(Press-News.org) Scents, such as coffee, flowers, or freshly-baked pumpkin pie, are created by odor molecules released by various substances and detected by our noses. In essence, we are smelling molecules, the basic unit of a substance that retains its physical and chemical properties.
A research team led by Dr. ZHOU Wen from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has discovered that this process of "smelling" involves an analysis of submolecular structural features.
The study was published online in Nature Human Behaviour on March 18.
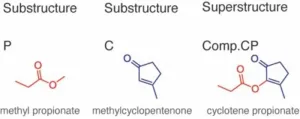
In this study, the researchers perturbed the processing of submolecular features by exploiting adaptation –– a fundamental mechanism by which specific neuronal responses decay after repetitive or prolonged stimulation. They also exploited the substructure-superstructure relationships among selected compounds.
Systematic behavioral assessments of over 400 participants revealed a breakdown in the unified "smell" of a compound following substructure adaptation, i.e., prolonged exposure to a substructure of that compound. The compound began to smell more like a different compound representing its unadapted part. Importantly, this change occurred independently of olfactory perceptual attributes such as intensity and pleasantness.
Further comparisons of the strengths and patterns of odor-induced brain responses before and after substructure adaptation indicate that activities in the anterior piriform cortex and amygdala carry local structural information. These olfactory regions project to the posterior piriform cortex, which is known to represent what something smells like through ensemble coding. In the posterior piriform cortex, substructure adaptation makes the response pattern to a compound more similar to the response to the unadapted part of the compound (as opposed to the adapted part), thus paralleling the behavioral observations.
The results shed new light on the neural computation underlying formation of an odor. They establish a direct correspondence between the coding of submolecular chemical features and what we smell, and demonstrate that the perceptual and neural representations of an odorous substance are not invariant but can be dynamically modified by recent olfactory encounters.
The odors we experience are thus manifestations of continuous analysis and synthesis in the olfactory system, breath by breath, of the structural features and relationships of volatile compounds in our ever-changing chemical environment, according to the researchers.
This study was supported by the STI2030-Major Projects, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
END
Scientists reveal chemical structural analysis in a whiff of smell
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using light to produce medication and plastics more efficiently
2024-03-18
Anyone who wants to produce medication, plastics or fertilizer using conventional methods needs heat for chemical reactions – but not so with photochemistry, where light provides the energy. The process to achieve the desired product also often takes fewer intermediate steps. Researchers from the University of Basel are now going one step further and are demonstrating how the energy efficiency of photochemical reactions can be increased tenfold. More sustainable and cost-effective applications are now tantalizingly close.
Industrial chemical reactions ...
Mapping the evolution of urinary tract cancer cells
2024-03-18
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have performed the most comprehensive analysis to date of cancer of the ureters or the urine-collection cavities in the kidney, known as upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). The study, which compared the characteristics of primary and metastatic tumors, provides new insights into the biology of these aggressive cancers and potential ways to treat them.
In the study, which appeared March 18 in Nature Communications, the researchers examined tissue samples from 44 primary and metastatic UTUC tumors. They compared gene mutations ...
Implantable sensor could lead to timelier Crohn’s treatment
2024-03-18
· Temperature sensor warns of disease flareups, tracks disease progression in real time
· Currently no way to quickly detect inflammation, leading to invasive surgeries
· Strategy could be useful in ulcerative colitis, another inflammatory bowel disease
CHICAGO --- A team of Northwestern University scientists has developed the first wireless, implantable temperature sensor to detect inflammatory flareups in patients with Crohn’s disease. The approach offers long-term, real-time monitoring and ...
Glucose levels affect cognitive performance in people with type 1 diabetes differently
2024-03-18
A new study led by researchers at McLean Hospital (a member of Mass General Brigham) and Washington State University used advances in digital testing to demonstrate that naturally occurring glucose fluctuations impact cognitive function in people with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). Results showed that cognition was slower in moments when glucose was atypical – that is, considerably higher or lower than someone’s usual glucose level. However, some people were more susceptible to the cognitive effects of large glucose fluctuations than others.
“In trying to understand how diabetes impacts the brain, our research shows that it is important to consider not only how people ...
Mimicking exercise with a pill
2024-03-18
NEW ORLEANS, March 18, 2024 — Doctors have long prescribed exercise to improve and protect health. In the future, a pill may offer some of the same benefits as exercise. Now, researchers report on new compounds that appear capable of mimicking the physical boost of working out — at least within rodent cells. This discovery could lead to a new way to treat muscle atrophy and other medical conditions in people, including heart failure and neurodegenerative disease.
The researchers will present their ...
New composite decking could reduce global warming effects of building materials
2024-03-18
NEW ORLEANS, March 18, 2024 — Buildings and production of the materials used in their construction emit a lot of carbon dioxide (CO2), a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming and climate change. But storing CO2 in building materials could help make them more environmentally friendly. Scientists report that they have designed a composite decking material that stores more CO2 than is required to manufacture it, providing a “carbon-negative” option that meets building codes and is less expensive than standard composite decking.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society ...
Artificial mucus identifies link to tumor formation
2024-03-18
NEW ORLEANS, March 18, 2024 – During cold and flu season, excess mucus is a common, unpleasant symptom of illness, but the slippery substance is essential to human health. To better understand its many roles, researchers synthesized the major component of mucus, the sugar-coated proteins called mucins, and discovered that changing the mucins of healthy cells to resemble those of cancer cells made healthy cells act more cancer-like.
The researcher will present her results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in person March 17-21; it features nearly 12,000 ...
Study explores homeless women’s experiences of ‘period poverty’
2024-03-18
Research from the University of Southampton has identified common issues women face when experiencing periods while homeless.
A review of research published in Women and Health has found homeless women experienced practical challenges in managing menstruation alongside feelings of embarrassment and shame, with many ‘making do’ due to inadequate provision.
The researchers say it’s high time to address the provision of menstrual health resources as a basic human right.
Dr Stephanie Barker, a teaching fellow at the University of ...
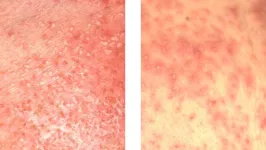
Keeping score: novel method might help differentiate 2 serious skin diseases
2024-03-18
Your skin becomes red and spots filled with pus appear, so you visit a dermatologist. When these symptoms spread to the skin throughout the body, it is difficult for the physician to distinguish whether it is generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) or acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), as both have similar symptoms. The two diseases run different courses and require different treatments. Without proper treatment, the symptoms can worsen severely and cause complications, so it is essential to distinguish between them.
Researchers ...
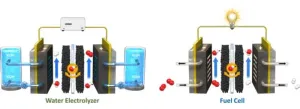
Developing bifunctional catalyst performance enhancement technology that will dramatically lower the cost of hydrogen production
2024-03-18
Dr. Hyung-Suk Oh and Dr. Woong-Hee Lee of the Clean Energy Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with POSTECH and Yonsei University, have developed a methodology to improve the reversibility and durability of electrodes using bifunctional platinum-nickel alloy catalysts with an octahedral structure that exhibits both oxygen reduction and generation reactions.
Bifunctional catalysts are a new generation of catalysts that simultaneously produce hydrogen and oxygen from water using a single catalyst. Currently, electrochemical systems such as water electrolysis technology and CCU (carbon dioxide ...