(Press-News.org) Dr. Hyung-Suk Oh and Dr. Woong-Hee Lee of the Clean Energy Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with POSTECH and Yonsei University, have developed a methodology to improve the reversibility and durability of electrodes using bifunctional platinum-nickel alloy catalysts with an octahedral structure that exhibits both oxygen reduction and generation reactions.
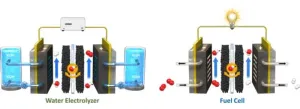
Bifunctional catalysts are a new generation of catalysts that simultaneously produce hydrogen and oxygen from water using a single catalyst. Currently, electrochemical systems such as water electrolysis technology and CCU (carbon dioxide capture and utilization) utilize separate catalysts for both electrodes, resulting in a high unit cost of hydrogen production. On the other hand, bifunctional catalysts that can be synthesized in a single production process are attracting attention as a technology that can reduce production costs and increase the economic efficiency of electrochemical energy conversion technologies.
However, the problem with bifunctional catalysts is that after each electrochemical reaction that generates hydrogen and oxygen, the performance of other reactions decreases due to structural changes in the electrode material. Therefore, in order to commercialize bifunctional catalysts, it is important to secure reversibility and durability that can maintain the catalyst structure for a long time after the reaction.
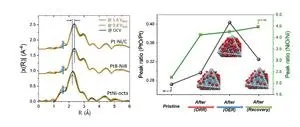
To enhance the reversibility and durability of the bifunctional catalyst, the team synthesized alloy catalysts with different structures by mixing platinum and nickel, which have high performance in oxygen reduction and generation reactions, respectively. The experimental results showed that the nickel-platinum interaction was most active in the octahedral structure, and the alloy catalysts performed more than twice as well as the platinum and nickel monoliths in oxygen reduction and generation reactions.
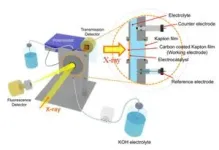
The researchers identified platinum oxide generated during the repeated generation reaction of the alloy catalyst as the cause of the performance degradation and developed a structure restoration methodology to reduce platinum oxide to platinum. The team confirmed through transmission electron microscopy that the methodology restored the catalyst's shape, and in large-area reactor experiments for commercialization, the team succeeded in restoring the catalyst shape and more than doubled the run time.
The team's bifunctional catalysts and structure recovery methodology are expected to accelerate the commercialization of unitized renewable fuel cells (URFCs) technology by replacing the separate catalysts for oxygen evolution and reduction reactions with bifunctional catalysts. URFCs that can produce both hydrogen and electricity can lower production costs by reducing the input of expensive catalysts while maintaining performance.
"The technology to improve the reversibility and durability of catalysts has provided a new direction for the development of bifunctional catalysts, which is an important technology for electrochemical energy conversion systems," said Hyung-suk Oh, lead researcher at KIST. "It will contribute to the commercialization and carbon neutrality of electrochemical systems such as URFCs in the future.“
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho) under the 'KIST Institutional Program', 'Carbon to X Project' (2020M3H7A109822921), and 'Creative Convergence Research Project' (CAP21013-100) of the National Research Council of Korea (Chairman Kim Bok-cheol). The results were published in the latest issue of the prestigious international journal Advanced Energy Materials (IF: 27.8, top 2.5% in JCR) and were selected for the back cover image.
END
Developing bifunctional catalyst performance enhancement technology that will dramatically lower the cost of hydrogen production
Overcoming the durability limits of bifunctional catalysts for simultaneous hydrogen and oxygen production. Presenting large area reactor drive technology for commercialization of electrochemical systems.
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Animal hair structure changes from summer to winter to fend off freezing weather
2024-03-17
NEW ORLEANS, March 17, 2024 — Unique adaptations allow wild animals to survive temperature extremes that would quickly kill an unprotected human. For example, certain animals can withstand bitterly cold weather, thanks to the insulating properties of the hollow hairs that make up their coats. Little has been known about the hairs, but now, researchers have discovered that their inner structure changes with the seasons.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in person March ...
The many flavors of edible ants
2024-03-17
NEW ORLEANS, March 17, 2024 — Insects are typically unwelcome visitors to a picnic, but they could be a flavorful, nutritious and sustainable addition to the menu. Eating insects is common in some parts of the world, and some species are even considered delicacies. Ants are one example, sometimes roasted whole for a snack or ground and used to add flavor and texture to dishes. Researchers now report the unique aroma profiles of four species of edible ants, which taste markedly different from one another.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held ...
Better kombucha brewing through chemistry
2024-03-17
NEW ORLEANS, March 17, 2024 — Kombucha is a fermented tea known for its health benefits and tangy kick. But brewers can find it challenging to keep kombucha’s alcohol levels low because the bacteria and yeast used in the fermentation process vary from batch to batch. Now, chemists from Shippensburg University are investigating ways to reliably minimize alcohol, tailor taste profiles and speed up the kombucha fermentation process to help home and commercial producers optimize their funky brews.
The ...
Very low calorie diets are safe and acceptable for teenagers with moderate to severe obesity when used short-term and supported by a dietitian, Australian study finds
2024-03-16
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
Short-term very low calorie diets are safe for teenagers living with moderate to severe obesity when closely monitored by an experienced dietitian, new research to be presented at the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024), has found.
In addition, many of the adolescents who took part in the Australian study found a very low calorie diet to be an acceptable way to lose weight, despite experiencing side-effects.
Very low energy diets (VLED) typically involve taking in ≤ 800 calories per day and include meal replacements ...
Mount Sinai experts to present new research at 71th Annual Meeting of the Society for Reproductive Investigation
2024-03-16
Reproductive health experts from the Women’s Biomedical Research Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai will present research at the 71th Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society for Reproductive Investigation (SRI) in Vancouver, Canada from March 12-16. The doctors and researchers are available for interview about their findings; they can also provide commentary on other women’s health and female biology topics, breaking news, and studies.
PRESENTATIONS and POSTER SESSIONS
(*All abstracts are under embargo until the below listed times*)
Friday, March 15, 2024
9:00 -11:00 a.m. PT (12:00-2:00 ...
Less is more: Not placing a drain improves distal pancreatectomy outcomes
2024-03-16
Research led by Amsterdam UMC across ten Dutch hospitals and two Italian hospitals has found that not placing a drain during surgery improves outcomes in patients undergoing a left-sided pancreatic resection, also known as ‘distal pancreatectomy’. The study, today published in Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, set out to confirm the safety of drainless surgery, as compared to the current routine practice of leaving a surgical drain. Ultimately, the study not only confirmed the safety of ‘drainless ...
UC study: Subcutaneous infusion pump safe, effective for Parkinson’s treatment
2024-03-16
An international, multisite phase 3 trial co-led by a University of Cincinnati researcher found Parkinson’s disease medication delivered through an infusion pump is safe and effective at reducing symptoms for longer periods of time.
These results, published March 15 in the Lancet Neurology journal, could lead to additional treatment options for patients with the condition.
Parkinson’s symptoms such as tremors, slowness and stiffness are caused by low levels of dopamine in the body. For decades, doctors ...
Oregon State researchers take deep dive into how much water is stored in snow
2024-03-15
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A heavy snowpack is fun for skiers and sledders, and it also acts like an open-air storage tank that melts away to provide water for drinking, irrigation and other purposes during dry months.
But exactly how much water is held in snowpacks, and for how long?
That information, critical to water managers around the globe, has taken on new clarity thanks to a new, more holistic calculation technique developed by researchers in the Oregon State University College of Engineering.
“Water managers tend to consider a portfolio of infrastructure options – surface water reservoirs, groundwater ...
Experts document a decade of progress under the workforce innovation and opportunity act benefiting students with disabilities
2024-03-15
Amsterdam, March 15, 2024 – Ten years ago, the United States passed into federal law the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA), broadening the mandate of state vocational rehabilitation agencies to facilitate successful school-to-work transitions for student populations. Among its many provisions, the measure provided an unparalleled opportunity to expand the scope of available experiences and training to help students with disabilities prepare for competitive integrated employment.
A special issue of the Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation, published by IOS Press, explores the state-of-the-art of pre-employment transition services (Pre-ETS) practices, and scholarship. ...
Why killer T cells lose energy inside of solid tumors
2024-03-15
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – T cells are often called “assassins” or “killers” because they can orchestrate and carry out missions to hunt down bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells throughout the body. Mighty as they may be, recent research has shown that once T cells infiltrate the environment of a solid tumor, they lose the energy needed to combat the cancer.
A research team led by Jessica Thaxton, PhD, MsCR, associate professor of cell biology and physiology and co-leader of the Cancer Cell Biology Program ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
DEGU debuts with better AI predictions and explanations
‘Giant superatoms’ unlock a new toolbox for quantum computers
Jeonbuk National University researchers explore metal oxide electrodes as a new frontier in electrochemical microplastic detection
Cannabis: What is the profile of adults at low risk of dependence?
Medical and materials innovations of two women engineers recognized by Sony and Nature
Blood test “clocks” predict when Alzheimer’s symptoms will start
Second pregnancy uniquely alters the female brain
Study shows low-field MRI is feasible for breast screening
Nanodevice produces continuous electricity from evaporation
Call me invasive: New evidence confirms the status of the giant Asian mantis in Europe
Scientists discover a key mechanism regulating how oxytocin is released in the mouse brain
Public and patient involvement in research is a balancing act of power
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
[Press-News.org] Developing bifunctional catalyst performance enhancement technology that will dramatically lower the cost of hydrogen productionOvercoming the durability limits of bifunctional catalysts for simultaneous hydrogen and oxygen production. Presenting large area reactor drive technology for commercialization of electrochemical systems.