealing the unique properties of quantum materials ...
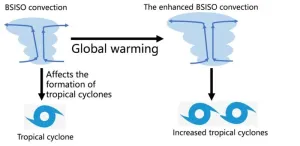
Global warming may intensify the modulation of tropical cyclone genesis by summer intraseasonal oscillation
2024-03-15
Global warming, the long-term warming of Earth’s overall temperature, has greatly accelerated in the last 100 years due to human factors such as the burning of fossil fuels. Along with this trend, certain atmospheric phenomena have also changed, such as typhoons and other types of disastrous weather becoming more intense than before and bringing about more serious impacts. The Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO), one of the most pronounced subseasonal variabilities in the tropics during boreal summer, provides an important basis for subseasonal forecasting. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the BSISO and its changes under global warming.
Recently, ...
Simple blood test could predict risk of long-term COVID-19 lung problems
2024-03-15
UVA Health researchers have discovered a potential way to predict which patients with severe COVID-19 are likely to recover well and which are likely to suffer “long-haul” lung problems. That finding could help doctors better personalize treatments for individual patients.
UVA’s new research also alleviates concerns that severe COVID-19 could trigger relentless, ongoing lung scarring akin to the chronic lung disease known as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, the researchers report. That type of continuing lung damage would mean that patients’ ability to breathe would continue to worsen over time.
“We are excited ...
Study of fatal and nonfatal shootings by police reveals racial disparities, dispatch risks
2024-03-15
A new study from researchers at the Johns Hopkins Center for Gun Violence Solutions and Vanderbilt University found that an average of 1,769 people were injured annually in police shootings from 2015 to 2020, 55 percent of them or 979 people, fatally. The study covered a total of 10,308 incidents involving shootings by police. The Center is based at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The majority of victims in shootings by police—84 percent overall—were reported as armed with a firearm or other weapon, such as a knife or vehicle, during ...